
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781305635180
Author: Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
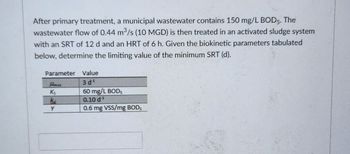
Transcribed Image Text:After primary treatment, a municipal wastewater contains 150 mg/L BOD5. The
wastewater flow of 0.44 m³/s (10 MGD) is then treated in an activated sludge system
with an SRT of 12 d and an HRT of 6 h. Given the biokinetic parameters tabulated
below, determine the limiting value of the minimum SRT (d).
Parameter
Hmax
Ks
ka
Y
Value
3 d¹
60 mg/L BOD,
0.10 d ¹¹
0.6 mg VSS/mg BODS
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A hydrometer test has the following result: Gs = 2.65, temperature of water = 26 C, and L = 10.4 cm at 45 minutes after the start of sedimentation (see Figure 2.25). What is the diameter D of the smallest-size particles that have settled beyond the zone of measurement at that time (that is, t = 45 min)? Figure 2.25 ASTM 152H type of hydrometer placed inside the sedimentation cylinder (Courtesy of Khaled Sobhan, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, Florida)arrow_forwardRefer to Figure 7.24. The following data were collected during the field permeability measurement of a confined aquifer using a pumping test. Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the permeable layer. Use Eq. (7.49). Thickness of the aquifer, H = 4.5 m Piezometric level and radial distance of the first observation well: h1 = 2.9 m; r1 = 17.8 m Piezometric level and radial distance of the second observation well: h2 = 1.8 m; r2 = 8.1 m Rate of discharge from pumping, q = 0.5 m3/minarrow_forwardRepeat Problem 2.14 with the following values: Gs = 2.75, temperature of water = 21C, t = 88 min, and L = 11.7 cm. 2.14 A hydrometer test has the following result: Gs = 2.65, temperature of water = 26 C, and L = 10.4 cm at 45 minutes after the start of sedimentation (see Figure 2.25). What is the diameter D of the smallest-size particles that have settled beyond the zone of measurement at that time (that is, t = 45 min)? Figure 2.25 ASTM 152H type of hydrometer placed inside the sedimentation cylinder (Courtesy of Khaled Sobhan, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, Florida)arrow_forward
- An existing rural 4-lane highway is to be replaced by a 6-lane divided expressway (3 lanes in each direction). Traffic volume data on the highway indicate that the AADT (both directions) during the first year of operation is 24,000 with the following vehicle mix and axle loads. Passengercars=50percent 2-axle single-unit trucks (12,000lb/axle)=40percent 3-axle single-unit trucks (16,000lb/axle)=10percent The vehicle mix is expected to remain the same throughout the design life of 20 years, although traffic is expected to grow at a rate of 3.5 percent annually. Using the AASHTO design procedure, determine the minimum depth of concrete pavement required for the design period of 20 years. Pi=4.5J=3.2Pt=2.5Cd=1.0Sc=650lb/in.2So=0.3Ec=5106lb/in.2R=95k=130lb/in.3arrow_forwardRefer to Problem 2.C.1. Results of the sieve analysis for Soils A, B, and C are given below. To obtain a more representative sample for further geotechnical testing, a ternary blend is created by uniformly mixing 8000 kg of each soil. Answer the following questions. a. If a sieve analysis is conducted on the mixture using the same set of sieves as shown above, compute the mass retained (as a percentage) and cumulative percent passing in each sieve. b. What would be the uniformity coefficient (Cu) and the coefficient of gradation (Cc) of the mixture?arrow_forwardTwo materials, A and B, are to be separated using two unit operations, 1 and 2. The feed has 10 tons/h A and 4 tons/h B. The split (fraction of material rejected by each operation) is given in Table P5-14. a. Which sequence of operations, (l?2) or (2?1), will yield the greatest recovery of material A? b. What will be the purity of material A using that sequence? c. What will be the efficiency of separation for the entire process train with regard to material A using the Worrell-Stesed equation?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Solid Waste Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635203
Author:Worrell, William A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning