
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
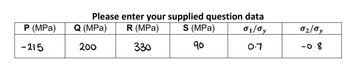
Transcribed Image Text:P (MPa)
-215
Please enter your supplied question data
R (MPa)
S (MPa)
01/0y
330
90
0.7
Q (MPa)
200
02/0y
-0.8
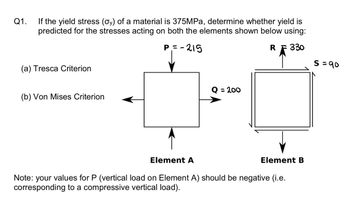
Transcribed Image Text:Q1. If the yield stress (oy) of a material is 375MPa, determine whether yield is
predicted for the stresses acting on both the elements shown below using:
P₁=-215
RF 330
(a) Tresca Criterion
(b) Von Mises Criterion
Q = 200
Element A
Note: your values for P (vertical load on Element A) should be negative (i.e.
corresponding to a compressive vertical load).
Element B
S=90
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The stresses on the surface of a hard bronze component are shown in the figure below. The yield strength of the bronze is σY = 345 MPa.a) What is the factor of safety predicted by the maximum-shear-stress theory of failure for the stress state shown? Does the component fail according to this theory?b) What is the value of the Mises equivalent stress for the given state of plane stress?c) What is the factor of safety predicted by the failure criterion of the maximum-distortion energy theory of failure? Does the component fail according to this theory?arrow_forward3) Referring to the plot below, a steel bar with a radius of 0.2523-inch exposes to 650°C. If the expected lifetime of the iron bar is 9 years, what is the maximum load allowed to carry? ( Stress (psi) 20,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000- 1,000 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 (36+0.78 In s) Larson-Miller parameter w 1000arrow_forwardQ1Barrow_forward
- A stress element is shown. The material has a yield strength of 200 MPa, an ultimate strength of 275 MPa, and a Young’s Modulus of 207 GPa.arrow_forwardmaterial mechanicsarrow_forwardFind the maximum normal stress in the bar pictured below. The parameter values are listed in the table. W2 P parameter value units དྷདྷ་ W1 30 mm W2 40 mm t 5 mm r 10 mm d 20 mm P 8 KN The maximum normal stress is σmax kd MPa. 080 BY NO SA 2021 Cathy Zupke Parrow_forward
- answer as soon as soon as possiblearrow_forwardA steel bolt of 6 mm in diameter has a tensile load of 40 kN. Find the average tensile stress at the section M and the screwed section N, where the diameter at the root of the thread is 2. 4 mm as shown in Figure QI.2. (6) M - 40 kN 40 kN - 4 mm diameter 6 mm diameter Figure Q1.2: Steel boltarrow_forwardQ2/ A force P = 1 KN applied to a right bar suspended by three wires, as shown below. all wires are of equal size and the same material. for each wire, A = 80 mm , E =200 GPa , and L =4 m. If initially, there were no slack in the wires, how will the applied load distribute between the wires? 200 100 100 4000 mm mm mm mmarrow_forward
- D 12KN B A 10KN 28kN + + 60KN 44kN + 120cm 80cm Ост 40cm Figure 1 a) Draw a Free Body Diagram for each section of the member above. b) Determine the force acting on the section BC. c) Draw a Normal Force Diagram for the figure above. d) Calculate the stress induced in the member BC if the diameter of the rod is 55.2791mm. e) Determine the total elongation of the rod.arrow_forwardi li. الامتحان هو سؤالان فقط Q. 1: If a material is cast iron (ultimate tensile strength = 300 Mpa, ultimate compressive strength - 900 Mpa) and the stress state at a point is shown in Fig. 1. Using a graphical method, find safety factor against static failure using 100 Mpa (a) Rankine failure theory (b) Coloumb - Mohr theory (c) Modified Coloumb - Mohr theory 50 Мра إضافة ملف Q.2 For a rotating shaft of diameter 15 mm as shown in Fig. 2. If the material is AISI-1045 CD, Find the safety factor II >arrow_forwardAL: 1₂ The above figure (not drawn to scale) shows a rod made up of two cylindrical sections of the same material. The left cylinder has diameter d, = 30mm and length 4 = 150mm. The right cylinder has diameter dy=10mm and length = 150mm. The rod is subjected to a force F = 50KN. Find the total extension in the rod, AL, given that E = 203kN/mm². Enter your answer in mm to 5 decimal places in the box below: mm -Farrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY