
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
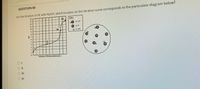
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 68
For the titration of HF with NaOH, which location on the titration curve corresponds to the particulate diagram below?
14
IV.-
Key
13
12
11
10
I.
I.
2.
Volume of titrant added (ml.)
OI.
O II.
O II.
O IV.
%3D
Hd
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you help me with this?arrow_forward13. What is indicated by the shape of the titration curve? PH a. b. C. d. e. Volume of titrant A diprotic acid was titrated with a strong base. A triprotic acid was titrated with a strong base. A diprotic base was titrated with a strong acid. A triprotic base was titrated with a strong acid. A strong acid was titrated with a strong base.arrow_forwardThe graph shows the titration of a polyprotic weak acid with a strong base. Label the following points. a. the point where the pH corresponds to a solution of H₂A in water b. the point where the pH corresponds to a solution of HA in water c. the point where the pH corresponds to a solution of A² in water d. the point where pH equals pK al e. the point where pH equals pK a2 Incorrect 7. a b Titrant (mL) O d Answer Bankarrow_forward
- Kerosene is a nonpolar solvent, which solute will dissolve in it? (No explanation needed) A. C6H14 B. CaCO3 C. CH3COOH D. KCl What is the purpose of titration? A. To find the concentration of unknown acid or a base B. To find the volume of unknown acid or a base C. To find the pH of a base substances D. Both A & Carrow_forwardThe graph below represents the titration curve of a A. 1 M strong acid with 1 M strong base B. 1 M weak base with 1 M strong acid C. 1 M strong base with 1 M strong acid D. 1 M weak base with 1 M weak acid E. 1 M weak acid with 1 M strong basearrow_forwardquestion 7!arrow_forward
- 49. A 25.00-mL sample of an H₂SO4 solution of unknown concentration is titrated with a 0.1322 M KOH solution. A volume of 41.22 mL of KOH is required to reach the equivalence point. What is the concentration of the un- known H₂SO4 solution?arrow_forward#52arrow_forwardQUESTION 12 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. The end point is the same as the equivalence point B. An indicator is not pH sensitive. C. A titration curve is a plot of pH vs. the [base]/[acid] ratio. D. At the equivalence point, the pH can be greater than, equal to or less than 7. O E. The equivalence point is where the volume of acid equals the volume of base during any acid-base titration.arrow_forward
- The titration curve attached was obtained from the titration of a 0.225 g sample of a solid acid with 0.100 M KOH. How many moles of acid are present? 14 12 10 8 6. 4. 2 10 15 20 25 30 Volume of KOH added (mL) A. 0.000800 moles Acid B. 0,00160 moles Acid O C. 0,00110 moles Acid D. 0.00255 moles Acidarrow_forwardTitration of 25.0 mL of an unknown concentration H2SO4 solution requires 37.6 mL of 0.1375 M NaOH solution. What is the concentration of the H2SO4 solution (in M)?arrow_forwardHCL Solution-- 20 mL HCl with 25.46 mL of 0.1240 M NaOHarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY