
Principles of Accounting Volume 2
19th Edition
ISBN: 9781947172609
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
None
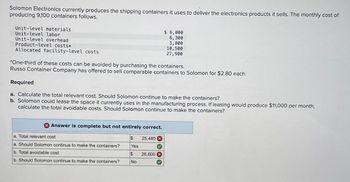
Transcribed Image Text:Solomon Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of
producing 9,100 containers follows.
Unit-level materials
Unit-level labor
Unit-level overhead
Product-level costs*
Allocated facility-level costs
$ 6,000
6,300
3,800
10,500
27,900
*One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers.
Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Solomon for $2.80 each.
Required
a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Solomon continue to make the containers?
b. Solomon could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $11,000 per month,
calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Solomon continue to make the containers?
Answer is complete but not entirely correct.
a. Total relevant cost
$
25,480
a. Should Solomon continue to make the containers?
Yes
b. Total avoidable cost
$
26,600x
b. Should Solomon continue to make the containers?
No
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Aril Industries is a multiproduct company that currently manufactures 30,000 units of Part 730 each month for use in production. The facilities now being used to produce Part 730 have fixed monthly overhead costs of 150,000 and a theoretical capacity to produce 60,000 units per month. If Aril were to buy Part 730 from an outside supplier, the facilities would be idle, and 40% of fixed costs would continue to be incurred. There are no alternative uses for the facilities. The variable production costs of Part 730 are 11 per unit. Fixed overhead is allocated based on planned production levels. If Aril Industries continues to use 30,000 units of Part 730 each month, it would realize a net benefit by purchasing Part 730 from an outside supplier only if the suppliers unit price is less than: a. 12.00. b. 12.50. c. 13.00. d. 14.00.arrow_forwardDimitri Designs has capacity to produce 30,000 desk chairs per year and is currently selling all 30,000 for $240 each. Country Enterprises has approached Dimitri to buy 800 chairs for $210 each. Dimitris normal variable cost is $165 per chair, including $50 per unit in direct labor per chair. Dimitri can produce the special order on an overtime shift, which means that direct labor would be paid overtime at 150% of the normal pay rate. The annual fixed costs will be unaffected by the special order and the contract will not disrupt any of Dimitris other operations. What will be the impact on profits of accepting the order?arrow_forwardPatz Company produces two types of machine parts: Part A and Part B, with unit contribution margins of 300 and 600, respectively. Assume initially that Patz can sell all that is produced of either component. Part A requires two hours of assembly, and B requires five hours of assembly. The firm has 300 assembly hours per week. Required: 1. Express the objective of maximizing the total contribution margin subject to the assembly-hour constraint. 2. Identify the optimal amount that should be produced of each machine part and the total contribution margin associated with this mix. 3. What if market conditions are such that Patz can sell at most 75 units of Part A and 60 units of Part B? Express the objective function with its associated constraints for this case and identify the optimal mix and its associated total contribution margin.arrow_forward
- Baird Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9,100 containers follows. $ 6,500 6,400 4,100 9,600 27,900 Unit-level materials Unit-level labor Unit-level overhead Product-level costs* Allocated facility-level costs *One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers. Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Baird for $2.60 each. Required a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Baird continue to make the containers? b. Baird could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $11,200 per month, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Baird continue to make the containers? a. Total relevant cost Should Baird continue to make the containers? b. Total avoidable cost Should Baird continue to make the containers?arrow_forwardCampbell Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9,200 containers follows. Unit-level materials Unit-level labor Unit-level overhead Product-level costs* Allocated facility-level costs $ 6,900 6,400 4,100 9,600 26,600 *One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers. Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Campbell for $2.80 each. Required a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Campbell continue to make the containers? b. Campbell could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $12,800 per month, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Campbell continue to make the containers? a. Total relevant cost Should Campbell continue to make the containers? b. Total avoidable cost Should Campbell continue to make the containers?arrow_forwardVernon Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9,100 containers follows. Unit-level materials Unit-level labor Unit-level overhead Product-level costs* Allocated facility-level costs $5,700 6,500 3,200 8,400 27,100 *One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers. Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Vernon for $2.60 each. Required a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Vernon continue to make the containers? b. Vernon could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $12,700 per month, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Vernon continue to make the containers? a. Total relevant cost a. Should Vernon continue to make the containers? b. Total avoidable cost b. Should Vernon continue to make the containers?arrow_forward
- Perez Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9,300 containers follows. Unit-level materials $ 6,000 6,900 3,600 8,400 26,500 Unit-level labor Unit-level overhead Product-level costs* Allocated facility-level costs *One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers. Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Perez for $2.80 each. Required a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Perez continue to make the containers? b. Perez could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $12,800 per month, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Perez continue to make the containers? a. Total relevant cost Should Perez continue to make the containers? b. Total avoidable cost Should Perez continue to make the containers?arrow_forwardRooney Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9,100 containers follows. Unit-level materials Unit-level labor Unit-level overhead Product-level costs* $ 5,200 6,500 3,600 9,300 26,600 Allocated facility-level costs *One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers. Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Rooney for $2.70 each. Required a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Rooney continue to make the containers? b. Rooney could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $11,500 per month, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Rooney continue to make the containers? a. Total relevant cost Should Rooney continue to make the containers? b. Total avoidable cost Should Rooney continue to make the containers?arrow_forwardFinch Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9,200 containers follows. Unit-level materials Unit-level labor Unit-level overhead Product-level costs* Allocated facility-level costs $ 6,400 6,000 4,000 11,400 27,300 *One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers. Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Finch for $2.70 each. Required a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Finch continue to make the containers? b. Finch could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $11,000 per month, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Finch continue to make the containers? a. Total relevant cost Should Finch continue to make the containers? b. Total avoidable cost Should Finch continue to make the containers?arrow_forward
- Rundle Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9,300 containers follows. Unit-level materials. Unit-level labor Unit-level overhead Product-level costs* Allocated facility-level costs One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers. Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Rundle for $2.60 each. Required a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Rundle continue to make the containers? b. Rundle could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $11,600 per month, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Rundle continue to make the containers? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. $ a. Total relevant cost a. Should Rundle continue to make the containers? b. Total avoidable cost b. Should Rundle continue to make the containers? 190.650,000 Yes $24,180,000 $ 5,200 6,100 4,000 7,800…arrow_forwardVishnuarrow_forwardAdams Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9,100 containers follows. Unit-level materials $ 5,400 Unit-level labor 6,400 Unit-level overhead 3,900 Product-level costs* 10,500 Allocated facility-level costs 28,200 *One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers.Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Adams for $2.80 each.Required Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Adams continue to make the containers? Adams could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $12,500 per month, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Adams continue to make the containers?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning