
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The I beam below is fixed to a rigid wall and subjected to a force 100 kN at its right end. The specifications of the I beam is shown on the right. Other relevant parameters include the section moment of inertia Iz = 45.2 x 10-6 m4, the elastic modulus E = 200 GPa, and Poisson’s ratio v = 0.3. To monitor the local strain, a small rosette of 3 strain gauges is mounted at the top surface in the middle of the beam (red dot).
a) Solve the stress tensor at the location of strain gauge (red dot). Find the principle stresses and maximum shear stress.
b) What is the strain tensor at the red-dot location?
c) What are the readouts of each strain gauge?
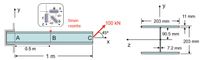
Transcribed Image Text:ах
45°
11 mm
Strain
203 mm
zT 45°
100 kN
rosette
450
90.5 mm
A
В
203 mm
0.5 m
+ 7.2 mm
1 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q4arrow_forwardA bar ABC of length L consists of two parts of equal lengths but different diameters. Segment AB has a diameter d 1 = 100 mm and segment BC has a diameter d 2 = 60 mm. Both segments have a length L / 2 = 0.6 m. A longitudinal hole of diameter d is drilled through segment AB in the middle of its length (distance L / 4 = 0.3 m). The bar is made of plastic with a modulus of elasticity. E = 4.0 GPa. Compressive loads P = 110 kN act at the ends of the bar. (a) If the shortening of the bar is limited to 8.0 mm, what is the maximum allowable diameter d max of the hole? (See figure part a.) (b) Now, if d max is set to d 2/2, at what distance b from the end C must the load P be applied to limit the shortening of the bar to 8.0 mm? (See Figure part b.) (C) Finally, if the loads P are applied at the ends and d max = d 2/2, what is the allowable length x of the hole if shortening is limited to 8.0 mm? (See figure part c.)arrow_forwardFor a conductive wire with length L=1cm,w=1mm, h=1mmunder uniaxial strain, the resistance change is given as. If the uniaxial strain is e= 1 and the Poisson’s ratio is n= 0.3. What is the gauge factor?arrow_forward
- 3. The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram for a steel alloy is shown in the figure below. The specimen from which it was obtained had an original diameter of 13 mm and a gauge length of 50 mm. If a load of P = 20 kN is applied to the specimen, determine its diameter and gauge length. Take v = 0.4 σ (MPa) 400 0.002 e(mm/mm)arrow_forwardA large thin rectangular plate is subjected to certain traction boundary conditions on its thin edges. The following stress function is proposed for this problem: 2 p(x,y) = A x¹ + B x²y² + Cy² (i) use the biharmonic equation to find restrictions, if any, on values of A, B, and C (ii) calculate all stress components (iii) calculate all strain components in terms of A, B, and C as well as the Young modulus and Poisson's ratio E and y, respectively. (iv) check that the equilibrium equations are satisfied (v) determine the traction boundary conditions at x=+a and y=+barrow_forwardLast 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY