
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Refer to the provided image drawn by a student trying to plan out their serial dilution protocol. The student diluted the original culture into bottle A and then diluted it further into B as shown. The student then proceeded with plating out 0.1ml of the culture from bottle B onto the plate (Note: plate A shows the 0.1ml that was plated, no further dilutions were done).
If 13 colonies grew on plate A, help the student figure out how many CFU (colony forming units) were in the original culture?
Select one:
a.
1,300
b.
13,000
c.
None of the Above
d.
130,000
e.
1,000,000
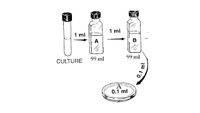
Transcribed Image Text:1 ml
1 ml
A
B
99 ml
99 ml
CULTURE
0.1 ml
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are transferring a bacterial culture from a tube of broth to a Petri dish containing trypticase soy agar. Please list the steps that are necessary to make the transfer successfully and with minimal risk. of contamination.arrow_forwardThe statement, “In the laboratory, a sterile inoculating loop is moved across the agar surface in a culture dish, thinning a sample and isolating individuals", describes which technique?arrow_forwardHow do eosin-methylene blue (EMB) agar plates work? What organism(s) are they designed to detect? How would a positive test appear on the plate?arrow_forward
- What is the purpose of diluting a culture by making "quadrant streaks" (or "streak plating") bacteria, and what can we use them for? Check all that apply A. To observe colony morphology/color B. To isolate viral plaques C. testing growth conditions or treatments (such as media, antibiotics, incubation temperature etc.,) D. To isolate a clonal population of bacteria from the rest of the culture E. For subculturing (transferring to new media so we can grow more bacteria, storing the plate in a fridge for repeated use so the bacteria don't die quickly) F. Accurate quantification (to calculate CFU/mL) G. To know what strain of bacteria you're working with, since you can tell based on how it looks on the plate. H. To lower risk of contamination/identify contaminationarrow_forwardYou have several different media onto which you inoculated eight strains of yeast (A-H). The media include a rich medium, an unsupplemented minimal medium, and minimal media each supplemented with one vitamin. Of the yeast strains, one is a prototroph and seven are auxotrophs for a vitamin. After overnight incubation, the following results were observed (tan patches represent growth): D plate 1 (A) B DE F GH plate 5 plate 4 plate 6 Which plate contains an unsupplemented minimal medium? [Select] Which plate contains a rich medium? [Select] plate 2 Which strain is a prototroph? [Select] Strain E is an auxotroph for niacin. Which plate reveals this specific auxotrophy? [ Select] plate 3 plate 7 One strain is an auxotroph for both choline and pantothenic acid. Which one is this most likely to be? [Select]arrow_forwardDraw a 4-inch circle. Draw out the streaking pattern used to isolate single colonies on a plate.arrow_forward
- You are given a mix culture of S. aureus,E. coli and P. aeruginosa. Besides the streak plate method what other methods could you use to separate the bacteria? Please state what method(s) you would use, the result you would be looking for to help identify each bacterium and the interpretation of the result.arrow_forwardAt the station there is a 2 mL microcentrifuge tube containing sheep blood and 3 tubes containing the following solutions: 0 mM, 300 mM, 600 mM of sucrose. The tubes are randomly labelled A, B, C. 2 mL of each solution were transferred to a different microcentrifuge tube, 20 ul of blood were then added to each tube, and they were mixed well by inverting the tube for multiple times. They were observed and it was determined whether the solution in each tube was hypotonic (Yes or No) relative to the blood cells. In addition, the solutions were diluted with water to help you determine which solution is which sucrose concentration. What sucrose concentration corresponds with each tube? Tube Hypotonic (Yes/No) Hypotonic after 1:1 dilution with water (Yes/No) Most likely Sucrose concentration (mM) A No Yes B Yes Yes C No Noarrow_forwardHuman error is a factor in the Kirby-Bauer procedure that often contributes to variation in zone size. Circle the effect on the zone size if the following occurred: ● ● Overinoculating the agar with bacteria: Waiting too long to place disks after inoculation: Using a culture that is less than 0.5 MacFarland: False increase False increase False increase False decrease False decrease False decreasearrow_forward
- you are given a mixed culture of s. aureus, E. coli and P. aeruginosa. how would you isolate each other from this mixed culture?( Besides using plate technique)arrow_forwardyou are given a mix culture of S aureus, E. coli and P. aeruginosa. besides using the streak plate method what other method could you choose to separate the bacteria? the result you will be looking for and interprete the result.arrow_forwardhow to find out the test is differential or selective in the microbiology lab test?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education