
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
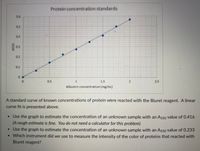
Transcribed Image Text:Protein concentration standards
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.5
1.5
2.5
Albumin concentration (mg/mL)
A standard curve of known concentrations of protein were reacted with the Biuret reagent. A linear
curve fit is presented above.
• Use the graph to estimate the concentration of an unknown sample with an A550 value of 0.416
(A rough estimate is fine. You do not need a calculator for this problem)
• Use the graph to estimate the concentration of an unknown sample with an A550 value of 0.233
• Which instrument did we use to measure the intensity of the color of proteins that reacted with
Biuret reagent?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Materials - 2021FA-CHM-1O X Bb 4427577 d-fleet02-xythos.content.blackboardcdn.com/6086c260d7e8f/4427577?X-Blackboard-Expiration=1633143600000&X-Blackboard-Sig 6 / 9 100% Exercise 1: Standard Curve for Protein Measurements: A standard curve for protein concentration is often created using known concentrations of bovine serum albumin (protein). This process is called the Bradford Assay; it is a colorimetric assay. A special reagent turns blue when it binds to amino acids present in protein. The intensity of the color is best measured with a spectrophotometer (a device for comparing two light radiations, wavelength by wavelength). In the case of the Bradford Assay the greater the absorbance, the higher the protein concentration. A series of tests were performed on some samples and spectrophotometer: following measurements were obtained using a Protein Concentration (mg/ml) Absorbance (A) 0.26 0.098 0.56 0.213 0.383 0.84 1.12 0.473 1.40 0.527 TASKS: 1. Enter the data into Excel - the…arrow_forwardYou are given a pure protein sample to characterize and provided the following information: Its molar extinction coefficient, ε280, is 0.25 liters micromole-1 cm-1 in both the folded and unfolded form Its ΔGo for unfolding is 1.5 kcal/mol at 37o (where RT = 0.59 kcal/mole) A) Using a 0.5 cm pathlength cell, you measure the absorbance at 280 nm of a 20-fold dilution of your pure protein in solution (by this, we mean that 50 ul of the protein sample was diluted to a final volume of 1 ml) and find A280 = 0.40. What is the original concentration of the protein before dilution? B) What is the concentration of the unfolded form of the protein in your sample?arrow_forward3L.6.2arrow_forward
- Please dont provide handwrittin solution.../.arrow_forwardYou run 5 standard proteins listed below on a size-exclusion (gel filtration) column with limit of 200,000Da. Please draw a chromatogram on a separate page with each peak and both axes labeled. Protein B-Amylase Alcohol dehydrogenase Bovine albumin Carbonic anhydrase Cytochome A280 MW 223,800 0.5 82,000 0.6 66,463 0.45 30,000 0.43 12,000 0.8arrow_forwardSDS-PAGE reagents that play a role in denaturing the protein sample include (Select all that applies) Bromophenol blue APS Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Acetic Acid Glycerol Heat Beta-Mercaptoethanol TEMEDarrow_forward
- b. Show calculations for making 10 mls each of the following dilutions of sucrose from the 0.30 M stock solution (Formula #3, Example D) CSTOCK (M) VSTOCK CDESIRED (M) V. X %3D X DESIRED -- . TI 0.30 M 0.25 M 0.20 M 0.15 Мarrow_forwardThe isoelectric point, pI, of the protein deoxyribonuclease I is 10.2 , while that of pepsin is 1. What is the net charge of deoxyribonuclease I at pH 7.3 ? What is the net charge of pepsin at pH 3.5 ? The isoelectric point of tryptophan is 5.89 ; phenylalanine , 5.48 . During paper electrophoresis at pH 6.5 , toward which clectrode does tryptophan migrate? During paper electrophoresis at pH 4.5, toward which electrode does phenylalanine migrate? [arrow_forwardThe fosfomycin disc (200/50) also contains glucose-6-phosphate (G-6-P). Which ONE of the following best describes why this is the case? Select one: A. G-6-P increases the solubility of fosfomycin B. G-6-P is used to promote active transport of fosfomycin into the bacterial cell C. G-6-P is used in the formulation to correct glucose deficiencies promoted by fosfomycin D. G-6-P stabilises fosfomycin from spontaneous hydrolysis in aqueous solution E. G-6-P is an inhibitor of FosA that inactivates fosfomycinarrow_forward
- The absorbance values for different BSA standards. How can the protein concentration be calculated? Which absorbance value should be used?arrow_forwardCalculate the amount of protein (in mg) in Sample 1 if the measurement at A280 = 0.636, taking into account the dilution factor as per question 6 (100ul) and the total volume of extract as per question 4 (140ml). Give your answer as a number with no decimal places.arrow_forwardstock aliquot - 1mg/ml use the sequence below to determine the molarity using ExPASy Translate and protProt Program atgggcgaggagtataaagttgtcctcacatttggatccccaatgagccctaatgcaaataacaaacagacttgggttaataaacctcttgatgcgccttcgggccattacaatgtgaaaattgcaaaggatgttgaccactatctaaccatgcagggtttcacttctatagcatctgttgactggtacactatagattttcaaccatctgaggcgcctgccccgataaaaggcttgcaggtacttgtgaacatctcgaaaaaagctgatgtgtatgccgtcaaacaatttgtcacagcgcagaccaacaacaagcaccaggttacaagcctgttcctagtaaaagtaacaactggttttcaggtgaacaactacctgagttacttttacagggcgtctgctactggggatgccacaactaacctgttggttagaggagacacatacacagcagggataagttttacccagggtggatggtatttgttgacaaatacatctattgttgatggggctatgccacctggctgggtctggaataacgtggaacttaaaactaacacagcgtatcacatggacaaaggcttggtccatctaataatgcctttgcctgagtccacgcaaatgtgttatgagatgctgacatctattccagcggccgcagagctcgctctggtgccacgcggtagttccgctcatcaccaccatcatcaccatcaccaccactarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON