
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305116399
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
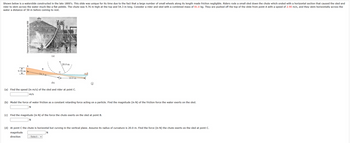
Transcribed Image Text:Shown below is a waterslide constructed in the late 1800's. This slide was unique for its time due to the fact that a large number of small wheels along its length made friction negligible. Riders rode a small sled down the chute which ended with a horizontal section that caused the sled and
rider to skim across the water much like a flat pebble. The chute was 9.76 m high at the top and 54.3 m long. Consider a rider and sled with a combined mass of 81.0 kg. They are pushed off the top of the slide from point A with a speed of 2.90 m/s, and they skim horizontally across the
water a distance of 50 m before coming to rest.
9.76 m
Engraving from Scientific American, July 1888
A
(a)
20.0 m
-54.3 m
50.0 m
(b)
(a) Find the speed (in m/s) of the sled and rider at point C.
m/s
(b) Model the force of water friction as a constant retarding force acting on a particle. Find the magnitude (in N) of the friction force the water exerts on the sled.
N
(c) Find the magnitude (in N) of the force the chute exerts on the sled at point B.
N
(d) At point C the chute is horizontal but curving in the vertical plane. Assume its radius of curvature is 20.0 m. Find the force (in N) the chute exerts on the sled at point C.
magnitude
direction
---Select--- ✓
N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Scissors are like a double-lever "Stem, Which of the Simple machines in Figure 9.23 and Figure 9.24 is most analogous to scissors? Figure 9.23 A nail puller is a lever with a large mechanical advantage. The external forces on the nail puller are represented by solid arrows. The force that the nail puller applies to the nail ( Fo ) is not a force on the nail puller. The reaction force the nail exerts back on the puller ( Fn ) is an external force and is equal and opposite to Fo. The perpendicular lever arms of the input and output forces are li and l0 Figure 9.24 (a) In the case of the wheelbarrow, the output force or load is between the pivot and the input force. The pivot IS the wheel's axle. Here, the output force is greater than the input force. Thus, a wheelbarrow enables you to lift much heavier loads than you could with your body alone. (b) In the case of the shovel, the input force is between the pivot and the load, but the input lever arm is shorter than the output lever arm. The pivot is at the handle held by the right hand. Here, the output force (supporting the shovel's load) is less than the input force (from the hand nearest the load), because the Input is exerted closer to the pivot than is the outputarrow_forwardShow that when A+B=C then A2+B2+2ABcos , where is the angle between vectors A and B .arrow_forwardTo give a pet hamster exercise, some people put the hamster in a ventilated ball andallow it roam around the house(Fig. P13.66). When a hamsteris in such a ball, it can cross atypical room in a few minutes.Estimate the total kinetic energyin the ball-hamster system. FIGURE P13.66 Problems 66 and 67arrow_forward
- Review. The mass of a car is 1 500 kg. The shape of the cars body is such that its aerodynamic drag coefficient is D = 0.330 and its frontal area is 2.50 m2. Assuming the drag force is proportional to 2 and ignoring other sources of friction, calculate the power required to maintain a speed of 100 km/h as the car climbs a long hill sloping at 3.20.arrow_forwardWhen a body slides down an inclined plane, does the work of friction depend on the body’s initial speed? Answer the same question for a body sliding down a curved surface.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true about the relationship between the dot product of two vectors and the product of the magnitudes of the vectors? (a) AB is larger than AB. (b) AB is smaller than AB. (c) AB could be larger or smaller than AB, depending on the angle between the vectors. (d) AB could be equal to AB.arrow_forward
- Sophia is playing with a set of wooden toys, rolling them offthe table and onto the floor. One of the toys is a small spherewith a mass of 0.024 kg and a radius of 0.020 m, and another isa small cylinder that also has a mass of 0.024 kg but a radius of0.013 m. She rolls each toy so that it has the same translationalspeed of 0.40 m/s. How much greater is the kinetic energy ofthe cylinder than the kinetic energy of the sphere?arrow_forwardA space probe is fired as a projectile from the Earths surface with an initial speed of 2.00 104 m/s. What will its speed be when it is very far from the Earth? Ignore atmospheric friction and the rotation of the Earth. P11.26 Ki+Ui=Kf+Uf12mvi2+GMEm(1rf1ri)=12mvf212vi2+GME(01RE)=12vf2orvf2=v122GMEREandvf=(v122GMERE)1/2,vf=[(2.00104)21.25108]1/2m/s=1.66104m/sarrow_forwardA pendulum consists of a small object called a bob hanging from a light cord of fixed length, with the top end of the cord fixed, as represented in Figure OQ5.6. The bob moves without friction, swinging equally high on both sides. It moves from its turning point A through point B and reaches its maximum speed at point C. (a) Of these points, is there a point where the bob has nonzero radial acceleration and zero tangential acceleration? If so, which point? What is the direction of its total acceleration at this point? (b) Of these points, is there a point where the bob has nonzero tangential acceleration and zero radial acceleration? If so, which point? What is the direction of its total acceleration at this point? (c) Is there a point where the bob has no acceleration? If so, which point? (d) Is there a point where the bob has both nonzero tangential and radial acceleration? If so, which point? What is the direction of its total acceleration at this point? Figure OQ5.6arrow_forward
- A system consists of five particles. How many terms appear in the expression for the total gravitational potential energy of the system? (a) 4 (b) 5 (c) 10 (d) 20 (e) 25arrow_forwardA student is asked to measure the acceleration of a glider on a frictionless, inclined plane, using an air track, a stopwatch, and a meterstick. The top of the track is measured to be 1.774 cm higher than the bottom of the track, and the length of the track is d = 127.1 cm. The cart is released from rest at the top of the incline, taken as x = 0, and its position x along the incline is measured as a function of time. For x values of 10.0 cm, 20.0 cm, 35.0 cm, 50.0 cm, 75.0 cm, and 100 cm, the measured times at which these positions are reached (averaged over five runs) are 1.02 s, 1.53 s, 2.01 s, 2.64 s, 3.30 s, and 3.75 s, respectively. (a) Construct a graph of x versus t2, with a best-fit straight line to describe the data. (b) Determine the acceleration of the cart from the slope of this graph. (c) Explain how your answer to part (b) compares with the theoretical value you calculate using a = g sin as derived in Example 4.3.arrow_forwardA 40.0-kg child swings in a swing supported by two chains, each 3.00 m long. The tension in each chain at the lowest point is 350 N. Find (a) the childs speed at the lowest point and (b) the force exerted by the seat on the child at the lowest point. (Ignore the mass of the seat.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill