
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
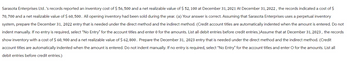
Transcribed Image Text:Sarasota Enterprises Ltd.'s records reported an inventory cost of $ 56, 500 and a net realizable value of $ 52, 100 at December 31, 2021 At December 31, 2022, the records indicated a cost of $
70, 700 and a net realizable value of $ 60,500. All opening inventory had been sold during the year. (a) Your answer is correct. Assuming that Sarasota Enterprises uses a perpetual inventory
system, prepare the December 31, 2022 entry that is needed under the direct method and the indirect method. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not
indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter 0 for the amounts. List all debit entries before credit entries.) Assume that at December 31, 2023, the records
show inventory with a cost of $ 60, 900 and a net realizable value of $ 62,800. Prepare the December 31, 2023 entry that is needed under the direct method and the indirect method. (Credit
account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter O for the amounts. List all
debit entries before credit entries.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Caterpillar Inc (CAT) has the following excerpts from their financial statements December 31, 2021 December 31, 2020 Inventory (in $ Millions) 14,038 11,402 Net Income(in $ Millions) 6,489 2,998 Inventories are principally determined using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method. The value of inventories on the LIFO basis. If the FIFO (first-in, first-out) method had been in use, inventories would have been $3,258 million and $2,921 million higher than reported at December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. Assume corporate tax rate of 21%. If CAT had used FIFO method instead of LIFO method What inventory (in $ Millions) would CAT report for 2021? What net income (profit) would CAT report in 2021? What is the cumulative amount of income tax savings that CAT generated through end of 2021 by using LIFO instead of FIFO? What…arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2024, a Company adopted the dollar-value LIFO method for its one inventory pool. The pool’s value on this date was $750,000. The 2024 and 2025 ending inventory valued at year-end costs were $793,000 and $882,000, respectively. The appropriate cost indexes are 1.04 for 2024 and 1.05 for 2025. Required: Complete the below table to calculate the inventory value at the end of 2024 and 2025 using the dollar-value LIFO method. Note: Round "Year end cost index" to 2 decimal places. Round other final answer values to the nearest whole dollars.arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2024, a Company adopted the dollar-value LIFO method for its one inventory pool. The pool’s value on this date was $660,000. The 2024 and 2025 ending inventory valued at year-end costs were $690,000 and $760,000, respectively. The appropriate cost indexes are 1.04 for 2024 and 1.08 for 2025. Required: Complete the below table to calculate the inventory value at the end of 2024 and 2025 using the dollar-value LIFO method.arrow_forward
- On December 31, 2023, Jen & Mink Clothing (J&M) performed the inventory count and determined the year-end ending inventory value to be $76500. It is now January 8, 2024, and you have been asked to double-check the year-end inventory listing. J&M uses a perpetual inventory system. Note: Only relevant items are shown on the inventory listing. # 1 2 ... Jen & Mink Clothing, Inventory Listing December 31, 2023 Inventory Number Inventory Description Quantity (units) Unit Cost ($) Total Value ($) 7649 10824 Blue Jackets Black pants 102 304 22 17 2,244 5,168 *** Total Inventory $76,500 The following situations have been brought to your attention: a. On January 3, 2024, J&M received a shipment of 102 blue jackets, for $2,244 (Item #7649). The inventory was purchased December 23, 2023, FOB destination from Global Threads. This inventory was included in J&M's inventory count and inventory listing. b. On December 29, 2023, J&M sold scarves (Item # 5566) to a customer with a sale price of $720 and…arrow_forwardBoulder, Incorporated is computing its inventory at December 31, 2022. The following information relates to the five major inventory items regularly stocked for resale: Item A B C D E Item A B Required: Using the lower of cost or net realizable value, compute the total valuation for each inventory item at December 31 2022, and the total inventory valuation. C Ending Inventory, Quantity on December 31, 2022 Unit Hand 140 190 45 340 740 D E Total Inventory Valuation $ Net Realizable Value (Market) at Cost when Acquired (FIFO) December 31, 2022 $44 $39 $54 $56 $104 $84 $66 $16 0 $64 $19arrow_forwardMercury Company has only one inventory pool. On December 31, 2024, Mercury adopted the dollar-value LIFO inventory method. The inventory on that date using the dollar-value LIFO method was $215,000. Inventory data are as follows: Year 2025 2026 2027 Ending Inventory at Year-End Costs $ 262,500 350,750 354,000 Ending Inventory at Base Year Costs $ 250,000 305,000 295,000 Required: Compute the inventory at December 31, 2025, 2026, and 2027, using the dollar-value LIFO method. Note: Round "Year end cost index" to 2 decimal places. Inventory Layers Converted to Base Year Cost Inventory Layers Converted to Cost Inventory at Date Year-End Cost Year-End Cost Index 12/31/2024 12/31/2025 12/31/2026 = Inventory DVL Cost Ending Inventory at Base Year Ending Inventory at Base Year Year-End Cost Index Cost Cost Inventory Layers Converted to Cost Base $ ° Base 2025 $ 0 Base 2025)arrow_forward
- Current Attempt in Progress Marigold Inc. uses a perpetual inventory system. At January 1, 2025, inventory was $368,080 at both cost and net realizable value. At December 31, 2025, the inventory was $491,920 at cost and $455,800 at net realizable value. Prepare the entry under (a) the cost-of-goods-sold method and (b) the loss method. (List all debit entries before credit entries. Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No entry" for the account titles and enter O for the amounts.) No. Account Titles and Explanation (a) (b) e Textbook and Media List of Accounts Save for Later Debit Credit Attempts: 1 of 3 used Submit Answerarrow_forwards Mercury Company has only one inventory pool. On December 31, 2024, Mercury adopted the dollar-value LIFO inventory method. The inventory on that date using the dollar-value LIFO method was $210,000. Inventory data are as follows: Year 2025 2026 2027 Date Required: Compute the inventory at December 31, 2025, 2026, and 2027, using the dollar-value LIFO method. Note: Round "Year end cost index" to 2 decimal places. 12/31/2024 12/31/2025 12/31/2026 Ending Inventory at Ending Inventory at Year-End Costs Base Year Costs $ 252,000 333,500 336,000 12/31/2027 $ 240,000 290,000 280,000 Inventory Layers Converted to Base Year Cost Inventory at Year-End Cost Year-End Cost Index = = = = Ending Inventory at Base Year Cost Base Base 2025 Base 2025 2026 Base 2025 2026 2027 Inventory Layers Converted to Cost Ending Inventory at Base Year Cost Year-End Cost Index = Inventory Layers Converted to Cost Inventory DVL Cost $ $ $ $ 0 0 0 0arrow_forwardCharleston Company has elected to use the dollar-value LIFO retail method to value its inventory. The following data has been accumulated from the accounting records: Merchandise inventory, January 1, 2024 Cost $ 299,390 661,388 Net purchases Net markups Net markdowns Net sales Pertinent retail price indexes: January 1, 2024 December 31, 2024 Required: Estimate the ending inventory for December 31, 2024. 1.00 1.10 Note: Round "Cost-to-retail percentage" to 2 decimal places. Estimated ending inventory (At Retail) Estimated ending inventory (At Cost) Retail $ 470,000 1,017,000 13,700 3,700 633,500arrow_forward
- Volata Company began operations on January 1, 2019. In the second quarter of 2020, it adopted the FIFO method of inventory valuation. In the past, it used the LIFO method. The company’s interim income statements as originally reported under the LIFO method follow: 2019 2020 1stQ 2ndQ 3rdQ 4thQ 1stQ Sales $ 14,000 $ 16,000 $ 18,000 $ 20,000 $ 22,000 Cost of goods sold (LIFO) 4,400 5,400 6,200 7,400 8,900 Operating expenses 2,400 2,600 3,000 3,400 3,600 Income before income taxes $ 7,200 $ 8,000 $ 8,800 $ 9,200 $ 9,500 Income taxes (25%) 1,800 2,000 2,200 2,300 2,375 Net income $ 5,400 $ 6,000 $ 6,600 $ 6,900 $ 7,125 If the FIFO method had been used since the company began operations, cost of goods sold in each of the previous quarters would have been as follows: 2019 2020 1stQ 2ndQ 3rdQ 4thQ…arrow_forwardBonita Company began operations in 2025 and determined its ending inventory at cost and at LCNRV at December 31, 2025, and December 31, 2026. This information is presented below. 12/31/25 12/31/26 Cost $312,750 393,920 Date Net Realizable Value $286,430 371,370 (a) Prepare the journal entries required at December 31, 2025, and December 31, 2026, assuming inventory is recorded at LCNRV and a perpetual inventory system using the cost-of-goods-sold method. (List all debit entries before credit entries. Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No entry" for the account titles and enter O for the amounts. Record journal entries in the order presented in the problem.) Account Titles and Explanation Debit Creditarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education