
Chemistry: Matter and Change
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780078746376
Author: Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

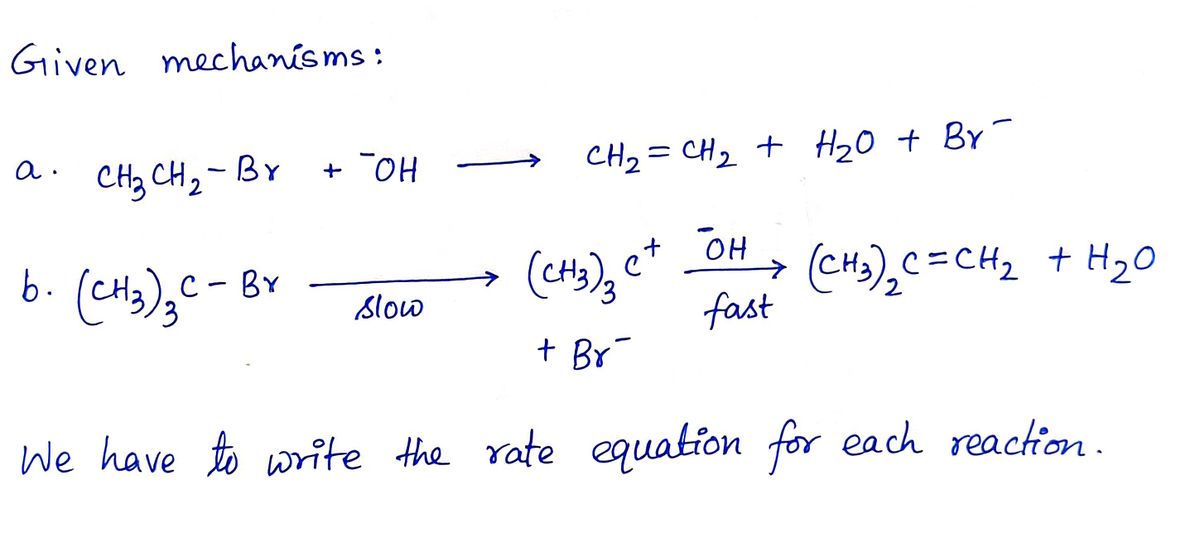
Transcribed Image Text:**Question 9:** Write a rate equation for each reaction, given the indicated mechanism.
**a.** CH₃CH₂Br + ⁻OH → CH₂=CH₂ + H₂O + Br⁻
**b.** (CH₃)₃CBr
slow → (CH₃)₃C⁺ + Br⁻
fast → (CH₃)₂C=CH₂ + H₂O
### Explanation:
- **Reaction a:** This is a substitution reaction where ethyl bromide (CH₃CH₂Br) reacts with hydroxide ion (⁻OH) to form ethylene (CH₂=CH₂), water (H₂O), and bromide ion (Br⁻).
- **Reaction b:** This involves a two-step mechanism. In the first, slow step, tert-butyl bromide ((CH₃)₃CBr) dissociates into a carbocation ((CH₃)₃C⁺) and a bromide ion (Br⁻). In the fast second step, the carbocation reacts to form an alkene ((CH₃)₂C=CH₂) and water (H₂O).
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help answer both questionsarrow_forwardSelect all of the correct statements about reaction rates from the choices below. 1. The lower the rate of a reaction the longer it takes to reach completion.2. The rate of a slow step has more effect on the overall reaction rate than the rate of a fast step.3. Reaction rates decrease with increasing temperature.4. As a reaction progresses its rate goes down.5. Solid catalysts increase reaction rates as their surface areas increase.6. The rate of a reaction is independent of temperature.7. Reaction rates can show little change as masses of solid reactants increase.arrow_forwardPlease help. Thank youarrow_forward
- Solve correctly please.arrow_forwardThe diagram shows the energy of a reaction as the reaction pro- gresses. Label each blank box in the diagram. Reaction progress a. reactants b. products c. activation energy (E,) d. enthalpy of reaction (AHxn) Energyarrow_forwardopy of reaction 4. When a lit match is touched to the wick of a candle, the candie begins to burn. When the match is removed, the candle continues to burn, what is the role of the match? A. behaves as a catalyst B. supplies the activation energy C. is part of the rate determining step D. lowers the activation energy barrier 5. How does a catalyst increase the rate of a reaction? A. increasing the concentration of reactant(s) B. decreasing the concentration of the reactant(s) C. increasing the activation energy of the overall reaction D. decreasing the activation energy of the overall reaction 6. Which of the following would NOT increase the rate of reaction. A. adding catalyst B. raising the temperature. C. increasing the volume of the container D. increasing the concentration of the reactants 7. Why do dust particles suspended in the air inside unheated grain elevators can sometimes react explosively? It is because the dust particles have A. high kinetic energy B. high activation…arrow_forward
- 19arrow_forwardComplete the sentences to describe the energy diagram shown. The energy diagram depicts a ___ step reaction. The fastest (i.e. has the lowest activation energy) step for this reaction is the ___ The ΔH of the overall reaction would be ___ .arrow_forwardWhat will happen if a catalyst is added to a reaction mixture? A. increases the rate of collisions between reactant B. provides reactant molecules with more C. slows down the rate of the back D. provides a new pathway (mechanism) for thearrow_forward
- Question #9 onlyarrow_forwardStudy the following reaction energy diagram: energy reactants Then answer the following questions about the chemical reaction. Does this reaction release or absorb energy? How many transition states occur during this reaction? Could this be an elementary reaction? If you said this reaction could not be elementary, then how many steps are in its mechanism? If you said this reaction could not be elementary, then enter the number of the step in its mechanism which is rate- determining. For example, if the first step is the rate- determining step, enter "1" here. П products release absorb neither yes noarrow_forwardThe question is based on your experimentally determined rate law, how would doubling the concentration of crystal violet affect the reaction rate? The reaction rate was second order and crystal violet we used was 1.5×10^–5 M crystal violet solution.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:9781559539418
Author:Angelica Stacy
Publisher:MAC HIGHER

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning