
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
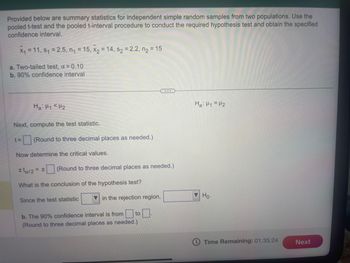
Transcribed Image Text:Provided below are summary statistics for independent simple random samples from two populations. Use the
pooled t-test and the pooled t-interval procedure to conduct the required hypothesis test and obtain the specified
confidence interval.
x₁ = 11, S₁ = 2.5, n₁ = 15, x₂ = 14, s₂ = 2.2, n₂ = 15
a. Two-tailed test, α = 0.10
b. 90% confidence interval
Ha: H1 H2
Next, compute the test statistic.
t= (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Now determine the critical values.
±ta/2= ±
What is the conclusion of the hypothesis test?
Since the test statistic
b. The 90% confidence interval is from to
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
in the rejection region,
Ha: H1 = H₂
Ho.
Time Remaining: 01:35:24
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The data below are yields for two different types of corn seed that were used on adjacent plots of land. Assume that the data are simple random samples and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of the difference between type 1 and type 2 yields. What does the confidence interval suggest about farmer Joe's claim that type 1 seed is better than type 2 seed?Type 1 2143 2024 2142 2433 2142 2034 2211 1484 Type 2 2089 1924 2078 2467 2132 1949 2197 1482arrow_forwardFind the 98% confidence interval for the difference between two means based on this information about two samples. Assume independent samples from normal populations. (Use conservative degrees of freedom.) (Give your answers correct to two decimal places.) Sample Number Mean Std. Dev. 1 16 38 29 2 29 28 29 Lower Limit Upper Limitarrow_forwardProvided below are summary statistics for independent simple random samples from two populations. Use the nonpooled t-test and the nonpooled t-interval procedure to conduct the required hypothesis test and obtain the specified confidence interval. x1=10, s1=2, n1=10, x2=14, s2=6, n2=10 a. Two-tailed test, α=0.05 b. 95% confidence interval a. What are the hypotheses for the t-test? A. H0: μ1=μ2 Ha: μ1≠μ2 B. H0: μ1≥μ2 Ha: μ1<μ2 C. H0: μ1=μ2 Ha: μ1>μ2 D. H0: μ1=μ2 Ha: μ1<μ2 Find the test statistic. t=_________ (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Find the critical values. ±tα/2=±___________ (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion of the hypothesis test? A. Do not reject H0. There is insufficient evidence that the two means are different. B. Reject H0. There is sufficient evidence that the two means are different. C. Reject H0. There is insufficient evidence that the…arrow_forward
- Estimate the minimum sample size needed to achieve the margin of error E = 0.029 for a 95% confidence interval The minimum sample size is (Round up to the nearest integer.)arrow_forwardYou may need to use the appropriate appendix table or technology to answer this question. The following results come from two independent random samples taken of two populations. Sample 1 Sample 2 n1 = 60 n2 = 25 x1 = 13.6 x2 = 11.6 ?1 = 2.4 ?2 = 3 (a) What is the point estimate of the difference between the two population means? (Use x1 − x2.) (b) Provide a 90% confidence interval for the difference between the two population means. (Use x1 − x2. Round your answers to two decimal places.) to (c) Provide a 95% confidence interval for the difference between the two population means. (Use x1 − x2. Round your answers to two decimal places.) toarrow_forwardTwo samples are drawn from populations that are independent of each other. Use this data to test the claim using a confidence interval approach that the means of both populations are the same. Use a significance level of 0.01. Sample A Sample B x¯=46.2 x¯=38.4 s=3.1 s=4.1 n=12 n=16 e) What is the margin of Error? E = f) What is the confidence interval for the difference of the two population means? ? < μ1μ1-μ2μ2< ? g) Based on our confidence interval in f) what is the decision? h) What is the conclusion?arrow_forward
- A random sample of high school seniors were asked whether they were applying for college. The resulting confidence interval for the proportion of students applying for college is (0.65,0.69). What is the margin of error?arrow_forwardCould you please help find p value, conclusion, and the confidence interval claim. Thank you!arrow_forward(2) Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Assume two independent random samples are available which provide sample proportions. For the first sample assume n₁ = 100 and x₁= 39. For the second sample, assume n₂= 100 and x₂= 49. Test the null hypothesis that the population proportions are equal versus the alternative hypothesis that the proportions are not equal at the 90% confidence level. Frame the test statistic by subtracting the proportion for population 1 from that for population 2. Pick an appropriate z value, p-value and conclusion. Round your answer to the nearest thousandth. Note that this is a two- tailed test. z-value = -1.425 p-value= 0.077 statistically significant z-value = 1.425 p-value= 0.077 statistically significant z-value = -1.425 p-value= 0.077 not statistically significant z-value = 1.425 p-value= 0.154 statistically not significantarrow_forward
- Suppose that 90% confidence interval for the difference between two proportions, p1-p2, is ( 0.013, 0.245). If we were testing the following hypotheses: H0: p1=p2 versus H1: p1≠p2 at the .10 significance level we wouldarrow_forwardProvided below are summary statistics for independent simple random samples from two populations. Use the nonpooled t-test and the nonpooled t-interval procedure to conduct the required hypothesis test and obtain the specified confidence interval. x1=11,s1=5,n1=10,x2=15,s2=6,n2=10 a. Two-tailed test,α=0.05 b.95%confidence interval a. What are the hypotheses for the t-test? A.H0:μ1=μ2 Ha:μ1>μ2 B.H0:μ1=μ2 Ha:μ1≠μ2 C.H0:μ1≥μ2 Ha:μ1<μ2 D.H0:μ1=μ2 Ha:μ1<μ2 Find the test statistic. t= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Find the P-value. P= (Round to four decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion of the hypothesis test? A.Reject H0.There is sufficient evidence that the two means are different. B. Do not reject H0. There is insufficient evidence that the two means are different. C.Do not reject H0. There is sufficient evidence that the two means are different. D.Reject H0.There is…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman