
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
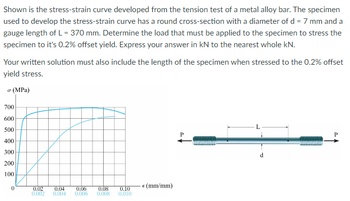
Transcribed Image Text:Shown is the stress-strain curve developed from the tension test of a metal alloy bar. The specimen
used to develop the stress-strain curve has a round cross-section with a diameter of d = 7 mm and a
gauge length of L = 370 mm. Determine the load that must be applied to the specimen to stress the
specimen to it's 0.2% offset yield. Express your answer in kN to the nearest whole kN.
Your written solution must also include the length of the specimen when stressed to the 0.2% offset
yield stress.
σ (MPa)
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.10
0.002
0.004 0.006 0.008 0.010
€ (mm/mm)
P
d
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Read and Solve carefully please Write clearly and Box the Final answer Express your answer to 3 Significant figures and include appropriate units. QUESTION : A long slender two-force member of cross-sectional area 2.17 mm2 is preloaded with a tensile force of 0.44 kN. A strain gauge is then applied to the member which is subject to time-varying loading with reading varying from -241 micro-strain to 50 micro-strain. Determine the minimum stress in the member in units of MPa.arrow_forwardConsider the state of plain “stress" for the following element. Derive the parametric value for the out of plane "strain" component. Applied tractions B Aarrow_forwardNeed correctly. Thank youarrow_forward
- The principal plane stresses and associated strains in a 35 ksi, 02 = 15 ksi, plane at a point are 01 1 €1 = 1.02(10-3), 2 = 0.180(10-³). ▼ Determine the modulus of elasticity. Express your answer using three significant figures and include the appropriate units. E= Submit Part B V= μA Value Request Answer Submit Determine the Poisson's ratio. Express your answer using three significant figures. ΠΑΠΙ ΑΣΦ | Η VE Units Request Answer ? vec POSSIA space ?arrow_forwardAn engine parts is being tested with a load of 60000 lb. The allowable tensile stress is 10000 psi, modulus of elasticity of 40x106 psi. If the original length of specimen is 42 inches with elongation not exceeding 0.0015 in, what diameter of the specimen is rejected? a. 4.2 in b. 3.0 in c. 2.5 in d. 5.17 inarrow_forwardKindly answer correctly. Please show the necessary stepsarrow_forward
- Hello, the stress and cycles required for this question is Stress 1 = 420MPa at 7 cycles, Stress 2 = 360MPa at 65 cycles and Stress 3 = 130MPa at 325 cycles. Use the first three cycles (which shows how many cycles at that stress level to failure) to calculate when the specimen will fail if it underwent test of 7 cycles at 420MPa, then undergoes 360MPa for 65 cycles and finally 130MPa at 325 cycles. Will the specimen fail? Please show calculations of failurearrow_forwardsolve first one only and use b h and x to find the strainarrow_forwardTo determine the nominal or engineering stress and strain experienced by a specimen of a material while it is subjected to a tension test, and to be able to read important values from a conventional stress-strain diagram obtained from the test. A tension test is being conducted on a steel-rod specimen with a gauge length of L0=50 mm and initial diameter of d0=13 mm. Data were collected to form the conventional stress-strain diagram as shown. From the diagram, f = 506 MPa , e = 689 MPa , g = 585 MPa , and h = 0.146 mm/mm . A) Assuming that the strain remains constant throughout the region between the gauge points, determine the nominal strain ε experienced by the rod if it is elongated to L = 53.0 mm . B) Assuming that the stress is constant over the cross-sectional area and if the tension force used is P = 16.0 kN , find the nominal stress experienced by the rod. C)Determine the force P needed to reach the ultimate stress in the steel-rod specimen.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY