
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
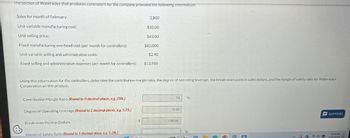
Transcribed Image Text:The section of Waterways that produces controllers for the company provided the following information.
Sales for month of February:
Unit variable manufacturing cost:
Unit selling price:
3,800
$10.00
$43.00
Fixed manufacturing overhead cost (per month for controllers):
$83,000
Unit variable selling and administrative costs:
$2.90
Fixed selling and administrative expenses (per month for controllers): $13,950
Using this information for the controllers, determine the contribution margin ratio, the degree of operating leverage, the break-even point in sales dollars, and the margin of safety ratio for Waterways
Corporation on this product.
Contribution Margin Ratio (Round to O decimal places, e.g. 25%.)
70
%
Degree of Operating Leverage (Round to 2 decimal places, e.g. 5.25.)
Break-even Point in Dollars
Margin of Safety Ratio (Round to 1 decimal place, ex. 5.2%)
6.56
138500
%
SUPPORT
8:34 PM
3/16/2024
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Contribution Margin Income Statement For Year Ended December 31 Sales (400,000 units) Variable costs Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Contribution margin Fixed costs Fixed overhead Fixed general and administrative Income Per Unit $ 6.00 Required 1 Required 2 1.44 0.36 0.60 3.60 0.20 0.15 $ 3.25 Required: 1. Compute income from the special offer. 2. Should the company accept or reject the special offer? Contribution margin A potential customer offers to buy 50,000 units for $3.20 each. These sales would not affect the company's sales through its normal channels. Details about the special offer follow. • Direct materials cost per unit and variable overhead cost per unit would not change. ● Direct labor cost per unit would be $0.54 because the offer would require overtime pay. • Accepting the offer would require incremental fixed general and administrative costs of $5,000. Accepting the offer would require no incremental fixed overhead costs. Fixed overhead Fixed general…arrow_forwardPrepare an absorption-costing income statement for last year. Round to nearest whole number.arrow_forwardThe manufacturing costs of Ackerman Industries for the first three months of the year follow: Total Costs Units Produced January $264,960 1,380 units February 392,730 2,330 March 412,160 3,680 Using the high-low method, determine (a) the variable cost per unit and (b) the total fixed cost. Round all answers to the nearest whole dollar. a. Variable cost per unit $fill in the blank 1 b. Total fixed cost $fill in the blank 2arrow_forward
- Calculate and Use Ovrehead Rate During the coming accounting year, Baker Manufacturing, Inc. anticipates the following costs, expenses, and operating data: Direct material (16,000 lb) $80,000 Direct labor (@10/hr) 200,000 Indirect materials 12,000 Indirect labor 22,000 Sales Commissions 34,000 Factory administration 16,000 Nonfactory administrative expenses 20,000 Other manufacturing overhead 80,000 a. Calculate the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the coming year for each of the following application bases: (1) direct labor hours, (2) direct labor costs, and (3) machine hours. b. For each item in requirement in requirement a, determine the proper application of manufacuring overhead to Job 63, to which 16 direct labor hours, $150 of direct labor cost, and 40 machine…arrow_forwardEstimated Income Statements, using Absorptionand Variable Costing Prior to the first month of operations ending October 31, Marshall Inc. estimated the following operating results: Sales (24,800 x $86) $2,132,800 Manufacturing costs (24,800 units): Direct materials 1,282,160 Direct labor 302,560 Variable factory overhead 141,360 Fixed factory overhead 168,640 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 45,900 Variable selling and administrative expenses 55,500 The company is evaluating a proposal to manufacture 27,200 units instead of 24,800 units, thus creating an ending inventory of 2,400 units. Manufacturing the additional units will not change sales, unit variable factory overhead costs, total fixed factory overhead cost, or total selling and administrative expenses. a. 1. Prepare an estimated income statement, comparing operating results if 24,800 and 27,200 units are manufactured in the absorption costing format. If an amount box does not…arrow_forwardLindquist Company has the following information for February: Line Item Description Amount Sales $370,000 Variable cost of goods sold 173,900 Fixed manufacturing costs 55,500 Variable selling and administrative expenses 40,700 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 22,200 Determine the following for Lindquist Company for the month of February: Line Item Description Amount a. Manufacturing margin $fill in the blank 1 b. Contribution margin $fill in the blank 2 c. Operating income $fill in the blank 3arrow_forward
- Farrow Company reports the following annual results. Contribution Margin Income Statement Per Unit Annual Total Sales (240,000 units) $ 15.00 $ 3,600,000 Variable costs Direct materials 2.00 480,000 Direct labor 4.00 960,000 Overhead 2.50 600,000 Contribution margin 6.50 1,560,000 Fixed costs Fixed overhead 2.00 480,000 Fixed general and administrative 1.50 360,000 Income $ 3.00 $ 720,000 The company receives a special offer for 24,000 units at $12 per unit. The additional sales would not affect its normal sales. Variable costs per unit would be the same for the special offer as they are for the normal units. The special offer would require incremental fixed overhead of $96,000 and incremental fixed general and administrative costs of $103,000. (a) Compute the income or loss for the special offer.(b) Should the company accept or reject the special offer? Compute the income or loss for the special offer. (Round your "Per Unit" answers to 2…arrow_forwardThe following monthly data in contribution format are available for the Ross Company and its only product. Product SD: Sales Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses Net operating income Total $ $ $ $ $ 224.000 177.800 46,200 34.500 11,700 Per Unit $ 160 127 33 $ company produced and sold 1.400 units during the month and had no beginning or ending inventories, a) What is the current operating leverage? b) Projections indicate that the market will contract by 15% next month. What is the projected net operating income given this increase?arrow_forwardEstimated Income Statements, using Absorption and Variable Costing Prior to the first month of operations ending October 31, Marshall Inc. estimated the following operating results: Sales (25,600 x $91) $2,329,600 Manufacturing costs (25,600 units): Direct materials 1,400,320 Direct labor 332,800 Variable factory overhead 153,600 Fixed factory overhead 184,320 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 50,100 Variable selling and administrative expenses 60,600 The company is evaluating a proposal to manufacture 28,800 units instead of 25,600 units, thus creating an ending inventory of 3,200 units. Manufacturing the additional units will not change sales, unit variable factory overhead costs, total fixed factory overhead cost, or total selling and administrative expenses. a. 1. Prepare an estimated income statement, comparing operating results if 25,600 and 28,800 units are manufactured in the absorption costing format. If an amount box does not…arrow_forward
- Locklear, Inc. reports the following information for the year ended December 31: Units sold Sales price Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative costs Fixed selling and administrative costs 650 units $160 per unit $25 per unit $11 per unit $15 per unit $25 per unit $6 per unit $12,600 per year The operating income calculated using variable costing and absorption costing amounted to $9,100 and $10,300, respectively. There were no beginning inventories. Determine the total fixed manufacturing overhead that will be expensed under absorption costing for the year. OA. $32,500 B. $16,250 C. $17,450 D. $33,150arrow_forwardGreen and White Company reported the following monthly data: 3,600 units $ 27 per unit $ 2 per unit $ 3 per unit $ 3.50 per unit $ 14,400 in total $0.50 per unit Units produced Sales price Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Variable selling and administrative expenses Fixed selling and administrative expenses What is Green and White's contribution margin for this month if 1,140 units were sold? Multiple Choice O $64,800 O $20,520 $30,780 $97,200 $3,600 in total $25,080arrow_forwardSims Company began operations on January 1. Its cost and sales information for this year follow. Direct materials $ 30 per unit Direct labor $ 50 per unit Variable overhead $ 20 per unit Fixed overhead $ 8,400,000 per year Variable selling and administrative expenses $ 11 per unit Fixed selling and administrative expenses $ 4,750,000 per year Units produced 105,000 units Units sold 75,000 units Sales price $ 360 per unit 1. Prepare an income statement for the year using variable costing.2. Prepare an income statement for the year using absorption costing.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education