
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:et
Insert Design
ion -
3'
Transitions
Animation
D
* Ω
BIUAS X² A &
Determine:
Slide Show
A A & E E EE ab A
v
Review
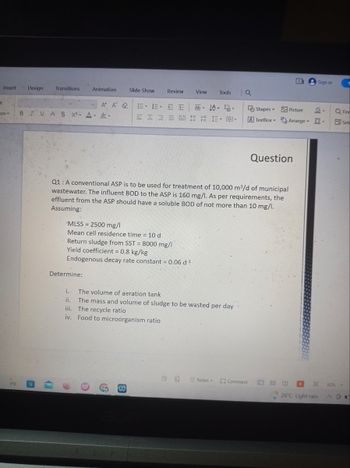
MLSS = 2500 mg/l
Mean cell residence time = 10 d
View
Return sludge from SST = 8000 mg/l
Yield coefficient = 0.8 kg/kg
Endogenous decay rate constant = 0.06 d-¹
**
====12111 (0) -
Tools
Q1: A conventional ASP is to be used for treatment of 10,000 m³/d of municipal
wastewater. The influent BOD to the ASP is 160 mg/l. As per requirements, the
effluent from the ASP should have a soluble BOD of not more than 10 mg/l.
Assuming:
i.
The volume of aeration tank
ii. The mass and volume of sludge to be wasted per day
iii.
The recycle ratio
iv. Food to microorganism ratio
Notes-
a
Comment
Y
Shapes
Picture
A TextBox Arrange -
4
Question
Sign in
26°C Light rain
Q Find
Sele
80%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please solve this with explanation of stepsarrow_forward1) Estimate the biomass concentration in a CSTR aeration tank with the following operating conditions: hydraulic residence time = 3 h; mean cell residence time = 6 d; yield coefficient = 0.6 mg VSS/mg BOD; decay rate = 0.1 d-1; influent soluble BOD = 200 mg/L; effluent BOD = 2 mg/L.arrow_forward1. A natural water with a flow of 4.0 MGD is to be treated with a commercial-grade alum dosage of 80 mg/l. Determine the amount of alum required (expressed in lbs/day), the amount of natural alkalinity required to complete the reaction (expressed in mg/l as CaCO3 and kg/day), and the amount of Al(OH)3(s) sludge produced (expressed in lbs/day and gal/day) if the sludge contains 2.2% solids by weight and the S.G. of the dry solids is 2.0.arrow_forward
- Hi Please try to solve Last time you solved this problem but result is incorrect.arrow_forwardA bio-tower composed of a modular plastic medium of 6 m is used as secondary treatment component in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Flow from the primary clarifier is 25000 m³/day with 200 mg/1 BOD. The treatability constant is 0.06 per min. To produce an effluent with a soluble BOD of 20 mg/1, the surface area as per Eckenfelder (coefficient related to medium is 0.5) is approximately:arrow_forward2aarrow_forward
- Please include Equations. This is for a water and wastewater review, it is not for a grade. I just need to understand the problem.arrow_forwardA complete-mixed activated sludge process is to be designed to treat 5.0 MGD of primary effluent having a BOD5 of 180 mg/L. The requirement is that the effluent BOD5 and TSS concentration be 20 mg/L or less on an annual average basis. The following biokinetic coefficient obtained at 15°C: Y = 0.6 mg VSS/mg BOD5, k=2.85d-¹, Ks = 70 mg/L BOD5, and kå = 0.041 d¹¹. Assume that the MLVSS concentration in the aeration basin is maintained at 2,500 mg/L. Determine: a. The minimum MCRT (d) b. The MCRT necessary to meet the requirement (d) C. The volume of the aeration basin (ft³)arrow_forwardBiomass and substrate mass balance equations can be merged giving QwXR/VX=Y/X (Qo/V) (So-S)-kd (i) Prove that X= SRT/HRT Note that HRT = t and SRT = tc. (ii) If you are an engineer working in a wastewater consultancy company, and obtained the following data: - SRT = 20 days HRT 20 hours = (Y(So-S)/1+kd(SRT)). So = 350 mg/L S = 100 mg/L Y = 0.15 kd = 0.22 per day Calculate the increment of MLSS (%) required in the aerobic tank if the discharge BOD5 in the effluent needs to achieve 10 mg/L.arrow_forward
- After primary treatment, a municipal wastewater contains 150 mg/L BOD5. The wastewater flow of 0.44 m³/s (10 MGD) is then treated in an activated sludge system with an SRT of 12 d and an HRT of 6 h. Given the biokinetic parameters tabulated below, determine the limiting value of the minimum SRT (d). Parameter Hmax Ks ka Y Value 3 d¹ 60 mg/L BOD, 0.10 d ¹¹ 0.6 mg VSS/mg BODSarrow_forwardThe 550-bed Atlanta Hospital has a small, activated sludge plant to treat wastewater from the hospital. The average daily hospital discharge is 1.50 m3 per day per bed, and the average soluble BOD5 after primary settling is 450 mg/L. The aeration tank effective liguid dimensions of 10 m x 10 m x 5 m. The plant operating parameters are as follows: MLVSS - 2,600 mg/L; MLSS - 1.20 (MLVSS); Settling sludge volume after 30 min. = 200 mL/L. The F/M ratio is nearly?arrow_forward1. It is estimated that the BOD of raw sewage received at a treatment plant serving a population of 20,000 will be 300 mg/L. It is estimated that the per capita BOD loading is 0.17 lbm/day. 30% of influent BOD is removed by settling. One single-stage high-rate trickling filter is to be used to reduce the plant effluent to 50 mg/L. Recirculation is from the filter effluent to the primary settling influent. Ten States' Standards is in effect, which specifies 100 gpcd in the absence of other information. (1) What is the design flow rate? (A) 0.9 MGD (B) 1.1 MGD (C) 1.4 MGD (D) 2.0 MGD (2) Assuming a design flow rate of 1.35 MGD, what is the total organic load on the filter? (A) 1700 lbm/day (B) 2100 lbm/day (C) 2400 lbm/day (D) 3400 lbm/day (3) Assuming an incoming volume of 1.35 MGD and an organic loading of 60 lbm/1000ft³.d, what flow should be recirculated? (A) 0.6 MGD (B) 1.1 MGD (C) 1.2 MGD (D) 2.2 MGD (4) What is the overall plant efficiency? (A) 45% (B) 76% (C) 83% (D) 91%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning