
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Reconsider Dr. Sameer's research question about how much time Cal Poly students spend on watching television. Dr. Sameer surveys a random sample of 100 Cal Poly students and finds that the mean number of hours per day watching TV turns out to be 3.0 hours.
Suppose that to answer the research question Dr. Sameer conducted a simulation under the null hypothesis. The plot below shows the null distribution with a total of 150 simulated samples (Tip: note that I did not run 1000 simulated samples here!).
- The mean of the null distribution is 2.79
- The standard deviation of the null distribution is 1.6.
-Calculate and report the p-value from the simulation provided (attached image). Leave your answer in a decimal format.
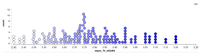
Transcribed Image Text:150
12 -
10 -
8
2
2.40
2.45
2.50
2.55
2.60
2.65
2.70
2.75
2.80
2.85
2.90
2.95
3.00
3.05
3.10
3.15
3.20
3.25
3.30
mean_TV_HOURS
count
000
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- I need help on this practice problemarrow_forwardA researcher takes sample temperatures in Fahrenheit of 16 days from San Francisco (Group 1) and 22 days from Atlanta (Group 2). Test the claim that the mean temperature in San Francisco is less than the mean temperature in Atlanta. Use a significance level of a = 0.10. Assume the populations are approximately normally distributed with unequal variances. You obtain the following two samples of data. Round answers to 4 decimal places. San Francisco 77.4 94.8 77 80.9 84 Ho: M₁ 73.4 84.9 92 60.6 83.6 92.5 76.3 93.4 87.2 81.5 70.4 What are the correct hypotheses? Note this may view better in full screen mode. Select the correct symbols for each of the 6 spaces. Atlanta 85.4 92.8 80.2 87.9 80.6 77.9 72.9 75.9 72.1 76.7 80.4 92.5 75.9 72.1 97.7 89.2 88.1 80 92.2 86 96.2 91.9 p-value H₁: M₁ Based on the hypotheses, find the following: Test Statistic = -0.635 X = 0.2494 × OH₂ The p-value is greater than alpha OF H₂ to alpha. The correct decision is to fail to reject the null hypothesis or The…arrow_forwardThe following information is available for two samples selected from independent normally distributed populations. Population A: n1=30 S2/1=25 Population B: n2=30 S2/2=36 a. Which sample variance do you place in the numerator of FSTAT? b. What is the value of FSTAT?arrow_forward
- A researcher takes sample temperatures in Fahrenheit of 17 days from New York City and 18 days from Phoenix. Test the claim that the mean temperature in New York City is different from the mean temperature in Phoenix. Use a significance level of α=0.05. Assume the populations are approximately normally distributed with unequal variances. You obtain the following two samples of data. New York City Phoenix 99 94.2 95.5 72 93.2 86.8 102 122.1 85.4 114.4 80 94.7 86.4 89.7 75.4 104.7 79.5 77.6 83.4 106.8 64.3 98.6 65.5 91.5 87.7 82 104 97.7 74.3 64.9 59.5 82 82.8 72 116.2 The Hypotheses for this problem are: H0: μ1 = μ2 H1: μ1μ2 Find the p-value. Round answer to 4 decimal places. Make sure you put the 0 in front of the decimal. p-value =arrow_forwardPlease answer the question contained in the following picturearrow_forwardQUESTION 1 A health researcher read that a 150-pound college-aged, male can burn an average of 530 calories per hour playing tennis with a standard deviation of 25 calories. 40 college-aged males were randomly selected at a commuter school and the mean number of calories burned per hour playing tennis was 540 calories. Do college-aged male tennis players at the commuter school burn more calories per hour than the college-aged, male tennis player population? Test with a 0.05 significance level. What are the hypotheses? Null and Alternatearrow_forward
- Need sub part B answered onlyarrow_forwardGn. don't provide handwriting solutionarrow_forwardThe Department of Agriculture wants to determine whether the mean yield per acre for a particular variety of soybeans is different this year compared to the historical avg yield of 520 bushels per acre. Thus, the null and alternative hypotheses are Ho: mu = 520 Ha: mu is not = to 520 You set out to conduct a hypothesis test at the 95% level. Mean yields are distributed Normally. You take a sample of 36 different acres. From this sample, you calculate a mean yield of 573 and a std deviation of 24. Do you reject or not-reject the null hypothesis? Group of answer choices Do not reject the null hypothesis. Reject the null hypothesis.arrow_forward
- Choose the appropriate statistical test. When computing, be sure to round each answer as indicated. A dentist wonders if depression affects ratings of tooth pain. In the general population, using a scale of 1-10 with higher values indicating more pain, the average pain rating for patients with toothaches is 6.8. A sample of 30 patients that show high levels of depression have an average pain rating of 7.1 (variance 0.8). What should the dentist determine? 1. Calculate the estimated standard error. (round to 3 decimals). [st.error] 2. What is thet-obtained? (round to 3 decimals). 3. What is the t-cv? (exact value) 4. What is your conclusion? Only type "Reject" or Retain"arrow_forwardIn this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer. In an effort to determine if rats perform certain tasks more quickly if offered larger rewards, the following experiment was performed. On day 1, a group of three rats was given a reward of one food pellet each time they ran a maze. A second group of three rats was given a reward of five food pellets each time they ran the maze. On day 2, the groups were reversed, so the first group now got five food pellets for running the maze and the second group got only one pellet for running the same maze. The average times in seconds for each rat to run the maze 30 times are shown in the following table. Do these data indicate that rats receiving larger rewards tend to…arrow_forwardA researcher predicts that smoking cigarettes decreases a person's sense of smell. On a test of olfactory sensitivity (smell), the mean for non-smokers is 18.4. A sample of 12 people who smoke a pack each day have a sample mean of 16.25 (sample variance = 4.75). Complete the following statement: We ["", ""] the null. Smokers have ["", "", ""] in olfactory sensitivity compared to non-smokers.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman