
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
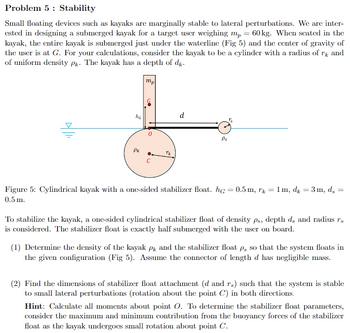
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 5 Stability
Small floating devices such as kayaks are marginally stable to lateral perturbations. We are inter-
ested in designing a submerged kayak for a target user weighing mp = 60 kg. When seated in the
kayak, the entire kayak is submerged just under the waterline (Fig 5) and the center of gravity of
the user is at G. For your calculations, consider the kayak to be a cylinder with a radius of rk and
of uniform density Pk. The kayak has a depth of dk.
mp
5
NG
D
Pk
TK
d
Ps
r
Figure 5: Cylindrical kayak with a one-sided stabilizer float. hc = 0.5 m, r = 1m, dk = 3m, ds
0.5 m.
=
To stabilize the kayak, a one-sided cylindrical stabilizer float of density ps, depth ds and radius rs
is considered. The stabilizer float is exactly half submerged with the user on board.
(1) Determine the density of the kayak PR and the stabilizer float p, so that the system floats in
the given configuration (Fig 5). Assume the connector of length d has negligible mass.
(2) Find the dimensions of stabilizer float attachment (d and rs) such that the system is stable
to small lateral perturbations (rotation about the point C) in both directions.
Hint: Calculate all moments about point O. To determine the stabilizer float parameters,
consider the maximum and minimum contribution from the buoyancy forces of the stabilizer
float as the kayak undergoes small rotation about point C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Evaluate the dimensionless groups hcD/k,UD/, and cp/k for water, n-butyl alcohol, mercury, hydrogen, air, and saturated steam at a temperature of 100C. Let D=1m,U=1m/sec, and hc=1W/m2K.arrow_forwardQ4/ A block of ice measuring 4 m long, 2 m wide, and 1.2 m deep is floating in seawater with a density of 10.1 kN/m³. If the density of ice is 9.2 kN/m³, calculate the depth of submersion and the position of the center of buoyancy.arrow_forwardA pontoon boat floats on two cylindrical pontoons (assume the ends are flat). Each pontoon is 6m long. The mass of the boat, pontoons, and gear (without any passengers) is 1950 kg. If exactly half of the pontoon volume was submerged without any passengers on the boat, what is the maximum volume of water that can be displaced to support the weight of passengers? The density of freshwater is 1000 kg/m³ . End view of pontoons: Waterline Pontoon D/2 is submergedarrow_forward
- A flotation buoy has mass 806 kg, volume 1.43 m, and is attached to the sea floor by a cable in such a way that the buoy is completely submerged. Calculate the magnitude of the tension in the cable, given the density of sea water is 1025 kg/m³. T=_ %3Darrow_forwardThe following questions consider the stability of a floating iceberg. Approximate the iceberg as a perfect cylinder of uniform density, If the iceberg has a diameter of 3 meters and a length of 0.5 meters find the location of the metacenter as measured from the bottom of the iceberg. Take the density of sea water to be 1030 kg/m3 and the density of the ice to be 920 kg/m3.arrow_forward1- Panel BC in the figure is circular. Compute (a) the hydrostatic force of the water on the panel; (b) its center of pressure; and (c) the moment of this force about point B. Given and unknowns: Assumptions: Schematic: Governing Equation(s): Analysis and Results: Water at 20°C C 50° B 3 m 3 m 3 marrow_forward
- what is the answer for number 4?a and barrow_forwardThe tank shown in Figure a is accelerated to the right. Calculate the acceleration ܽax needed to cause the free surface, shown inFigure b, to touch point A. Also find ܲPB, and the total force acting on the bottom of the tank if the tank width is 1m.arrow_forwardA float sensor for the determination of the level of water in a vessel has a cylindrical float of mass 2.0 kg, cross-sectional area 20 cm= and a length of 1 5 in. It floats vertically in the water and presses upwards against a beam attached to its upward end. What will be the minimum and maximum up thrust forces exerted by the float on the beam? Suggest a means by which the deformation of the beam under the action of the force could be monitoredarrow_forward
- 1A square boat of area = 2 m2 floats on the water with 1 m of boat submerged in the water. Estimate the buoyant force on the boat and the pressure at the bottom of the boat. The density of water is 997 kg/m3. Fb = 30,000 N and P = 20,000 Pa Fb = 10,000 N and P = 20,000 Pa Fb = 100 N and P = 200 Pa Fb = 20,000 N and P = 10,000 Pa 2Explain the basic functioning of a hydraulic lift. Be sure to include the terms pressure, density, and buoyant force in your explanation. Give one example of a hydraulic lift you have encountered. 3A common practice when parenting is to take a jar of baby food and place it into hot water to heat the food up. Describe this process in terms of heat transfer. Be sure to include the terms specific heat capacity, hot, cold, transfer, and thermal equilibrium. professor can you answer these questions please?arrow_forwardThe plastic block shown below measures l.5 m x/.S m x(.7 m and has a specific gravity of 0.38. The concrete block B (density = 2400 kg/m) is suspended from the corner of the plastic block by means of a cable and the plastic block is thus floating in the lake (T = 15°C) in the orientation shown. Determine the volume of the concrete block (units of liters) noting that it does not rest on the bottom of the lake, Neglect the weight and volume of the cable in your analysis. %3D %3D 1.7 m 0.5m Water Cable Barrow_forwardA pontoon boat floats on two cylindrical pontoons (assume the ends are flat). Each pontoon is 6m long. The mass of the boat, pontoons, and gear (without any passengers) is 1950 kg. What is the required diameter of the pontoons such that exactly half of the pontoons are submerged when no passengers are on the boat? The density of freshwater is 1000 kg/m3. End view of pontoons: Waterline Pontoon D/2 is submergedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning