
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
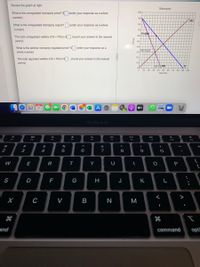
Transcribed Image Text:Review the graph at right.
Monopoly
100-
What is the unregulated monopoly price? $ (enter your response as a whole
number)
90-
MC
What is the unregulated monopoly output? (enter your response as a whole
80
number)
70-
P=$00
60-
The total unregulated welfare (CS + PS) is $- (round your answer to the nearest
penny)
50-
40
What is the optimal monopoly regulated price? $ (enter your response as a
whole number)
MCE$30
30-
20
The total regulated welfare (CS + PS) is $. (round your answer to the nearest
penny)
FQ=30 MR
50 60 70 80 90 100
Quantity
10
20 30
40
20
tv
MacBook Air
80
DII
DD
F2
F3
F4
F6
F7
F8
F9
F10
F11
@
%23
2$
2
3
4
8
{
W
E
Y
U
P
S
D
F
G
н
J
K
>
C
V
N
M
and
command
opti
.. .-
• V
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Review the graph at right for a monopoly market (enter all of your responses as whole numbers). Price 100- How much is the consumer surplus? S 90- MC How much is the producer surplus? s 80- 70- How much is the deadweight loss? S 60 80- Monopoly total surplus is $ 50- Monopoly total surplus is V competitive total surplus. 40- 30- 20- 10- MR D 10 30 40 50 60 70 90 100 Quantityarrow_forwardIs a monopoly always bad for society? Question 6 options: None of the other answers is correct Yes. Monopoly is always bad Monopoly is not bad if its owner gives back to society in charity No. For example, patents on medications create monopolies, and increase the price and reduce the quantity sold, but without them, no one would take the high costs of developing new drugs and the quantity will be... zero!arrow_forward6. The following graph shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves for a single-price monopolist that produces a drug that helps relieve arthritis pain.arrow_forward
- Question 2 – Monopoly Draw the diagram for a monopoly that is making profits. In your diagram from part 1 indicate the area that represents the deadweight loss.arrow_forwardPete has developed a new virtual reality headset that is so far advanced he effectively has a monopoly. His marginal cost is a constant $200, and his inverse demand is P = 800 – 4Q. What is the deadweight loss in this monopoly? a.) $0 b.) $45,000 c.) $11,250 d.) $22,500 Give typing answer with explanation and conclusionarrow_forwardQuestion 5 The following figure describes the market demand curve of a monopoly market: 10 Price, cost 9 8 7 6 3 2 1 a. b. C. d. 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 D a). 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 quantity Draw the marginal revenue (MR) curve for the monopoly given the above market demand curve. If the monopoly firm can produce any output level with the extra cost $3 per unit, how would the marginal cost (MC) curve be? List the mathematical equation and draw the MC curve on the same figure of question The fixed cost for the monopoly company is $25. Find the optimal output level and the related profit/loss for it. There are two proposals concerning the market efficiency: Plan A: regulate the market price at $4. Plan B: allow and help the monopoly enforce the perfect price discrimination. If you represent consumers to vote for one plan, which one would you choose? Explain with proper calculation (Hint: consumers only care about their welfare).arrow_forward
- 8 A monopoly has the following demand and Total Cost curve: Demand: P=1000-10Q TC=100Q+5Q2 1. How much profits does the monopoly make at the profit-maximizing level of quantity? $ 2. What is the DWL from the monopoly? $arrow_forwardThe Puerto Rico Electric Power Authority (PREPA) is a natural monopoly. The graph shows the market demand curve and the firm's marginal cost curve. The monopoly is unregulated and maximizes profit. Draw the firm's marginal revenue curve. Label it MR. Draw a point at the profit-maximizing price and quantity. Label it 1. The monopoly makes a positive economic profit. Draw the firm's average total cost curve. Label it ATC. Draw a point on the ATC curve at the quantity produced. Label it 2. Draw shapes that show 1) the monopoly's economic profit. Label it EP. 2) the consumer surplus. Label it CS. 3) the deadweight loss. Label it DWL. 100- 90- 80- 70- 60- 50- 40- 30- 20- 10- Price and cost (cents per kWh) MC D 40 44 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 Quantity (millions of kWh per month) >>> Draw only the objects specified in the question. + Garrow_forward2. A monopolist produces its output in two factories, whose cost curves are given by C1 (q1) = 10q and C2 (q2) demand for the firm's product is given by P = 700 – 5Q where Q is the total quantity sold by the monopolist. (a) On a diagram, illustrate the monopolist's decision about how much to produce at each factory and overall and the price to charge. Briefly explain your diagram. (b) Numerically calculate the monopolist's optimal choices for qı, q2, Q, and P. (c) Suppose that labor costs increase in Factory 1 but not in Factory 2. How should the firm change (i.e. raise, lower, or leave unchanged) each of the values you found in (b)? Your answer should be qualitative, not quantitative. 10q3 where q1 and q2 are the amounts produced at each factory. The diagram might be useful but is not necessary.arrow_forward
- Mailings Review View Help Advanced Threat Protection and it hasn't detected any threats. If you need to edit this file, click enable editing. 2-) Hypothetical monopoly costs and revenue Quantity Price Total cost $500 $400 2 450 650 3 400 950 350 1,300 300 1,700 Table 1 In Table 1, using the profit-maximization rule, calculate MC, MR and write the profit- maximization quantity and the price:arrow_forwardTable: Prices and Demand Quantity of Hats Demanded 0 1 2345699 7 8 Price per Hat $30 XHHNARY 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 14 (Ref 27-8 Table: Prices and Demand) Use Table 27-8: Prices and Demand. The New Orleans Saints have a monopoly on Saints logo baseball hats. The Saints sell at most 1 hat to each customer, and the table shows each customer's willingness to pay. The marginal cost of producing a hat is $18, and there are no fixed costs. How much is the Saints' profit at the profit-maximizing output? O a. $18 O b. $24 O c. $12 O d. $30arrow_forwardYou are the owner of a monopoly firm. The demand curve that you face is: 100 0. 5Q - Your Total Cost and Marginal Cost are: 1035 +10Q +0. 5Q2 10 +Q TC |3| MC The government decides to regulate your firm and imposes the Efficient Price. What is the price you must set? Regulated Efficient price $77.5 Regulated Efficient price = $55 Regulated Efficient price = $60 Regulated Efficient Price = $70arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education