
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
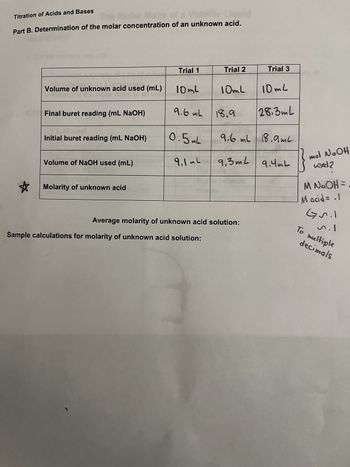
Transcribed Image Text:Titration of Acids and Bases
fa Vola!!
Part B. Determination of the molar concentration of an unknown acid.
Volume of unknown acid used (mL)
Final buret reading (mL NaOH)
Initial buret reading (mL NaOH)
Volume of NaOH used (mL)
an unknown
and
Molarity of unknown acid
Trial 1
10mL
9.6 mL
0.5mL
9,1mL
Trial 2
Sample calculations for molarity of unknown acid solution:
10mL
18,9
Trial 3
Average molarity of unknown acid solution:
10mL
28.3mL
9.6 ml 18,9ml
9,3m² 9.4mL
mol NaOH
used?
M N₂OH =
M acid= .1
Gril
n.1
To multiple
decimals
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need help please calculating the values!arrow_forwardIn the case of over-titration, what should be done to the sample? Select one: a. Dilute the sample with water b. Discard and prepare another sample c. Add acid to revert the color back to faint pink or colorless d. Add more phenolphthalein indicatorarrow_forward3. Titration: Strong Acid / Weak Base. (I warned you to be ready!) Here's the cool chart! Analyte: 20.00 mL 0.100 M Hydrazine (N₂H4) Hd A: initial Vertical (Value) Axis Title 0 B: half equivalence C: equivalence 5 10 15 20 Titrant: mL of 0.100 M HCI added 25 20.00 mL of 0.100 M hydrazine (N₂H4, pKb = 5.77) is titrated with 0.100 M HCl. a) Find the initial pH (point A) and the pH at the equivalence point (point C). b) Find the pH at the half equivalence point (point B).arrow_forward
- 1 Normal 1 Nó Spa... Heading 1 Heading 2 Paragraph Styles 1. What is an equivalence point? a) enough base has been added to neutralize all the acid in the sample b) enough acid has been added to neutralize all the base in the sample c) pH = pKa d) a) or b) 2. If the pH of the equivalence point is 7, acid titrated with a strong base is a a) strong acid b) water c) weak acid d) none of these 3. If the pH of the equivalence point is above 7, acid titrated with a strong base is a a) strong acid b) water c) weak acid d) none of these * Accessibility: Good to go DiFo Text Predictions: On re to search 99+ IA ASUS ZenBook F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 24 & 4. 5. R U. SD G H. liliarrow_forwardWhat is the best sequence of steps for filling the burette with NaOH for a titration? Lower the burette to eye' level, insert the funnel in the top of the burette, slowly add the NaOH through the funnel, check the burette stopcock is closed O Check the burette stopcock is closed, lower the burette to eye level, insert a funnel in the top of the burette, slowly add the NaOH through the funnel Check the burette stopcock is closed, insert the funnel in the top of the burette, slowly add the NaOH through the funnel, lower the burette to eye levelarrow_forwardThe graph below represents the titration curve of a A. 1 M strong acid with 1 M strong base B. 1 M weak base with 1 M strong acid C. 1 M strong base with 1 M strong acid D. 1 M weak base with 1 M weak acid E. 1 M weak acid with 1 M strong basearrow_forward
- ou let your partner do a trial since you're nice. He/she adds a few mL of NaOH, but you realize that nobody recorded the initial buret level! RATS! What do you do? a) Just get light pink since that's the point of titrations anyways. b) Finish the titration and record the final buret reading. Ask your instructor what the initial buret reading was since he knows all of them by heart...right? c) Just record the current level as the "initial" reading. Precision isn't THAT important. d) Restart the trial since you have no idea how much NaOH was added so far.arrow_forwardFill in the blanks by writing the name of the definition: __________ is a substance which is added to the reaction mixture and changes color at the equivalance point. a. titrant b. Primary standard c. İndicator d. analytearrow_forwardWhich one of the following is NOT a source of error during a titration? Group of answer choices Adding too much sodium hydroxide solution to the analyte Refilling the buret during a titration trial Rinsing the buret with the analyte Adding indicator to the analytearrow_forward
- A different titration experiment using a 0.122M standardized NaOH solution to titrate a 26.48 mL solution with an unknown Molarity concentration (M) of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) gave the following molarities for 3 trials. Initial Burette Reading (mL) Final Burette Reading (mL) Delivered vol (mL) Acid Concentration (M) Trial 1 0.0345 Trial 2 0.0334 Trial 3 0.0381 From the 3 trials, determine the average Molarity concentration of the H2SO4 to 3 significant digits. Don't include a unit.arrow_forwardTrue/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Write T if the statement is true while F if statement is false on the before each number 13. In sampling, a producer's risk (type 1 error) is usually occur when a bad batch was accepted 14.A blank titration is a titration conducted without the use of indicator 15.In double indicator titration, If the volume of the standard acid consumed in phenolphthalein end point is more than in methyl orange end point, the sample is a mixture of Na₂CO2 & NaHCO3 Earrow_forwardIncorrect Your answer is incorrect. • KC: Your answer is incorrect. • Cacl, Vour answer is incorrect. For each of the following compounds, decide whether the compound's solubility in aqueous solution changes with pH. If the solubility does change, pick the pH at which you'd expect the highest solubility. You'll ind K, data in the ALEKS Data tab. Does enlubility change with pH? hiyhest solubility compound pll 5 pll 6 pll 8 yes O no yes Ba(OH), O no O yes Caci, e noarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY