
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
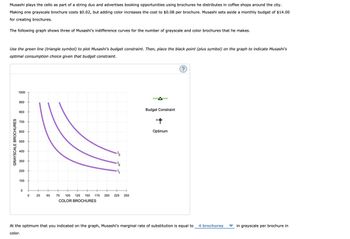
Transcribed Image Text:Musashi plays the cello as part of a string duo and advertises booking opportunities using brochures he distributes in coffee shops around the city.
Making one grayscale brochure costs $0.02, but adding color increases the cost to $0.08 per brochure. Musashi sets aside a monthly budget of $14.00
for creating brochures.
The following graph shows three of Musashi's indifference curves for the number of grayscale and color brochures that he makes.
Use the green line (triangle symbol) to plot Musashi's budget constraint. Then, place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate Musashi's
optimal consumption choice given that budget constraint.
GRAYSCALE BROCHURES
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
2
0
0 25 50
75 100 125 150 175 200 225
COLOR BROCHURES
250
Budget Constraint
Optimum
?.
At the optimum that you indicated on the graph, Musashi's marginal rate of substitution is equal to 4 brochures
color.
in grayscale per brochure in
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Reese thinks peanut butter and chocolate are great when separate, but when they combine they are even more epic. In other words, Reese likes to eat either peanut butter or chocolate, but when he eats them together, he gets additional satisfaction from the combination. His preference over peanut butter (x) and chocolate (y) is represented by the utility function: u(x, y) = xy + x + y Suppose that now Reese loses almost his entire income, so that he is left with only one dollar, i.e. his new income is I0 = 1. If prices are still px = 2, py = 4, what is his new optimal consumption of x and y (Hint: Remember that consumption of both goods must be weakly positive, i.e. x∗ ≥ 0 and y∗ ≥ 0) (a) x∗ = 0.5, y∗ = 0(b) x∗ = 0.25, y∗ = 0(c) x∗ = 0.75, y∗ = 0.25(d) x∗ = 0.75, y∗ = 0(e) x∗ = 0.5, y∗ = 1arrow_forwardKate’s utility function includes coffee (c) and sugar (s). She only consumes coffee and sugar together, and she only consumes in the ratio of one unit (cup) of coffee with two units (spoons) of sugar. Her utility function is What is her marginal utility of sugar if she has 4 cups of coffee and 6 spoons of sugar? Remember that unit are infinitely divisible (you can have parts of units). (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) ½ (d) 2arrow_forwardSuppose that you are given $20,000 to split between two people, Jane and Fred. The income and marginal utility for each of them is shown in the following table. Amount to Jane Amount to Fred MU of Jane's Last Dollar Spent MU of Fred's Last Dollar Spent $ 5,000 $ 15,000 80 65 $ 7,000 $ 13,000 70 70 $ 9,000 $ 11,000 60 75 $ 11,000 $ 9,000 50 80 $ 13,000 $ 7,000 40 85 Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. If you want to maximize their combined utility, how much of the $20,000 should go to Jane? How much should go to Fred? Amount to Jane = $ Amount to Fred = $arrow_forward
- In Workout problem 5.1, Charlie has a utility function U(xA, xB) = xAxB, the price of apples is $1, and the price of bananas is $2. If Charlie's income were $160, how many units of bananas would he consume if he chose the bundle that maximized his utility subject to his budget constraint?arrow_forwardPROBLEM (4) You have the Cobb-Douglas utility function u(x, y) = xy over apples (x) and plums (y) and you have $120 budget to spend and can carry at most 480 ounces in weight in your backpack going back to the dorm. Each apple costs $1 and weighs 8 ounces, and each plum costs $3 and weighs 4 ounces. You can only leave the store with a bundle of fruits you can afford and carry. (a) Drawing the relevant lines, intercepts, marking the points and hence identifying the feasible set of bundles, calculate the optimal bundle. (b) Forget about (a). If you were to choose a backpack before going on this shopping trip, for the weight constraint not to be an issue for you, how many ounces of weight capacity would you need for your backpack? HINT: That is, for this weight capacity of the backpack, you'd be able to carry the best bundle you can afford, i.e, the weight constraint is not binding for your decision. (c) Forget about (b). In (a), just before going out for shopping with your backpack to…arrow_forwardSuppose the utility possibility frontier for two individuals is given by U_a+2U_b=200 Please plot the utility frontier on a graph.arrow_forward
- Suppose that the price of good X is $6 and the price of good Y is $2. You have $144 to spend and your preferences over X and Y are defined as: U(x,y) = x2/3y1/3 Calculate the marginal utility of X Calculate the Marginal Utility of Y What is the optimal Choice of X and Y given the PX = $6, PY = $2 and I = $144 If Income is increased to $150 calculate how the optimal choice of X and Y changearrow_forwardAyana is pitching an idea for a startup company that makes and sells solar-powered phonechargers (C). Her market research has found that consumer demand for this product can beexpressed as a function of the price of the charger itself (PC), the price of phones (PF), andthe consmer’s income (I). Consumer demand can be described by the function C(PC, PF, I) =(i−10PC)/ (PF) Suppose her chargers come in all different capacities to meet any quantity demanded, so youdon’t need to worry about restricting C to whole numbers for this problem. (a) Does this product satisfy the law of demand?Explain.arrow_forwardQuestion 22: Kathy gets utility from three things: the number of flowers in her local park (F), reading books in this park (R), and eating sushi (S). Four utility functions that might describe Kathy's preferences are shown below. In each case, discuss whether reading in the park (R) is non-essential and whether reading (R) and the number of flowers in the park (F) are weak complements. [medium] (a) U(F, R, S) = 2FR+S (b) U(F, R, S) = /2FR+S (c) U(F, R, S) = (V2FR)S (d) U(F, R, S) = v2F + RSarrow_forward
- 10.6 For every two boxes of strawberries that she consumes, Millicent insists on having one pitcher of cream. She does not, however, insist on consuming the same amount every week. Her utility function is U = min{$₁,2c₁}min{$2,2c2} where s₁ and s2 are the number of boxes of strawberries she consumes this week and next week and c₁ and c₂ are the number of pitchers of cream she consumes this week and next. Strawberries cost $2 a box and cream costs $1 a pitcher. She has a present value of $100 to spend on these goods in the next two weeks. The weekly interest rate is 1%. How many boxes of strawberries will she consume this week? (a) 10 (b) 20 (c) 22 (d) 14.1 (e) 6.06arrow_forwardEvery month, a family of three spends $2,000 on food (F) and other items (O). The family’s preferences are represented by the utility function U(F,O) = F1/5O4/5. The unit price of food and the unit price of other items are both $1. Find this family’s monthly food expenditure.The family could join a consumers’ club. At the club, food costs 20% less than in other stores (i.e., at the food club PF = $0.8)arrow_forwardQuestion 22: Kathy gets utility from three things: the number of flowers in her local park (F), reading books in this park (R), and eating sushi (S). Four utility functions that might describe Kathy's preferences are shown below. In each case, discuss whether reading in the park (R) is non-essential and whether reading (R) and the number of flowers in the park (F) are weak complements. [medium] (a) U(F, R, S) = 2FR+ S (b) U(F, R, S) = /2FR+ S (c) U(F, R, S) = (V2FR)S (d) U(F, R, S) = /2F+ RSarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education