
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
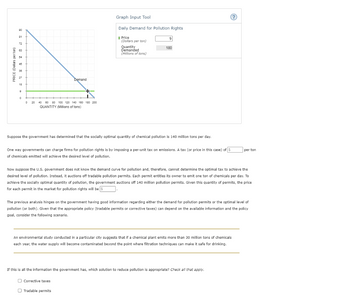
Transcribed Image Text:PRICE (Dollars perton)
90
81
72
63
54
45
30
27
18
9
0
0
+
I
40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
QUANTITY (Millions of tons)
20 40
Demand
Graph Input Tool
Daily Demand for Pollution Rights
Price
(Dollars per ton)
Quantity
Demanded
(Millions of tons)
9
180
Suppose the government has determined that the socially optimal quantity of chemical pollution is 140 million tons per day.
Corrective taxes
Tradable permits
One way governments can charge firms for pollution rights is by imposing a per-unit tax on emissions. A tax (or price in this case) of S
of chemicals emitted will achieve the desired level of pollution.
(?)
Now suppose the U.S. government does not know the demand curve for pollution and, therefore, cannot determine the optimal tax to achieve the
desired level of pollution. Instead, it auctions off tradable pollution permits. Each permit entitles its owner to emit one ton of chemicals per day. To
achieve the socially optimal quantity of pollution, the government auctions off 140 million pollution permits. Given this quantity of permits, the price
for each permit in the market for pollution rights will be $
The previous analysis hinges on the government having good information regarding either the demand for pollution permits or the optimal level of
pollution (or both). Given that the appropriate policy (tradable permits or corrective taxes) can depend on the available information and the policy
goal, consider the following scenario.
An environmental study conducted in a particular city suggests that if a chemical plant emits more than 30 million tons of chemicals
each year, the water supply will become contaminated beyond the point where filtration techniques can make it safe for drinking.
If this is all the information the government has, which solution to reduce pollution is appropriate? Check all that apply.
per ton
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No written by hand solutionarrow_forwardquestion 3arrow_forward3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantity of consumption Consider the market for electric cars. Suppose that a electric car manufacturing facility dumps sludge into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the facility. Producing additional electric cars imposes a constant per-unit external cost of $600. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for electric cars. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $600 per unit. PRICE (Dollars per unit of electric cars) 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 0 + 1 O □ ☐ O 2 3 4 5 QUANTITY (Units of electric cars) The market equilibrium quantity is ☐ Supply (Private Cost) 6 Demand (Private Value) 7 Social Cost (?) units of electric cars, but the socially optimal quantity of electric car production is To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal…arrow_forward
- Im confused on this question.arrow_forwardBN12.2 (a) Case: The market for dry cleaning is reflected by the demand and supply curves (Q is in thousands): Pa = 5-Q Ps= 2+2Q Producing dry cleaning creates ground water pollution with a constant marginal external cost of 1.2. Question: (a) Sketch a graph that shows the Dsoc, Spriv, Ssoc, Qopt (societal perspective) and DWL in an unregulated market (No need to label the values in the graph)?arrow_forwardDescribe the key symmetry between a pollution emissions tax and an emissions trading scheme. Outline some reasons you might wish to choose one approach in favour of the other when dealing with an emissions-reduction problem.arrow_forward
- Only typed answer You are an industry analyst that specializes in an industry where the market inverse demand is P = 100 - 3Q. The external marginal cost of producing the product is MCExternal = 6Q, and the internal cost is MCInternal = 14Q. Instruction: Round your answers to the nearest two decimal places. a. What is the socially efficient level of output? units b. Given these costs and market demand, how much output would a competitive industry produce? units c. Given these costs and market demand, how much output would a monopolist produce? units d. Which of the following are actions the government could take to induce firms in this industry to produce the socially efficient level of output. Instructions: You may select more than one answer. Click the box with a check mark for the correct answers and click twice to empty the box for the wrong answers. You must click to select or deselect each option in order to receive full credit. Pollution taxes…arrow_forward4 This is a graph reprinted from Section 12.1 the Economics of Pollution. Please explain the graph with particular attention paid to why there are two supply curves. How can a government use this graph to establish pollution controls?arrow_forwardConsider a firm that emits pollution into the air. Suppose that the marginal damage costs associated with the emissions are given by MDC -15+ 4 c, where e is the quantity of the emissions. The firm's marginal costs of abatement are given by (a) (b) 390 (c) MAC 1200 - 20 c. Determine the quantity of emissions that the firm would discharge in the absence of government policy. Determine the socially efficient level of emissions. Calculate the total costs to society for both a and b and draw a diagram illustrating these costs.arrow_forward
- $ 15 7 0 Marginal Control Costs A 50 0 150 Marginal Damages 250 Emissions (tons) | What is the benefit to society from reducing emissions from 250 tons to 150 tons?arrow_forwardNo hand written solution Afirm has an industrial plant that emits pollutants into a town’s lake. The plant’s marginal abatement function is MAC= 200 – 0.5E and damages caused by its emissions are given by MD = 2E where emissions are in kg. per day. What is the socially efficient level of emissions from this plant? Illustrate this in a graph. As an incentive to reduce emissions to the socially efficient level, government offers to pay the firm for each kg. of emissions it abates per day from this plant. What subsidy per kg. should the government offer? If the plant abates to the socially efficient level of emissions, what total subsidy payment would the firm receive? Identify the area in your graph. How much better or worse off would the firm be compared to if it did no abating? Identify the area in your graph. What would be the net benefit to society if we pay the firm to reduce the plant’s emissions to the socially efficient level? Identify this area in your graph.arrow_forwardIn the graph below, circle the efficient level of emissions.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education