
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
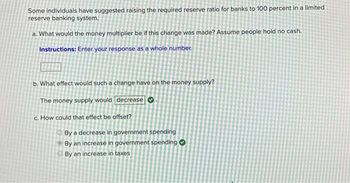
Transcribed Image Text:Some individuals have suggested raising the required reserve ratio for banks to 100 percent in a limited
reserve banking system.
a. What would the money multiplier be if this change was made? Assume people hold no cash.
Instructions: Enter your response as a whole number.
b. What effect would such a change have on the money supply?
The money supply would decrease
c. How could that effect be offset?
By a decrease in government spending
By an increase in government spending
By an increase in taxes
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assume that the banking system has total reserves of Rs.250 billion. Assume also that required reserves are 10 percent of checking deposits and that banks hold no excess reserves and households hold no currency. a. Calculate the money multiplier? b. Calculate the money supply? If the State Bank of Pakistan now raises required reserves to 12.5 percent of deposits, c. Calculate the money multiplier? d. What will be the effect on Reserves? (Please write only one word "Increase", "Decrease", or "No Change" in the blank) e. The amount of money supply will decline to (Write a number in the box) Note: Write amount in Billions only and ignore typing % sign for reserve ratearrow_forwardUse the following example to answer the questions that follow: Imagine that you deposit $25,000 in currency (which had been storing in your closet), into your checking account at the bank. Assume that this institution has a required reserve ratio of 25%. you As a result of this deposit, what is the maximum amount in loans that can be made by all the banks in the banking system? a. $31,250 b. $18,750 C. $100,000 d. $25,000 е. $0arrow_forwardNo written by hand solution and no imagearrow_forward
- Assume that the bank makes these loans. What will the new balance sheet look like? By how much has the money supply increased or decreased? If the money multiplier is 5, how much money will ultimately be created by this event?arrow_forwardSuppose the Federal Reserve increases the amount of reserves by $150 million and the total money supply increases by $600 million. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. a. What is the money multiplier? b. Using the money multiplier from part a, how much will the money supply change if the Federal Reserve increases reserves by $40 million? $ millionarrow_forwardAnswer the following questions: Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. a. If the required reserve ratio is 25 percent, what is the monetary multiplier? 10 b. If the monetary multiplier is 50, what is the required reserve ratio? 25 percentarrow_forward
- Suppose the Federal Reserve increases the amount of reserves by $150 million and the total money supply increases by $750 million. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. a. What is the money multiplier? b. Using the money multiplier from part a, how much will the money supply change if the Federal Reserve increases reserves by $50 million? 2$ millionarrow_forwardIn 2010 M1 was $2 trillionCurrency was $850 MillionTravelers checks were $20 BillionDemand deposits were $1030 billionThe fed decides to reduce the money supply by increasing the reserve requirement ratio from0.11 to 0.12Banks are loaned up and the amount of currency in the economy does not change.How much does the change in the reserve requirement change the money supply? Explain.arrow_forwardH3. The Fed wants to change the reserve requirement ratio in order to increase the money supply (Which is currently $5,000 in demand deposits. There is no currency in this economy and banks hold no excess reserves.) by $500. The money multiplier is currently 5. What is the current reserve requirement ratio and how should the Fed change it? Carefully Explain.arrow_forward
- The reserve requirement, open market operations, and the money supply Assume that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency, so the only form of money is checkable deposits. To simplify the analysis, suppose the banking system has total reserves of $500. Determine the simple money multiplier and the money supply for each reserve requirement listed in the following table. Reserve Requirement Simple Money Multiplier Money Supply (Percent) (Dollars) 5 10 A lower reserve requirement is associated with a ______(SMALLER/LARGER) money supply. Suppose the Federal Reserve wants to increase the money supply by $200. Again, you can assume that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency. If the reserve requirement is 10%, the Fed will use open-market operations to _____(BUY/SELL)$ ________ worth of U.S. government bonds. Now, suppose that, rather than…arrow_forwardAssume that banks lend out all their excess reserves and individuals deposit all their money. If the Required Reserve Ratio is .20, what does the Fed have to do to decrease the supply of money by $300 billion? Select one: a. Sell $60 billion worth of government bonds to commercial banks b. Sell $80 billion worth of government bonds to commercial banks c. Sell $200 billion worth of government bonds to commercial banks d. Buy $100 billion worth of government bonds from commercial banks e. Buy $60 billion worth of government bonds from commercial banksarrow_forwardsuppose the required reserve ratio is 11%. How much additional money can BBB lend out at a maximum? suppose the required reserve ratio is lowered to 8%. What is the Maximum amount of additional money that BBB can lend out? Is this different than the maximum amount of new money BBB can create by itself? 3. suppose the required reserve ratio is raised to 15%. What is the maximum amount of additional money BBB can lend out?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education