
Concept explainers
Variable costing and absorption costing, the Z-Var Corporation. (R. Marple, adapted) It is the end of 2017. Z-Var Corporation began operations in January 2016. The company is so named because it has no variable costs (Zero VARiable). All its costs are xed; they do not vary with output. Z-Var Corp. is located on the bank of a river and has its own hydroelectric plant to supply power, light, and heat. The company manufactures a synthetic fertilizer from air and river water and sells its product at a price that is not expected to change. It has a small staff of employees, all paid xed annual
salaries. The output of the plant can be increased or decreased by pressing a few buttons on a keyboard. The following budgeted and actual data are for the operations of Z-Var. The company uses budgeted production as the denominator level and writes off any production-volume variance to cost of goods sold.
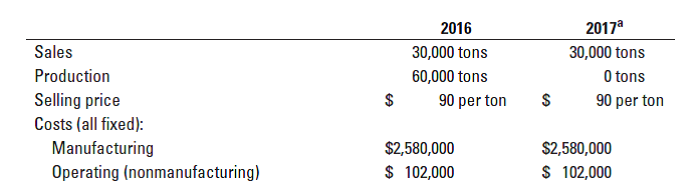

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 6 images

- SixthZ incurred the following costs during 2018: Variable costs treehouse Manufacturing: Direct Materials $500 Direct Labor $270 VMO $40 Variable Selling & Admin $75 Fixed costs per year Fixed Manufacturing Overhead $125,000 Fixed Selling & Admin $60,000 During the year, SixthZ produced 1,100 treehouses and sold 950 treehouses. The selling price of each set was $1,000. Assuming SixthZ uses variable costing, what is the unit product cost? O $941.58 O $885 O $923.64 O $810arrow_forwardVik Don't upload any imagearrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Henna Company produces and sells two products, Carvings and Mementos. It manufactures these products in separate factories and markets them through different channels. They have no shared costs. This year, the company sold 44,000 units of each product. Income statements for each product follow. Sales Variable costs Contribution margin Fixed costs Income 3. Assume that the company expects sales of each product to increase to 58,000 units next year with no change in unit selling price. Prepare a contribution margin income statement for the next year (as shown above with columns for each of the two products). (Round "per unit" answers to 2 decimal places.) Contribution margin Income (loss) Carvings $ 774,400 464, 640 309,760 Mementos $ 774,400 154,880 619,520 187,760 497,520 $ 122,000 $ 122,000 HENNA COMPANY Contribution Margin Income Statement Carvings Units $ Per unit Total Mementos $ Per unit Total Totalarrow_forward
- Witt Recreation Company (WRC) makes e-bikes. The company currently manufactures two models, the Coaster and the Traveler, in one of the WRC factories. Both models require the same assembling operations. The difference between the models is the cost of materials. The following data are available for the second quarter. Number of bikes assembled Materials cost per bike Other costs: Direct labor Depreciation and lease Supervision and control Factory administration Operation cost Materials cost Total cost Unit cost Coaster 750 $626 Coaster Traveler 450 $ 1,202 Required: Witt Recreation Company uses operations costing and assigns conversion costs based on the number of units assembled. Compute the cost of each model assembled in the second quarter. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to nearest whole number. Total 1,200 Traveler $ 299,400 382,400 247,400 340,400 Totalarrow_forwardFollowing a strategy of product differentiation, Cold Lake Company makes a high-end appliance, AP15. Cold Lake Company presents the data in the table for years 1 and 2. (Click the icon to view the table.) Cold Lake Company produces no defective units, but it wants to reduce direct materials usage per unit of AP15 in year 2. Manufacturing conversion costs in each year depend on production capacity, defined in terms of AP15 units that can be produced. Selling and customer-service costs depend on the number of customers that the customer and service functions are designed to support. Neither conversion costs nor customer-service costs are affected by changes in actual volume. Cold Lake Company has 46 customers in year 1 and 50 customers in year 2. The industry market size for high-end appliances increased 5% from year 1 to year 2. What is the Cold Lake Company's operating income in Year 2? OA. $200,000 OB. $188,000 OC. $4,620,000 OD. $1,440,000 OE. $1,804,500arrow_forwardThe Chopin Company has decided to introduce a new product. The new product can be manufactured by either a computer-assisted manufacturing (CAM) or a labor-intensive production (LIP) system. The manufacturing method will not affect the quality of the product. The estimated manufacturing costs for each of the two methods are as follows. CAM System: Direct Material = $5.0 Direct Labor (DLH) = 0.5 DLH X $12 = $6 Variable Overhead = 0.5DLHx$6 = $3 Fixed Iverhead* = $ 2,440,000 LIP System: Direct Material = $5.6 Direct Labor (DLH) = 0.8 DLH X $9 = $7.2 Variable Overhead = 0.8 DLH X $6 = $4.8 Fixed Overhead* = $1,320,000 *These costs are directly traceable to the new product line. They would not be incurred if the new product were not produced. The company’s marketing research department has recommended an introductory unit sales price of $30. Selling expenses are estimated to be $500,000 annually plus $2 for each unit sold. (Ignore income taxes.) Required: Calculate the estimated…arrow_forward
- DK manufactures three products, W, X and Y. Each product uses the same materials and the same type of direct labour but in different quantities. The company currently uses a cost plus basis to determine the selling price of its products. This is based on full cost using an overhead absorption rate per direct labour hour. However, the managing director is concerned that the company may be losing sales because of its approach to setting prices. He thinks that a marginal costing approach may be more appropriate, particularly since the workforce is guaranteed a minimum weekly wage and has a three month notice period.e a) Given the managing director's concern about DK's approach to setting selling prices, discuss the advantages and disadvantages of marginal cost plus pricing AND total cost-plus pricing. The direct costs of the three products are shown below: Product- Budgeted annual production (units) 15,000- 24,000 20,000 $ per unita $ per unite $ per unita Direct materials 354 40 45a…arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Celestial Products, Inc., has decided to introduce a new product, which can be manufactured by either a computer- assisted manufacturing system or a labor-intensive production system. The manufacturing method will not affect the quality of the product. The estimated manufacturing costs by the two methods are as follows: Direct material Direct labor (DLH denotes direct-labor hours) Variable overhead Fixed overhead* Computer-Assisted Manufacturing System $ Volume 0.5DLH @ $25.50 0.5DLH @ $16.50 9.00 12.75 8.25 $4,410,000 units Labor-Intensive Production System $ 0.8DLH @ $21.00 0.8DLH @ $16.50 *These costs are directly traceable to the new product line. They would not be incurred if the new product were not produced. 9.90 16.80 13.20 $2,730,000 The company's marketing research department has recommended an introductory unit sales price of $75.00. Selling expenses are estimated to be $900,000…arrow_forwardSagararrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





