
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Economic
Use the graph below and the following information to answer the next question. The world price of soybeans is five dollars per bushel and the importing country is small enough to not affect the real price. Suppose the government puts a tariff of one dollars per bushel on soybean imports how much revenue will the government raise from a one dollar per bushel tariff on soybean imports.
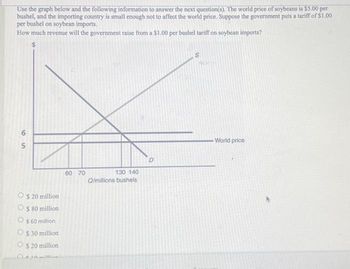
Transcribed Image Text:Use the graph below and the following information to answer the next question(s). The world price of soybeans is $5.00 per
bushel, and the importing country is small enough not to affect the world price. Suppose the government puts a tariff of $1.00
per bushel on soybean imports.
How much revenue will the government raise from a $1.00 per bushel tariff on soybean imports?
65
$ 20 million
O $ 80 million
$ 60 million
$
$
30 million
20 million
10 million
60 70
130 140
Q/millions bushels
D
S
-World price
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following image shows the market for wheat for the country of Palatino. sº is the domestic supply of wheat, and DD is the domestic demand for wheat. Suppose the world price of wheat is $9 per bushel. Suppose a specific tariff of $6 is imposed on each bushel of wheat imported. The net welfare loss from the tariff is represented by the area Figure 19.4 SO Price($) 25 H 15 A E DD 200 300 600 700 Quantity of Wheat (thousands of bushels) a. B and D b. I and H O c. E O d. F e. A and Carrow_forwardIs the following statement TRUE or FALSE? Briefly explain why. "If the OPEC countries decide to restrict their oil exports, it will decrease the world price of this product."arrow_forwarda. In the absence of trade, what is the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity? b. The government opens the wheat market to free trade and U.S enters the Turkish market, pricing wheat at $40 per ton. What will happen to the domestic price of wheat? What will be the new domestic quantity supplied and domestic quantity demanded? How much wheat will be imported from U.S? c. The government imposes a $10 per ton tariff on all imported wheat. What will happen to the domestic price of wheat? What will be the new domestic quantity supplied and domestic quantity demanded? How much wheat will now be imported from U.S? d. How much revenue will the Turkish government receive from the $10 per ton tariff?arrow_forward
- Korea’s demand for computers isQK = 2, 000 − PkIts supply isQK = −200 + PkChina’s demand for computers isQC = 1, 000 − Pc Its supply isQC = Pc1. Suppose that Korea imposes a specific tariff of $100 on computerimports. Calculate the price of computers in each country and thequantity of computers supplied and demanded in each country. Alsocalculate the volume of trade.arrow_forwardfast urgent.arrow_forwardWhat would happen if the European Union (E.U.) put a quota on American jeans and only allowed their countries to import 5,000 pairs of jeans? A. American jeans would become very expensive and desirable in the EU. B. French jeans would be more popular than any jeans and America would stop importing jeans to Europe. C. American jeans would be less desirable in the EU and there would be no demand. D. Nothing, because European countries dislike American products.arrow_forward
- Q3: Using a domestic-market demand- and supply-curve graph, show the impact of tariff on a small country's import price, domestic demand, domestic supply, import quantity, consumer surplus, producer surplus, government revenue, and total welfare; Is the country unambiguously worse off as a result of the tariff? In the same graph, show how to achieve the same import quantity with an import quota; When would the tariff and the import quota lead to the same amount of welfare change? How will the answer to (a) and (b) change if the country uses a subsidy that is equivalent to the tariff rate to help domestic producers? How would the answers to (a) and (b) change for a large country? Your answer:arrow_forward. The United States currently imports all of its coffee. The annual demand for coffee by U.S. consumers is given by the demand curve Qd = 150 − 10P, where Qd is quantity (in millions of pounds) and P is the market price per pound of coffee. Suppose the domestic supply is Qs = 10P −50. The U.S. coffee market is competitive. Suppose that the world price of coffee is $6. Congress is considering a tariff on coffee imports of $2 per pound. (a) Find the producer and consumer surplus if there was no trade. (b) Calculate the consumer and producer surplus after we engage in free trade. (c) If the tariff is imposed calculate the changes to consumer and producer surplus. (d) Other than lower prices, provide two benefits that can occur as a result of free trade.arrow_forwardWhy do consumers in the United States pay more than double the world price for sugar?arrow_forward
- The following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for soybeans in Zambia. Zambia is open to international trade of soybeans without any restrictions. The world price (Pw) of soybeans is $550 per ton and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout this problem, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of soybeans and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in soybeans. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. PRICE (Dollars per ton) 1000 950 900 850 800 750 700 650 600 550 500 X ++. 1 Supply Demand Pw W I 0 40 80 120 160 200…arrow_forwardAnalyze the impact of the tariff on domestic production, consumption, and imports of solar panels. Include a graph with properly labeled axes, demand and supply curves, and tariff levels to illustrate your answer.arrow_forwardLesson 12 Question 6arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education