
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Because this market is monopolistically competitive, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that
for each firm. Further, the quantity the firm produces in long-run equilibrium is
at the optimal quantity
the efficient scale.
True or False: This indicates that there is excess capacity in the market for jackets.
○ True
○ False
Monopolistically competitive markets may be socially inefficient due to the presence of too many or too few firms. The presence of the
externality implies that there is too little entry of new firms in the market.
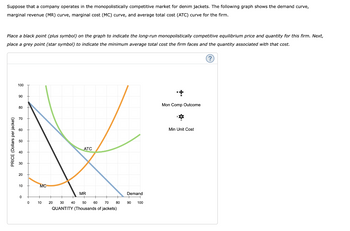
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that a company operates in the monopolistically competitive market for denim jackets. The following graph shows the demand curve,
marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve for the firm.
Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next,
place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost.
PRICE (Dollars per jacket)
100
90
80
50
ATC
30
2 8 8 2 2 2 2 °
60
MC
MR
Demand
0
+
0
10
20 30
40
50 60
70
80
90
100
QUANTITY (Thousands of jackets)
Mon Comp Outcome
Min Unit Cost
(?)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose that a company operates in the monopolistically competitive market for denim jackets. The following graph shows the demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve for the firm. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost. ? PRICE (Dollars per jacket) 100 90 80 70 60 40 30 20 MC 10 ATC MR Demand 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 QUANTITY (Thousands of jackets) + Mon Comp Outcome Min Unit Cost Because this market is monopolistically competitive, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that. firm. Further, a monopolistically competitive firm's average total cost in long-run equilibrium is at the optimal quantity for each the minimum average total cost.arrow_forwardThe following graph represents a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. Place the black point (cross sign) on the graph to indicate the short-run profit-maximizing price and quantity for this monopolistically competitive company. Next, place the grey star on the graph to indicate the point where the LRAC reaches a minimum. PRICE PER UNIT (Dollars) 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 MC 0 0 50 LRAC MR Demand 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Units) Monopolistically Competitive Outcome Minimum of the LRAC The long-run equilibrium price is $ (Hint: Use the graph to find the numeric value of the price at equilibrium.) The long-run equilibrium quantity is units. The LRAC curve is at its minimum at a quantity of The long-run equilibrium price is units. the marginal cost of producing the equilibrium output. ?arrow_forwardSuppose that a firm produces wooden train engines in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve: Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm, Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost.arrow_forward
- Suppose that a firm produces wooden train engines in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost. PRICE (Dollars per engine) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 MC 0 0 10 O True ATC Demand False MR 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 QUANTITY (Thousands of engines) 90 100 Mon Comp Outcome Min Unit Cost True or False: This indicates that there is excess capacity in the market for engines. Because this market is a monopolistically competitive market, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that optimal quantity. Furthermore, the quantity the firm produces in long-run equilibrium…arrow_forwardSuppose that a firm produces wooden train engines in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost. ? PRICE (Dollars per engine) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 II MC + 10 Ⓒ True O False MR ATC I Demand I 20 30 40 50 60 70 QUANTITY (Thousands of engines) 80 90 100 Mon Comp Outcome Because this market is a monopolistically competitive market, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that P = ATC at the optimal quantity for each firm. Furthermore, the quantity the firm produces in long-run equilibrium is less than the efficient scale. Min Unit Cost True or…arrow_forwardPRICE (Dollars per shirt) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 MC 0 10 ATC True Demand MR + 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 QUANTITY (Thousands of shirts) O False 90 100 + Mon Comp Outcome Min Unit Cost Because this market is a monopolistically competitive market, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that optimal quantity. Furthermore, the quantity the firm produces in long-run equilibrium is average total cost. at the the quantity at which firms minimize True or False: In long-run equilibrium, a monopolistically competitive firm charges a price that is above marginal cost.arrow_forward
- Suppose that a firm produces polo shirts in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost PRICE (Dollars per shirt) 0 10 20 True O False MR Demand 60 QUANTITY (Thousands of shirts) ATC 40 BO 190 100 Mon Comp Outcorne Because this market is a monopolistically competitive market, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that optimal quantity for each firm. Furthermore, the quantity the firm produces in long-run equilibrium is Min Unit Cost True or False: This indicates that there is a markup on marginal cost in the market for shirts. at the the efficient scale.arrow_forwardSuppose that a firm produces polo shirts in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost.arrow_forwardSuppose that a firm produces baseball bats in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost. 100 90 80 Mon Comp Outcome 70 Min Unit Cost 50 ATC 40 30 20 10 MC MR Demand 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 QUANTITY (Thousands of bats) Because this market is a monopolistically competitive market, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that ▼ at the optimal quantity for each firm. Furthermore, the quantity the firm produces in long-run equilibrium is the efficient scale. PRICE (Dollars per bat)arrow_forward
- Economicsarrow_forwardSuppose that a firm produces wool jackets in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost. 100 90 80 Mon Comp Outcome 70 Min Unit Cost 50 30 ATC 20 10 MC MR Demand 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 QUANTITY (Thousands of jackets) Because this market is a monopolistically competitive market, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that quantity for each firm. Furthermore, a monopolistically competitive firm's average total cost in long-run equilibrium is at the optimal average total cost. the minimum PRICE (Dollars per jacket)arrow_forwardSuppose that a firm produces wool jackets in a monopolistically competitive market. The following graph shows its demand curve, marginal revenue (MR) curve, marginal cost (MC) curve, and average total cost (ATC) curve. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the long-run monopolistically competitive equilibrium price and quantity for this firm. Next, place a grey point (star symbol) to indicate the minimum average total cost the firm faces and the quantity associated with that cost. Because this market is a monopolistically competitive market, you can tell that it is in long-run equilibrium by the fact that at the optimal quantity. Furthermore, the quantity the firm produces in long-run equilibrium is the efficient scale.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education