
Principles of Accounting Volume 2
19th Edition
ISBN: 9781947172609
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I need answer
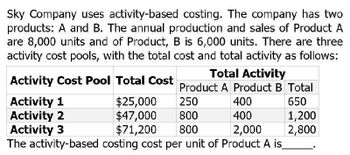
Transcribed Image Text:Sky Company uses activity-based costing. The company has two
products: A and B. The annual production and sales of Product A
are 8,000 units and of Product, B is 6,000 units. There are three
activity cost pools, with the total cost and total activity as follows:
Total Activity
Activity Cost Pool Total Cost
Product A Product B Total
Activity 1
$25,000
250
400
650
Activity 2
$47,000
800
400
1,200
Activity 3
$71,200
800
2,000
2,800
The activity-based costing cost per unit of Product A is_
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Rex Industries has two products. They manufactured 12,539 units of product A and 8.254 units of product B. The data are: What is the activity rate for each cost pool?arrow_forwardThe following product Costs are available for Haworth Company on the production of chairs: direct materials, $15,500; direct labor, $22.000; manufacturing overhead, $16.500; selling expenses, $6,900; and administrative expenses, $15,200. What are the prime costs? What are the conversion costs? What is the total product cost? What is the total period cost? If 7,750 equivalent units are produced, what is the equivalent material cost per unit? If 22,000 equivalent units are produced, what is the equivalent conversion cost per unit?arrow_forwardThe following product costs are available for Stellis Company on the production of erasers: direct materials, $22,000; direct labor, $35,000; manufacturing overhead, $17,500; selling expenses, $17,600; and administrative expenses; $13,400. What are the prime costs? What are the conversion costs? What is the total product cost? What is the total period cost? If 13,750 equivalent units are produced, what is the equivalent material cost per unit? If 17,500 equivalent units are produced, what is the equivalent conversion cost per unit?arrow_forward
- Wrappers Tape makes two products: Simple and Removable. It estimates it will produce 369,991 units of Simple and 146,100 of Removable, and the overhead for each of its cost pools is as follows: It has also estimated the activities for each cost driver as follows: Â How much is the overhead allocated to each unit of Simple and Removable?arrow_forwardCicleta Manufacturing has four activities: receiving materials, assembly, expediting products, and storing goods. Receiving and assembly are necessary activities; expediting and storing goods are unnecessary. The following data pertain to the four activities for the year ending 20x1 (actual price per unit of the activity driver is assumed to be equal to the standard price): Required: 1. Prepare a cost report for the year ending 20x1 that shows value-added costs, non-value-added costs, and total costs for each activity. 2. Explain why expediting products and storing goods are non-value-added activities. 3. What if receiving cost is a step-fixed cost with each step being 1,500 orders whereas assembly cost is a variable cost? What is the implication for reducing the cost of waste for each activity?arrow_forwardThe following product costs are available for Kellee Company on the production of eyeglass frames: direct materials, $32,125; direct labor, $23.50; manufacturing overhead, applied at 225% of direct labor cost; selling expenses, $22,225; and administrative expenses, $31,125. The direct labor hours worked for the month are 3,200 hours. A. What are the prime costs? B. What are the conversion costs? C. What is the total product cost? D. What is the total period cost? E. If 6.425 equivalent units are produced, what is the equivalent material cost per unit? F. What is the equivalent conversion cost per unit?arrow_forward
- Cool Pool has these costs associated with production of 20,000 units of accessory products: direct materials, $70; direct labor, $110; variable manufacturing overhead, $45; total fixed manufacturing overhead, $800,000. What is the cost per unit under both the variable and absorption methods?arrow_forwardBaxter Company has a relevant range of production between 15,000 and 30,000 units. The following cost data represents average variable costs per unit for 25,000 units of production. Using the costs data from Rose Company, answer the following questions: A. If 15,000 units are produced, what is the variable cost per unit? B. If 28,000 units are produced, what is the variable cost per unit? C. If 21,000 units are produced, what are the total variable costs? D. If 29,000 units are produced, what are the total variable costs? E. If 17,000 units are produced, what are the total manufacturing overhead costs incurred? F. If 23,000 units are produced, what are the total manufacturing overhead costs incurred? G. If 30,000 units are produced, what are the per unit manufacturing overhead costs incurred? H. If 15,000 units are produced, what are the per unit manufacturing overhead costs incurred?arrow_forwardPatterson Company produces wafers for integrated circuits. Data for the most recent year are provided: aCalculated using number of dies as the single unit-level driver. bCalculated by multiplying the consumption ratio of each product by the cost of each activity. Required: 1. Using the five most expensive activities, calculate the overhead cost assigned to each product. Assume that the costs of the other activities are assigned in proportion to the cost of the five activities. 2. Calculate the error relative to the fully specified ABC product cost and comment on the outcome. 3. What if activities 1, 2, 5, and 8 each had a cost of 650,000 and the remaining activities had a cost of 50,000? Calculate the cost assigned to Wafer A by a fully specified ABC system and then by an approximately relevant ABC approach. Comment on the implications for the approximately relevant approach.arrow_forward
- Pat Company uses activity-based costing. The company has two products: A and B. The annual production and sales of Product A is 8,000 units and of Product B is 2,000 units. There are three activity cost pools, with estimated total cost and expected activity as follows: Expected Activity Activity Cost Pool Estimated Cost Product A Product B Total Activity 1…………… $12,000 750 250 1,000 Activity 2…………… $16,000 400 100 500 Activity 3…………… $36,000 2,000 1,000 3,000 The cost per unit of Product B under activity-based costing is closest to: A. $10.67. B. $6.40. C. $6.00. D. $9.10.arrow_forwardAnnika Company uses activity-based costing. The company has two products: A and B. The annual production and sales of Product A is 4,000 units and of Product B is 1,000 units. There are three activity cost pools, with total cost and activity as follows: Total Activity Activity Cost Pool Total Cost Product A Product B Total Activity 1 $ 18,000 700 300 1,000 Activity 2 $ 24,000 500 100 600 Activity 3 $ 60,000 800 400 1,200 The activity-based costing cost per unit of Product A is ?arrow_forwardThe activity based costing cost per unitarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning