
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305251052
Author: Michael Cummings
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
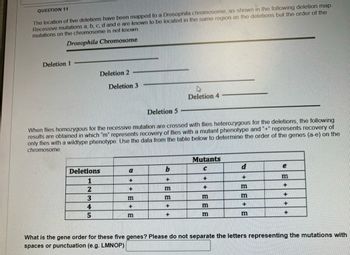
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 11
The location of five deletions have been mapped to a Drosophila chromosome, as shown in the following deletion map.
Recessive mutations a, b, c, d and e are known to be located in the same region as the deletions but the order of the
mutations on the chromosome is not known.
Drosophila Chromosome
Deletion 1
Deletion 2
Deletion 3
Deletion 4
Deletion 5
When flies homozygous for the recessive mutation are crossed with flies heterozygous for the deletions, the following
results are obtained in which "m" represents recovery of flies with a mutant phenotype and "+" represents recovery of
only flies with a wildtype phenotype. Use the data from the table below to determine the order of the genes (a-e) on the
chromosome.
Mutants
Deletions
a
b
C
d
e
1
+
+
+
+
m
2
+
m
+
m
3
m
m
m
m
4
+
+
m
+
+
5
m
+
m
m
+
What is the gene order for these five genes? Please do not separate the letters representing the mutations with
spaces or punctuation (e.g. LMNOP)
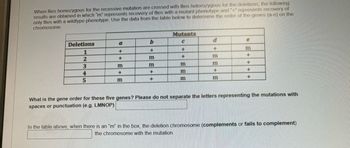
Transcribed Image Text:When flies homozygous for the recessive mutation are crossed with flies heterozygous for the deletions, the following
results are obtained in which "m" represents recovery of flies with a mutant phenotype and "+" represents recovery of
only flies with a wildtype phenotype. Use the data from the table below to determine the order of the genes (a-e) on the
chromosome.
Deletions
a
b
Mutants
C
1
+
+
+
m
2
+
m
+
m
+
3
m
m
m
m
4
+
+
m
+
5
m
+
m
m
+
What is the gene order for these five genes? Please do not separate the letters representing the mutations with
spaces or punctuation (e.g. LMNOP)
In the table above, when there is an "m" in the box, the deletion chromosome (complements or fails to complement)
the chromosome with the mutation.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Below is shown an annotation indicating the protein coding genes of a Drosophila genomic region. Below this map is shown the structure of an inversion (the vertical lines indicate the breakpoints), three deletions (indicated by the gaps) and three Insertions (indicated by the triangles) 100 S עולם Sara N Deletion Insortion Insertion 2 13829 Inversion 1 Execst PART Deletion? Deletion 3 Insertion 3 You have a mutation in a gene required for the development of the wings. Drosophila homozygous for this mutation have no wings. You cross these Drosophila homozygous for the wingless mutant allele with Drosophila homozygous for the seven mapped DNA changes. Mapped change Phenotype Inversion 1 wingless Deletion 1 wingless Deletion 2 wild type Deletion 3 wild type Insertion 1 wild type Insertion 2 wingless Insertion 3 wild type You conclude that the mutated allele is in which of the below genes? hh unk Irk1 CG46310 cnc Ⓒfzo CG4467 Rad60 EloA wda Pex11c orbarrow_forward16 - The phenotype of vestigial (short) wings (vg) in Drosophila melanogaster is caused by a recessive mutant gene that independently assorts with a recessive gene for hairy (h) body. Assume that a cross is made between a fly the is homozygous for normal wings with a hairy body and a fly with vestigial wings that is homozygous for normal body hair. The wild-type F1 flies were crossed among each other to produce 1024 offspring. Which phenotypes would you expect among the 1024 offspring, and how many of each phenotype would you expect? a) Phenotypes: wild, vestigial, hairy, and vestigial hairy; Numbers expected: wild (256), vestigial (256), hairy (256), and vestigial hairy (256). b) O Phenotypes: wild, vestigial, hairy, and vestigial hairy; Numbers expected: wild (576), vestigial (192), hairy (192), and vestigial hairy (64). C) O Phenotypes: wild, vestigial, hairy, and vestigial hairy; Numbers expected: wild (192), vestigial (256), hairy (64), and vestigial hairy (192). d) All vestigial…arrow_forward8.18 Irradiatioh of Drosophila sperm produces transloca- tions between the X chromosome and autosomes, between the Y chromosome and autosomes, and between different autosomes. Translotations between the X and Y chromosomes are not produced. Explain the absence of X-Y translocations. The birth of this child prompted the Dentons' physician to order a chromosome study of parents and child. The results of the study are shown in the accompanying fig- ure. Chromosome banding was done, and all chromo- somes were normal in these individuals, except some copies of number 6 and number 12. The number-6 and number-12 chromosomes of mother, father, and child are shown in the figure (the number 6 chromosomes are the larger pair): Child Mrs. Denton Mr. Denton a. Does either parent have an abnormal karyotype? If so, which parent has it, and what is the nature of the abnormality? b. How did the child's karyotype arise? (What pairing and segregation events took place in the parents?) e. Why is the child…arrow_forward
- Question 4. Recalling the eye pigment pathway in Drosophila, match the following fly genotypes with the appropriate phenotypes (w=white, bw-brown, cn=cinnabar red, st=scarlet red, se=sepia brown) a. b. d. W W W W ; ; ; ; bw + bw + + cn bw + Genotype A + cn bw cn bw cn Genotype B Genotype C + cn Genotype D ; ; ; ; st+ st se st se + se st se + se st se + se Scarlet Sepia Sepia White < < <arrow_forwardQuestion is attachedarrow_forwardCan I get an explanation for 1a, 1d, 1e, 2c, 2d and the calculations for the level of interference please.arrow_forward
- A Drosophila male is heterozygous for a reciprocaltranslocation between an autosome and the Y chromosome. The part of the autosome now present onthe Y chromosome contains the dominant mutationLyra (shortened wings); the other (normal) copyof the same autosome is Lyra+. This male is nowmated with a true-breeding, wild-type female. Whatkinds of progeny would be obtained, and in whatproportions?arrow_forwardPlease send me the question in 20 minutes it's very urgent plzarrow_forwardConsidering the following chromosome which is represented as a series of genes on each arm separated by the centromere. Describe the type of mutation required to produce each of the mutant chromosomes below. ABCDEFG*HIJKLMNarrow_forward
- 7. please answer thisarrow_forwardThe locations of six deletions have been mapped to a Drosophila chromosome, as shown in the following deletion map. Recessive mutations a, b, c, d, e, and f are known to be located in the same region as the deletions, but the order of the mutations on the chromosome is not known.arrow_forwardPlease help and explainarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning