
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
2-Record the interest payment and amortization on June 30.
3-Record the interest payment and amortization on December 31.
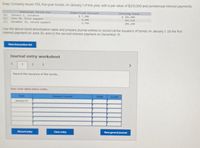
Transcribed Image Text:Snap Company issues 13% five-year bonds, on January 1 of this year, with a par value of $210,000 and semiannual interest payments.
Seianmual Periad-End
Unanortized Discount
(4) January 1, issuance
June , firt paynent
(1)
(2)
Decenber 31, secand payment
$7,200
6,480
5,76
Carrying Value
$ 202,800
203,520
204, 240
Use the above bond amortization table and prepare journal entries to record (ah the issuance of bonds on January 1, (by the first
nterest payment on June 30, and (a the second interest payment on December 31.
Vwansation list
Journal entry worksheet
2.
Record the issuance of the bonds.
Nate Eter debio before credits
Date
General Jeurnal
Debit
Credit
January 01
Resed endry
Clear ny
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the due date and the amount of interest due at maturity on the following notes: Date of Note January 5 * February 15 * May 19 August 20 e. October 19 a. $87,000 27,000 66,000 34,000 52,000 * Assume a leap year in which February has 29 days. Assume 360 days in a year when computing the interest. Note b. C. d. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Face Amount Due Date $ Interest Interest Rate 1000 6% 4 8 5 7 Term of Note 120 days 30 days 45 days 90 days 90 daysarrow_forwardA debtor firm’s 12/31/21 statement of financial position is to be issued of 4/15/22. A long-term obligation contracted in 2019 for settlement on 1/15/22 was extinguished through cash payment on its due date. On 1/20/22, a 5-year note was issued to replace the cash used up for the payment made on 1/15/22. Which of the following statements is correct? Group of answer choices The original obligation should be reported in the 2021 statement of financial position as a current liability because the entity does not have an unconditional right to defer settlement of the liability for at least twelve months after the reporting period. The new obligation entered into on 1/20/22 should be reported in the 2022 statement of financial position as a non-current liability because it is due to be settled beyond twelve months after the reporting period. The original obligation should be reported in the 2022 statement of financial position as a non-current liability because the entity does have an…arrow_forwardWhich of the following is not considered a current liability? The current portion of a noncurrent note payable O Unearned Revenue O Accounts Payable Bonds payable due in 2 yearsarrow_forward
- Year 1 Dec. 16 Accepted a $10,800, 60-day, 8% note in granting Danny Todd a time extension on his past-due account receivable. 31 Made an adjusting entry to record the accrued interest on the Todd note.arrow_forwardwhat is the due date for a loan dated Nov 7 for 120 days?arrow_forwardPlease help me figure out the notes and general journal for this problem.arrow_forward
- The following amortization schedule indicates the interest and principal to be repaid on an installment note established January 1, 2021, for a company with a March 31 fiscal year-end. Period 1/1-12/31, Year 1 Interest Expense on Notes Payable $ 560 424 #TITT 286 144 1,414 1/1-12/31, Year 2 1/1-12/31, Year 3 1/1-12/31, Year 4 Total Beginning Notes Payable $ 28,000 21, 207 14, 278 Repaid Principal Ending Notes 7,210 $ 6,793 6,929 7,068 7,210 28,000 Payable $ 21,207 14,278 7,210 Required: 1. Assuming the company makes the required annual payments on December 31, use the amortization schedule to determine (a) the amount of the (rounded) annual payment; (b) the amount of Interest Expense to report in the year ended March 31, 2021; (c) the amount of Interest Expense to report in the year ended March 31, 2022; (d) the Notes Payable balance at January 1, 2024; and (e) the total interest and total principal paid over the note's entire life 2. Assuming the company makes adjustments at the end…arrow_forwardWhich of the following accounts could not be classified as a current liability? Multiple Choice Unearned revenues. Accounts payable. Notes payable (due in 11 months). Current portion of long-term note payable. Notes payable (due in 5 years).arrow_forwardThe debt in the table below is retired by the sinking fund method. Interest payments on the debt are made at the end of each payment interval and the payments the sinking fund are made at the same time. Determine the following (a) the size of the periodic interest expense of the debt, (b) the size of the periodic payment into the sinking fund, (c) the periodic cost of the debt, (d) the book value of the debt at the time indicated. Debt Principal $19,000 Term of debt 10 years Payment Interval Interest Rate on Debt Interest Rate on Fund Conversion Period 3 months 6.5% 7% quarterly Book Value Required After 8 years (a) The size of the periodic interest expense is $ (Round the final answer to the nearest cent as needed. Round all intermediate values to six decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- Journalize the first annual interest payment on December 31, 20X1.arrow_forwardCullumber Company borrowed $760,000 on December 31, 2019, by issuing an $760,000, 8% mortgage note payable. The terms call for annual installment payments of $113,262 on December 31.arrow_forwardCompute the principal (in $) for the loan. Use ordinary interest when time is stated in days. Principal Rate (%) Time Interest $ 787.5 6 months $1,575 9arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education