
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780134746241
Author: Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
please answer in text form and in proper format answer with must explanation , calculation for each part and steps clearly
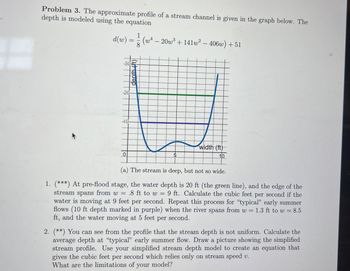
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 3. The approximate profile of a stream channel is given in the graph below. The
depth is modeled using the equation
d(w) =
=
-20-
-1-0-
0
8
(w4-20w3+141w² - 406w) +51
width (ft)
10
(a) The stream is deep, but not so wide.
1. (***) At pre-flood stage, the water depth is 20 ft (the green line), and the edge of the
stream spans from w = .8 ft to w = 9 ft. Calculate the cubic feet per second if the
water is moving at 9 feet per second. Repeat this process for "typical" early summer
flows (10 ft depth marked in purple) when the river spans from w = 1.3 ft to w = 8.5
ft, and the water moving at 5 feet per second.
2. (**) You can see from the profile that the stream depth is not uniform. Calculate the
average depth at "typical" early summer flow. Draw a picture showing the simplified
stream profile. Use your simplified stream depth model to create an equation that
gives the cubic feet per second which relies only on stream speed v.
What are the limitations of your model?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Recommended textbooks for you
 Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134746241
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134041360
Author:Greg Carbone
Publisher:PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:9781260153125
Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Earth Science (15th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134543536
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:PEARSON

Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)
Earth Science
ISBN:9781337569613
Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott Spoolman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Geology
Earth Science
ISBN:9781259916823
Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, Lisa
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,