
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
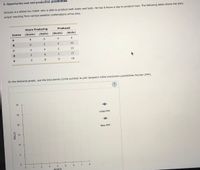
Transcribed Image Text:5. Opportunity cost and production possibilities
Jacques is a skilled toy maker who is able to produce both boats and balls. He has 8 hours a day to produce toys. The following table shows the daily
output resulting from various possible combinations of his time.
Hours Producing
Produced
Choice
(Boats)
(Balls)
(Boats)
(Balls)
A
8
4
6.
3
10
4
4
15
1
17
0.
8.
18
On the following graph, use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot Jacques's initial production possibilities frontier (PPF).
30
Initial PPF
20
New PPF
15
0.
1.
2.
3.
4
6.
7.
8.
BOATS
10
25
BALLS

Transcribed Image Text:Suppose Jacques is currently using combination D, producing one boat per day. His opportunity cost of producing a second boat per day is
per day.
Now, suppose Jacques is currently using combination C, producing two boats per day. His opportunity cost of producing a third boat per day is
per day.
From the previous analysis, you can determine that as Jacques increases his production of boats, his opportunity cost of producing one more boat
Suppose Jacques buys a new tool that enables him to produce twice as many boats per hour as before, but it doesn't affect his ability to produce balls.
Use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot his new PPF on the previous graph.
Because he can now make more boats per hour, Jacques's opportunity cost of producing balls is
it was previously.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose Yakov is currently using combination D, producing one train per day. His opportunity cost of producing a second train per day is _________ per day. Now, suppose Yakov is currently using combination C, producing two trains per day. His opportunity cost of producing a third train per day is ________ per day. From the previous analysis, you can determine that as Yakov increases his production of trains, his opportunity cost of producing one more train increases or decreases? . Suppose Yakov buys a new tool that enables him to produce twice as many trains per hour as before, but it doesn't affect his ability to produce balls. Use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot his new PPF on the previous graph. Because he can now make more trains per hour, Yakov's opportunity cost of producing balls is higher than/lower than or stays same it was previously.arrow_forwardPaul, Ringo, and George have a business where they visit people's homes to mow lawns and wash cars. Paul can wash 6 cars or mow 3 lawns in one hour. Ringo can wash 3 cars or mow 3 lawns in one hour. George can wash 3 cars or mow 6 lawns in one hour. They each work 6 hours per day. If two of them wash cars and one mows lawns then at most they can wash cars and mow lawns. Enter whole numbers.arrow_forwardA weaver working with a handloom is able to produce 11 yards of fabric per day. The typical weaver is paid £10 for a day's work. A loom powered by a steam engine is able to produce 82 yards of fabric per day. The powered loom still needs a worker to operate it, earning £10 per day, but also needs 24 pounds of coal to power it. At what price per pound of coal does the cost of producing fabric by power loom equal the cost of producing it by handloom? Round your final answer to two decimal places.arrow_forward
- Consider Figure 2-2 in Chapter 2. Assume the numbers on the y-axis 820 and 610 were changed to respectively 800 and 700. The opportunity cost of going from 240 to 480 units of food would now be _ and the law of increasing (opportunity) cost__ still hold. a) 100 // would b) 800 // would c) 700 // would not d) 100 // would notarrow_forwardWould the opportunity cost be a benefit to UPS shipping or a benefit to UPS international shipping for this example? “To begin, I began selling prints of my pictures in 2019 throughout 2020. It's now closed. USPS and UPS were the options I had during this period to ship out orders. Smaller or lighter packages were more expensive to ship with UPS, but USPS provided a low-cost alternative. UPS ships more than 220 internationally, whereas; USPS is strict about shipping to specific international destinations. I have chosen USPS over UPS; by doing this, orders were delivered on time and without damage by the United States Postal Service.”arrow_forward2. The relationship between marginal and average costs Consider the following scenario to understand the relationship between marginal and average values. Suppose Latasha is a professional basketball player, and her game log for free throws can be summarized in the following table. Fill in the columns with Latasha's free-throw percentage for each game and her overall free-throw average after each game. Game Game Result Total Game Free-Throw Percentage Average Free-Throw Percentage 1. 8/10 8/10 80 80 6/10 14/20 3 1/5 15/25 4 3/5 18/30 5 8/10 26/40 On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot Latasha's free-throw percentage for each game individually, and use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot her overall average free-throw percentage after each game. Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.arrow_forward
- Steffie's Stationary Services can produce cards and tablets. The daily production possibilities for the two products are shown below. Steffie's Stationary Services Production Possibilities (daily) Combination Cards Tablets A 150 0 B 140 10 C 120 20 D 90 30 E 50 40 F 0 50 If a card sells for $1, Steffie's Stationary Services will need a price per tablet of $ produce 50 tablets. in order toarrow_forwardFor a certain company, the cost for producing x items is 60x + 300 and the revenue for selling x items is 100x – 0.5x². - The profit that the company makes is how much it takes in (revenue) minus how much it spends (cost). In economic models, one typically assumes that a company wants to maximize its profit, or at least wants to make a profit! Part a: Set up an expression for the profit from producing and selling x items. We assume that the company sells all of the items that it produces. (Hint: it is a quadratio polynomial.) Part b: Find two values of x that will create a profit of $300. The field below accepts a list of numbers or formulas separated by semicolons (e.g. 2; 4; 6 or x + 1; x – 1). The order of the list does not matter. To enter va, type sqrt(a). x = Part c: Is it possible for the company to make a profit of $15,000?arrow_forwardcan you help me solve and give me step by step how you did it, i believe the answer is c=786.6arrow_forward
- Amy and Bill are fixing up their house by painting walls and installing electrical outlets. In one hour, Amy can paint 8 walls, or install 6 outlets. In one hour, Bill can paint 5 walls, or install 5 outlets In order to maximize their work per hour, (Click to select) should just paint walls, and (Click to select) ♥ should just install outletsarrow_forwardDouglas Fur is a small manufacturer of fake-fur boots in New York City. The following table shows the company’s total cost of production at various production quantities.arrow_forwardKwami and Adzga quit their jobs and decided to start a piggery joint venture business. The company processes and packs pork for sale. The output from this firm is described by the Cobb-Douglas production function, q=K¹/² A¹/2 Where q is the number of pigs processed in a quarter, K is the number of hours invested by Kwami in a quarter, and A is the number of hours invested by Adzoa in a quarter. Kwami and Adzoa value 1 hour of their time at $12 and $3 respectively based on what each was earning before quitting their jobs. a) Obtain the number of hours that Adzoa needs to invest (as a function of q and K) for 150 pigs to be processed in a quarter b) How many hours should Adzoa invest for 150 pigs to be processed in a quarter if it is known that Kwami invested 750 hours? c) The cost function for this company may be written as, C= vK + WA where v and w are unit costs for Kwami and Adzoa. wwwwwwww www Substituting for v and w gives C= 12K + 3A Express this cost of production function as a…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education