
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
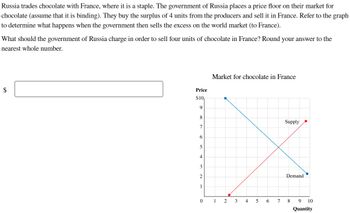
Transcribed Image Text:**Russia and France Chocolate Trade Analysis**
Russia trades chocolate with France, where chocolate is considered a staple. The Russian government has implemented a price floor for chocolate (a level above the equilibrium price). As a result, a surplus is created, with the government purchasing 4 excess units from producers. This surplus is then sold in France. Use the graph provided to analyze the market implications when Russia sells this excess chocolate on the world market (specifically to France).
### Market Analysis
**Question:**
What price should the Russian government charge to sell four units of chocolate in France? Provide your answer rounded to the nearest whole number.
**Graph Explanation:**
The graph titled "Market for chocolate in France" illustrates the supply and demand curves for chocolate, measured by price and quantity (in units).
- **Price Axis (vertical):** Ranges from $0 to $10.
- **Quantity Axis (horizontal):** Ranges from 0 to 10 units.
**Supply Curve (Red):**
- Begins at $2 for 2 units and rises linearly to $10 for 10 units.
**Demand Curve (Blue):**
- Starts at $10 for 0 units and decreases linearly to $2 for 8 units.
**Equilibrium Point:**
- The intersection of the supply and demand curves occurs at $6 for 6 units of chocolate.
**Government Intervention:**
- Given the surplus of 4 units, the Russian government should evaluate the demand curve to determine an optimal price point for selling these units in France.
Please enter the price in the provided box: $ ___
The goal is to match these 4 units with demand in the French market, ensuring competitive pricing that maximizes revenue while addressing market conditions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- South Korea to Resume US Beef Imports South Korea will open its market to most U.S. beef. South Korea banned imports of U.S. beef in 2003 amid concerns over a case of mad cow disease in the United States. The ban closed what was then the third-largest market for U.S. beef exporters. Source: CNN, May 29, 2008 The graph shows the market for beef in the United States. Assume that South Korea is the only importer of U.S. beef. Draw a point of the quantity demanded and the price when South Korea allows imports of beef from the United States. Label this point 1. Draw a point at the quantity supplied by U.S. beef farmers and the price when South Korea allows imports of beef from the United States. Label this point 2. Draw a point to show the price and quantity of beef when South Korea bans imports of U.S. beef. In the United States, the winners from the ban on U.S. beef are losers are A. producers; consumers OB. consumers; producers and the 12- 10- 4- 2- Price (dollars per pound) 80 S World…arrow_forwardhelp please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forwardWhen NAFTA was being debated in the U.S. Congress, Representative Jerry Lewis of California said: “Bill Johnson owns the largest Caterpillar distributorship in the West. There is currently a 20% tariff on his products sold in Mexico. Caterpillar has a 50 percent share of the Mexican market. The other half is dominated by Komatsu Company of Japan. Bill says, 'Imagine what will happen when the 20 percent tariff comes off our tractors and it remains on the ones from Japan.' Under what circumstances will this effect of NAFTA be beneficial, and when will it be harmful, to (i) the U.S., (ii) Mexico, and (iii) Japan?arrow_forward
- What Type of attraction are in Uk? and which are the main Characteristcs of supply? (what make different from the rest of the world)arrow_forwardSuppose you have the following for white t-shirts market:Market demand is P=125-(3/8)QMarket supply is P=5+(1/8)Q. there is now a global supply that is horizontal at $15. But the government now imposes a tariff of $5 per unit of t-shirt.a. Obviously the world price and domestic price will now be $20. Calculate the quantityproduced and demanded domestically? b. Using graphs show the changes in CS (Consumer Surplus) and PS (Producer Surplus) comparedto Free Trade. Show also the government revenue, which is tariff per t-shirt times the new level of imports. Who gains in comparison to Free Trade scenario? Who loses? What is the welfare gain or loss? Show by using graphs.arrow_forwardSuppose Kenya is open to free trade in the world market for wheat. Because of Kenya's small size, the demand for and supply of wheat in Kenya do not affect the world price. The following graph shows the domestic wheat market in Kenya. The world price of wheat is Pw =$250 per ton. On the following graph, use the green triangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing consumer surplus (CS) when the economy is at the free-trade equilibrium. Then, use the purple triangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing producer surplus (PS). (? 490 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 460 CS 430 400 370 PS 340 310 280 Pw 250 220 190 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of wheat) If Kenya allows international trade in the market for wheat, it will import tons of wheat. Now suppose the Kenyan government decides to impose a tariff of $60 on each imported ton of wheat. After the tariff, the price Kenyan consumers pay for a ton of wheat is s and Kenya will import tons of…arrow_forward
- Kazakhstan is a grape producer, as well as an importer of grapes. Suppose the following graph shows Kazakhstan's domestic market for grapes, where SK is the supply curve and Dk is the demand curve. The free trade world price of grapes (Pw) is $800 per ton. Suppose Kazakhstan's government restricts imports of grapes to 120,000 tons. The world price of grapes is not affected by the quota. Analyze the effects of the quota on Kazakhstan's welfare. On the following graph, use the purple line (diamond symbol) to draw the Kazakhstan's supply curve including the quota SK+Q. (Hint: Draw this as a straight line even though this curve should be equivalent to the domestic supply curve below the world price.) Then use the grey line (star symbol) to indicate the new price of grapes with a quota of 120,000 grapes. PRICE (Dollars per ton) 4000 3600 3200 2800 2400 2000 1600 1200 800 400 0 0 40 80 120 160 200 SK 240 10 0² W 280 320 360 400 SK+Q Price with Quota A Change in PS Quota Rents DWL ?arrow_forwardEconomic Use the graph below and the following information to answer the next question. The world price of soybeans is five dollars per bushel and the importing country is small enough to not affect the real price. Suppose the government puts a tariff of one dollars per bushel on soybean imports how much revenue will the government raise from a one dollar per bushel tariff on soybean imports.arrow_forwardSuppose Guatemala is open to free trade in the world market for wheat. Since Guatemala is small relative to the international market, the demand for and supply of wheat in Guatemala have no impact on the world price. The following graph shows the domestic market for wheat in Guatemala. The world price of a ton of wheat is Pw = $400. On the following graph, use the green triangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing consumer surplus (CS) when the economy is at the free-trade equilibrium. Then, use the purple triangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing producer surplus (PS). (?) PRICE (Dollars per ton) 1200 1100 1000+ 900 800 700 600 500 400 300- 200 0 Domestic Demand 20 40 Domestic Supply 60 80 100 120 140 QUANTITY (Tons of wheat) PW 160 180 200 A CS T PS Because Guatemala participates in international trade in the market for wheat, it will import tons of wheat. Now suppose the Guatemalan government decides to impose a tariff of $200 on each imported ton of…arrow_forward
- Based on the following table, what is the no-trade equilibrium quantity supplied and demanded for Country 2? Enter your answer in the box below. Price 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Country 1: Quantity Supplied 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Type your answer... Country 1: Quantity Demanded 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 Country 2: Quantity Supplied 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Country 2: Quantity Demanded 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3arrow_forwardEconomics Questionarrow_forwardThe U.S. is an importer of ethanol, and let’s assume they are a price-taker in the world market. Suppose that a technological advance in ethanol production in Brazil, the world’s largest exporter, drives down the world price of ethanol by $5. Draw a graph and explain how this change in world price affects consumer surplus, producer surplus, and total surplus in the U.S. market. Now suppose the U.S. government institutes an import tariff of $5 in response to the fall in the world price. On your graph label the revenue raised by the tariff and the deadweight loss created (if it exists). Who is likely to support this policy? Suppose that the fall in price is attributable not to a technological advance but to a subsidy from the Brazilian government to Brazilian ethanol producers. How would this affect your analysis?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education