
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
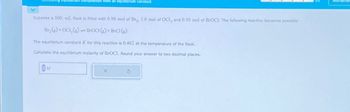
Transcribed Image Text:composition from an equilibrium constant
Suppose a 500, mL flask is filled with 0.90 mol of Br₂, 1.0 mol of OCI, and 0.50 mol of BrOCI. The following reaction becomes possible:
Br₂(g) + OC1₂(g) BroCI (g) + BrC1 (g)
M
1
The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.462 at the temperature of the flask.
Calculate the equilibrium molarity of BrOCI. Round your answer to two decimal places.
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 1.8 mol of Cl,, 1.6 mol of CHCI, and 1.7 mol of HCl. The following reaction becomes possible: Cl,(g) +CHCI, (g) HCl(g)+CCl,(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.642 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of CHCI,. Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardConsider the following equilibrium system at 355 K. 2NOBr(g) -----> 2NO(g)+Br2(g). If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases at 355 K contains 3.21x10^-2 M NOBr, 2.01x10^-2 M NO,and 3.98x10^-2 M Br2 what is the value of the equilibrium constant Karrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, K, for the following reaction is 1.29x10-2 at 600 K. COC,(g) CO(g) + Cl2(g) + C2(g) Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactant and products when 0.262 moles of COCI,(g) are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 600 K. [COCI,] = [CO] [Ch] MMMarrow_forward
- The equilibrium constant, K, for the following reaction is 6.30 at 723 K. 2NH3(g) ⇒N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases in a 10.9 L container at 723 K contains 0.409 mol of NH3(g) and 0.291 mol of N₂, the equilibrium concentration of H₂ is M.arrow_forwardAt a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 0.0036: H₂(g) + 1₂(g) → 2 HI(g) Use this information to complete the following table. O There will be very little H₂ and I2. Suppose a 6.0 L reaction vessel is filled with 1.9 mol of H₂ and 1.9 mol of I₂. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? O There will be very little HI. ONeither of the above is true. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = 2 HI(g) H₂(9)+1₂(9) What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = 2 H₂(g) +21₂(g) 4 HI(g) 0x10 ?arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kp, for the following reaction is 1.04×10-² at 548 K. NH4CI(S)2NH3(g) + HCI(g) If an equilibrium mixture of the three compounds in a 6.72 L container at 548 K contains 1.63 mol of NH4Cl(s) and 0.190 mol of NH3(g), the partial pressure of HCI(g) is I atm.arrow_forward
- Phosphorus pentachloride decomposes according to the chemical equation PC15(g) PC13(g) + Cl₂(g) Kc = 1.80 at 250 °C A 0.1584 mol sample of PC1, (g) is injected into an empty 2.00 L reaction vessel held at 250 °C. Calculate the concentrations of PCl, (g) and PC13 (g) at equilibrium.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 0.00650 at 298 K. 2NOBr(g) ⇒ 2NO(g) + Br₂ (g) If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases in a 15.6 L container at 298 K contains 0.201 mol of NOBr(g) and 0.284 mol of NO, the equilibrium concentration of Br₂ is | M.arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. ml. flask is filled with 0.60 mol of Br₂, 0.70 mol of BrOCI and 0.20 mol of BrCl. The following reaction becomes possible: Br₂(g) +OCI, (8) BrOCI(g) + BrCI(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 7.17 at the temperature of the flask Calculate the equilibrium molarity of OCI, Round your answer to two decimal places. Marrow_forward
- Suppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.70 mol of Cl,, 1.4 mol of CHCI, and 0.50 mol of CCl,. The following reaction becomes possible: 3 Cl,(g)+ CHC1,(g) – HC1 (g)+ CCl,(g) 4 The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 1.78 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of HCl. Round your answer to two decimal places. ||Marrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.60 mol of CO, 0.30 mol of NO and 1.7 mol of CO,. The following reaction becomes possible: NO,(9) + CO(2) = No(g) + CO,(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.953 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of NO. Round your answer to two decimal places. 0.37 M ?arrow_forwardA chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: CH₂(g) + 2H₂S(g) → CS₂(g) + 4H₂(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 1.7 × 10³. р The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with methane and hydrogen sulfide, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction vessel A B compound CH4 H₂S CS₂ H₂ CHA H₂S CS₂ H₂ pressure 5.65 atm 3.56 atm 5.77 atm 7.93 atm 4.69 atm 1.62 atm 6.73 atm 11.81 atm OO expected change in pressure ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase olo ↓decrease ↓decrease ↓ decrease ↓decrease ↓ decrease ↓decrease ↓ decrease ↓ decrease (no change) (no change) (no change) (no change) (no change) (no change) (no change) (no…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY