
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
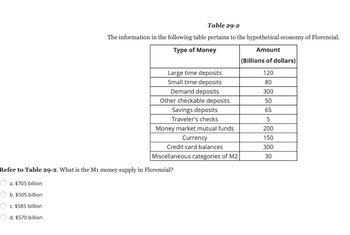
Transcribed Image Text:Table 29-2
The information in the following table pertains to the hypothetical economy of Florencial.
Type of Money
Large time deposits
Small time deposits
Demand deposits
Other checkable deposits
Savings deposits
Traveler's checks
Money market mutual funds
Currency
Credit card balances
Miscellaneous categories of M2
Refer to Table 29-2. What is the M1 money supply in Florencial?
a. $705 billion
O b. $505 billion
c. $585 billion
Od. $570 billion
Amount
(Billions of dollars)
120
80
300
50
65
5
200
150
300
30
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The table to the right shows hypothetical values, in billions of dollars. Use the table to calculate the M1 and M2 money supply for each year. (Enter your responses rounded to the nearest dollar.) Total M1 Total M2 2009 2010 2011 2012 ・・・ A. Currency B. Money market mutual fund shares C. Saving account deposits D. Money market deposit accounts E. Demand and checkable deposits Small-denomination time deposits F. G. Traveler's checks H. 3-month Treasury bills 2009 920 678 5,300 2010 2011 2012 930 932 937 683 681 690 840 3 1,990 5,580 5,768 5,905 1,210 1,241 1,270 1,325 1,010 982 871 1,133 1,576 3 2 1 2,378 2,440 2,506 990 1,003arrow_forward12arrow_forwardWhich group in the federal goverment is responsible for counting M1 and M2 money amounts? A. Department of the Treasury B. US Mint C. Internal Revenue Service D. Federal Reservearrow_forward
- Balance sheet of Bank National Assets Liabilities Vault Cash $1,500 Deposit in Fed $ 500 Loans $4,000 Total Assets $6,000 Deposits $6,000 Total Liabilities $6,000 (1) If r = 10%, how much can the whole banking system expand the money supply? a. $20,000 b. $54,000 c. $40,000 d. $11,000 e. $5,000 (2) If the Fed changed the reserve requirement from 10% to 5% - the bank’s Excess Reserves (ER) would: a. Increase by $300 b. Increase by $1700 c. Decrease by $1400 d. Decrease by $2000 e. Increase by $5700 (3) If the Fed changed the reserve requirement from 10% to 25% the money supply (MS) in the whole banking system could: a. Decrease by $18000 b. Decrease by $54000 c. Increase by $18000 d. Decrease by $36000 e. Increase by $36000 (4) If the Fed changed the reserve requirement from 10% to 39% Bank National would now have ER of: a. -$340 b. -$3,660 c. -$2,340 d. -$500 e. -$250arrow_forwardB. Consider the following data Currency Checkable deposits Savings deposits $1,200 billion $1,500 billion $2,500 billion Banking system's reserve-to-deposit ratio is 30%. Calculate (show your werk) 1. Bank reserves = 2. Monetary base = 3. M1 money supply = %3D 4. Realistic money multiplier =arrow_forwardV2arrow_forward
- 8. The reserve requirement, open market operations, and the money supply Consider a system of banking in which the Federal Reserve uses required reserves to control the money supply (as was the case in the United States before 2008). Assume that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency, so the only money exists in the form of demand deposits. To further simplify, assume the banking system has total reserves of $400. Determine the money multiplier as well as the money supply for each reserve requirement listed in the following table. Reserve Requirement Simple Money Multiplier Money Supply (Percent) (Dollars) 20 10 A higher reserve requirement is associated with a money supply. Suppose the Federal Reserve wants to increase the money supply by $200. Maintain the assumption that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency. If the reserve requirement is 10%,…arrow_forward8. A bank's "required reserves" are: none of the answers given is correct held as deposits with the Federal Reserve System equal to its transactions deposits equal to its checkable depositsarrow_forwardn the table below, the money supply, defined by M3, is equal to ........ Currency held by the non-bank public ($ billion) Current deposits at banks ($, billion) Other deposits at banks and other deposits held by other deposit -taking institutions ($, billion) 60 240 1500 Select one: a. 1200 billion b. 1800 billion c. 1500 billion d. 1740 billionarrow_forward
- 2. Discuss why fiat money can coexist with other assets that have higher rate of returns.arrow_forward4. What components of money are counted as part of M1? A) currency, M2 and checking accounts. B) currency, travelers' checks, checking accounts and M2 O c. C) C) currency, travelers' checks and checking accounts. D) currency, travelers' checks and money market accounts 10. Explain what will happen to the money multiplier process if there is an increase in the reserve requirement? A) An increase in the reserve requirement means that banks will be less likely to have your money when you demand it, but it would increase the money multiplier B) An increase in the reserve requirement means that banks will be more likely to have your money when you demand it, increasing the money multiplier C) Since a greater portion of each deposit is being lent out, the multiplier will increase. This means more loans lent and more economic growth. D) Since a smaller portion of each deposit is being lent out, the multiplier will decrease. This means fewer loans lent and less economic growth.arrow_forward2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education