
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Identify the states, inputs, and output
• Show your work to get the dynamics
• Present the state space model, including the state equations and output equation
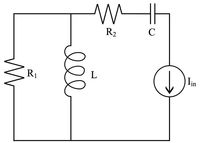
Transcribed Image Text:R2
C
R1
L
Iin
ell
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You have been asked to investigate the loading effects on an alternator supplying a load and also charging a car battery at the same time. The output of the alternator has been rectified to smooth dc, and the circuit is shown below. Using Kirchhoff analysis, determine the initial current in each section along with its direction and the potential difference across the load.arrow_forwardR +Vcc -Vcc C Vout R R a. Quantify how the resistors and the capacitor influence the output voltage of the circuit, Vout. What are the upper and lower limits of Vc? b. Howlong does it take for the capacitor to be charged from minimum to maximum voltage and vice versa?arrow_forwardA rectifier uses two diodes, the transformer r.m.s. secondary voltage from centre tap to each end of secondary is 45 V and load resistance is 850 Ω, the internal resistance of each diode may be assumed constant at 25 Ω. Find : (i) the mean load current (ii) the r.m.s. value of load current.arrow_forward
- For the last two parts, use the diagram to the right. d. V = -1.14V, R = 62, and the voltage across the diode is equal to 0.68V when it is "on". i V = e. V = -0.16V, R = 52, and the voltage across the diode is equal to 0.64V when it is "on". V= i = Vo ww R≤ KHI (Enter at least 3 significant digits. Each answer must be within 1% to be marked correct.) + ひ -arrow_forwardRefer to your lecture notes. In a CRT, electrons leave the filament as the current through the filament heats it up. An anode then attracts the free electrons. As the electrons emerge from the small aperture of the anode, they move in the z direction toward the X- and Y-plates. If an oscillating voltage is applied to the Y-plates, this will happen. a. The electron beam will be deflected up and down. O b. The electron beam will stop. O c. The electron beam will continue as normal. O d. The electron beam will be deflected to the right and to the left.arrow_forwardAnswer: + There are two questions, first about an ideal diode and then about a modeled diode. For the modeled diode, the voltage across its terminals is 0.7V when it is "on". Which of the following statements are true about the ideal diode above? a. It is possible for i to be positive. b. If i= 0, then v ≤ 0. c. If i > 0, then the diode can be replaced by an independent current source. d. If v = 0, then the diode can be replaced by an independent current source. e. If i = 0, then the diode can be replaced by an independent current source. f. It is impossible for v to be negative. g. None of these statements is true. Enter a single string of letters, in alphabetical order ("abcdef"). V Answer: Which of the following statements are true about the modeled diode above? a. If i= 0, then the diode can be replaced by a open circuit. b. It is possible for i to be equal to 0. c. If v = 0, then i = 0. d. If v<0, then the diode can be replaced by a open circuit. e. If v = 0, then the diode can be…arrow_forward
- Please answer in typing format solution Sir please help Thanks in advancearrow_forwardA diode is a two-terminal, electronic device made using semiconductors that is designed to prevent current from flowing in a particular direction. The symbol is a triangle pointing in the direction that (positive) current is allowed to flow and a wall preventing (positive) current from flowing in the opposite direction: 1: A diode has two modes, "on" and "off". When "on", current flows, and when "off", no current flows. We generally view diodes as either "ideal" or "modeled", as described below. "Ideal" view of a diode + The "ideal" diode is either a short circuit or an open circuit. Specifically, when the voltage across its terminals is negative, no current flows, and when current flows, there is zero voltage across its terminals, as pictured below: Diode "Modeled" view of a diode +51 Diode V Ideal Diode "Off" i=0| + U≤0 + I Therefore, with current i and voltage v defined as shown on the left above, for an "ideal" diode: • Current i cannot be negative. Voltage v cannot be positive. .…arrow_forwardQuestion 4. In the circuit below I is a DC current, and v. is a sinusoidal signal. Given the diode has vo-0.75V at ip=1.5mA, calculate both the AC and DC voltage across the diode (v.) when I=1mA, R=5002, and Vs=100cos(10*n*t). Assume the capacitors are very large. R₂ www -0 ▷ +1₁ 15 B ANarrow_forward
- ASAP plzarrow_forwardA diode is a two-terminal, electronic device made using semiconductors that is designed to prevent current from flowing in a particular direction. The symbol is a triangle pointing in the direction that (positive) current is allowed to flow and a wall preventing (positive) current from flowing in the opposite direction: 1: A diode has two modes, "on" and "off". When "on", current flows, and when "off", no current flows. We generally view diodes as either "ideal" or "modeled", as described below. "Ideal" view of a diode + The "ideal" diode is either a short circuit or an open circuit. Specifically, when the voltage across its terminals is negative, no current flows, and when current flows, there is zero voltage across its terminals, as pictured below: Diode "Modeled" view of a diode +51 Diode V Ideal Diode "Off" i=0| + U≤0 + I Therefore, with current i and voltage v defined as shown on the left above, for an "ideal" diode: • Current i cannot be negative. Voltage v cannot be positive. .…arrow_forwardThe specific capacitance in F/g can be estimated by using both cyclic voltammetry curves atdifferent voltage scan rate and Galvanostatic charge-discharge curves. The following graphshows the charge-discharge curves of a typical MnO2 pseudocapacitive electrode. There is acharge drop in the voltage at the onset of the discharge curve (one such drop is denoted bydeltaV2). What is the reason behind it?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,