
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Could you help me with this question? All info has been provided.
Transcribed Image Text:Question Completion Status:
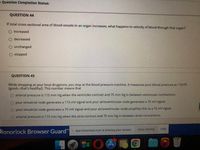
QUESTION 44
If total cross-sectional area of blood vessels in an organ increases, what happens to velocity of blood through that organ?
increased
O decreased
O unchanged
O stopped
QUESTION 45
While shopping at your local drugstore, you stop at the blood pressure machine. It measures your blood pressure as 115/75
(good-that's healthy!). This number means that
O arterial pressure is 115 mm Hg when the ventricles contract and 75 mm Hg in between ventricular contractions.
O your sinoatrial node generates a 115 mV signal and your atrioventricular node generates a 75 mV signal.
O your sinoatrial node generates a 75 mV signal and your atrioventricular node amplifies this to a 75 mV signal.
arterial pressure is 115 mm Hg when the atria contract and 75 mm Hg in between atrial contractions.
Honorlock Browser Guard
™ app.honorlock.com is sharing your screen.
Stop sharing
Hide
TM
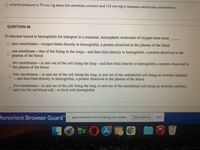
Transcribed Image Text:arterial pressure is 75 mm Hg when the ventricles contract and 115 mm Hg in between ventricular contractions.
QUESTION 46
To become bound to hemoglobin for transport in a mammal, atmospheric molecules of oxygen must cross
O zero membranes –oxygen binds directly to hemoglobin, a protein dissolved in the plasma of the blood
one membrane-that of the lining in the lungs-and then bind directly to hemoglobin, a protein dissolved in the
plasma of the blood
two membranes-in and out of the cell lining the lung-and then bind directly to hemoglobin, a protein dissolved in
the plasma of the blood
four membranes-in and out of the cell lining the lung, in and out of the endothelial cell lining an alveolar capillary
and then bind directly to hemoglobin, a protein dissolved in the plasma of the blood
five membranes-in and out of the cell lining the lung, in and out of the endothelial cell lining an alveolar capillary,
and into the red blood cell-to bind with hemoglobin
Honorlock Browser Guard" app.honorlock.com is sharing your screen.
TM
Stop sharing
Hide
MacBook Po.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- https://wowzahttp.cengage.com/geyser/corey_9780357764428/video/video.html?asset=5_personcentered After watching the video, please respond in writing to both of the following questions: 1). What feelings did you experience about the counseling session portrayed in this video? 2). Did your feelings change after viewing Dr. Corey’s reflections on the counseling session? If so, please explain how your feelings changed.arrow_forwardPlease answer the attached questionsarrow_forwardsorry, but it is hard to read for me , I understand certain words. Thank for helping me though.arrow_forward
- Hello, I am working in an assignment about San Diego but firts I need to describe the community including demographics, literacy levels, etc. Can you please help me with this? Thank you in advance!arrow_forwardI have persuasive speech on Wednesday. So please help me write about outline of topic that convince people should own the dog. Thank youarrow_forwardI have attached 2 pictures with an example my Professor gave. Thank you.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education