
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
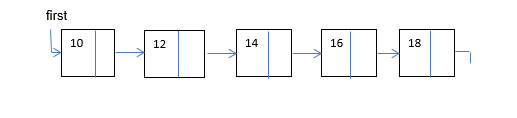
- Consider the following linked list of the form. This list already exists, so you do not need to write the code to create the list below:
struct nodeType {
int infoData;
nodeType * next;
};
nodeType *first;
… and containing the values (see image) :
- Write a code segment that prints all the current values in the linked list.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Input code in the "Write code here" sectionsarrow_forwardnumUniqueValues ♡ Language/Type: Related Links: Java Set collections List Write a method named numUnique Values that accepts a List of integers as a parameter and returns the number of unique integer values in the list. For example, if a list named 1 contains the values [3, 7, 3, -1, 2, 3, 7, 2, 15, 15], the call of numUniqueValues (1) should return 5. If passed the empty list, you should return 0. Use a Set as auxiliary storage to help you solve this problem. Do not modify the list passed in. 6 7 8 9 10 Method: Write a Java method as described, not a complete program or class. 12345arrow_forwardLab 19 Building a linked list Start this lab with the code listed below. The LinkedList class defines the rudiments of the code needed to build a linked list of Node objects. You will first complete the code for its addFirst method. This method is passed an object that is to be added to the beginning of the list. Write code that links the passed object to the list by completing the following tasks in order: 1. Create a new Node object. 2. Make the data variable in the new Node object reference the object that was passed to addFirst. 3. Make the next variable in the new Node object reference the object that is currently referenced in variable first. 4. Make variable first reference the new Node. Test your code by running the main method in the LinkedListRunner class below. Explain, step by step, why each of the above operations is necessary. Why are the string objects in the reverse order from the way they were added? public class LinkedList { private Node first; public LinkedList () {…arrow_forward
- SingleLinkedList head- Node next - data- String value = "Tom" Node next- data- String value = "Dick" Node nodeRef = nodeRef.next; nodeRef.next = new Node("Peter"); next- data- String value="Harry" What change will be made to the list after the following codes are run? Node nodeRef = head; While (nodeRef.next!=null) Node next = null data- String value="Sam"arrow_forwardvoid listEmployees (void) { for (int i=0; i 10000. Make a guess about why the comparison function takes 2 struct Employee parameters (as opposed to struct Employee *) **arrow_forwardFor any element in keysList with a value smaller than 40, print the corresponding value in itemsList, followed by a comma (no spaces). Ex: If keysList = {32, 105, 101, 35} and itemsList = {10, 20, 30, 40}, print: 10,40, #include <iostream>#include <string.h>using namespace std; int main() { const int SIZE_LIST = 4; int keysList[SIZE_LIST]; int itemsList[SIZE_LIST]; int i; cin >> keysList[0]; cin >> keysList[1]; cin >> keysList[2]; cin >> keysList[3]; cin >> itemsList[0]; cin >> itemsList[1]; cin >> itemsList[2]; cin >> itemsList[3]; /* Your code goes here */ cout << endl; return 0;}arrow_forward
- Duplicate Set This function will receive a list of elements with duplicate elements. It should add all of the duplicate elements to a set and return the set containing the duplicate elements. A duplicate element is an element found more than one time in the specified list. The order of the set does not matter. Signature: public static HashSet<Object> duplicateSet(ArrayList<Object> list) Example: INPUT: [2, 4, 5, 3, 3, 5] OUTPUT: {5, 3}arrow_forwardFor any element in keysList with a value greater than 50, print the corresponding value in itemsList, followed by a comma (no spaces). Ex: If the input is: 32 105 101 35 10 20 30 40 the output is: 20,30, 1 #include 2 3 int main(void) { const int SIZE_LIST = 4; int keysList[SIZE_LIST]; int itemsList[SIZE_LIST]; int i; 4 6 7 8 scanf("%d", &keysList[0]); scanf ("%d", &keysList[1]); scanf("%d", &keysList[2]); scanf("%d", &keysList[3]); 10 11 12 13 scanf ("%d", &itemsList[0]); scanf ("%d", &itemsList[1]); scanf("%d", &itemsList[2]); scanf ("%d", &itemsList[3]); 14 15 16 17 18 19 /* Your code goes here */ 20 21 printf("\n"); 22 23 return 0; 24 }arrow_forwardCreate a node class named LinkedNodes that uses up to 4 dynamic pointers to connect it to the other 8 nodes in the structure (a total of 9). The data in each node will be a unique integer number from 1 through 9. Include in your class definition these functions at a minimum: getVal(), setVal(), getNext(), setNext(), getPrev(), setPrev(), constructor(s) and destructor. Write a simple program to load these nodes into a linked structure. Do not use an array, the pointers will do that for you. You should be able to reach any node from any other node in the structure by traversing a maximum of 2 nodes from the current one. The output from your program should report the traversals between all nodes in the structure, starting with the node whose value is one. (See the example below) Node 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 -> Traverses to Node 1 Node 2 1->2 2->6->1 3->6->1 3->7->2 4->6->1 4->7->2 4->8->3 5->6->1 5->7->2 5->8->3 6->1->2 6->1->3 7->1->3 8->3 6->1 7->1 8->1 9->1 Node 3 1->3 2->3 7->2 8->2 9->2…arrow_forward
- 5 partition_list (head) This is a little like split_list() from the Short problem, except that, instead of splitting the list into two by cutting it into the middle, you will now build two lists to return, using alternate values. The first value in the input list should be returned at the head of the first new list; the second value should be the head of the second list. Keep on alternating from there, putting one new value on the first list, and one on the second. (But remember that the length of the input list might be odd.) Example Suppose you have the following input list: 10 - 13 -> -1 -> 1000 - 0 It should return the following two lists: 10 1 0 13 -> 1000arrow_forwardpython code easy way pleasethe one that i provide the image with code is just starting codearrow_forwardIn Javaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education