
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
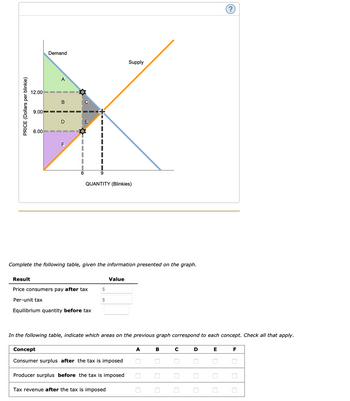
Transcribed Image Text:PRICE (Dollars per blinkie)
12.00
9.00
6.00
Demand
I
A
B
D
F
I
с
E
QUANTITY (Blinkies)
Complete the following table, given the information presented on the graph.
Result
Price consumers pay after tax
Per-unit tax
Equilibrium quantity before tax
$
$
Value
Supply
In the following table, indicate which areas on the previous graph correspond to each concept. Check all that apply.
Concept
Consumer surplus after the tax is imposed
Producer surplus before the tax is imposed
Tax revenue after the tax is imposed
A
B
с
D
E
000
F
00
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Consider the market for candy bars given below. Suppose that the government imposes a tax of $2 per candy bar in this market. Show on the graph and calculate the following: Price 5 $4.50 $4 $3.50 Supply 53 $2.50 $2 $1.50 $1 Demand S0.50 400 800 1200 1600 2000 2400 2800 3200 3600 4000 Candy Bars A. The quantity the market will produce with the tax. B. The government revenue from the tax. C. The deadweight loss from the tax. D. The consumer surplus with the tax. E. The producer surplus with the tax.arrow_forwardThe following graph represents the demand and supply for blinkies (an imaginary product). The black point (plus symbol) indicates the pre-tax equilibrium. Suppose the government has just decided to impose a tax on this market; the grey points (star symbol) indicate the after-tax scenario. PRICE (Dollars per blinkie) Demand 42.00---== 36.00 30.00 B II Supply QUANTITY (Blinkies)arrow_forwardIf the state government would like to increase tax revenue, please give three examples of products/commodities that the government should impose tax on so that they can collect the highest amount of tax revenue. Please explain your reasons clearly.arrow_forward
- PRICE (Dollars per handbag) 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 Demand Tax Wedge 160 320 480 640 800 960 1120 1280 1440 1600 QUANTITY (Handbags) Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus After Tax Tax Revenue + Supply Deadweight Loss Before Tax (Dollars) Complete the following table by using the previous graphs to determine the values of consumer and producer surplus before the tax, and consumer surplus, producer surplus, tax revenue, and deadweight loss after the tax. Note: You can determine the areas of different portions of the graph by selecting the relevant area. 0 0 Tax Revenue After Tax (Dollars) A Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus Deadweight Loss Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardSuppose the market for cigarette is competitive. An economist estimates the price elasticity of demand and supply for cigarette are -0.6 and 0.8 respectively. a. Suppose the government imposes a per-unit tax on the cigarette sellers. Who, buyers or sellers, would share a heavier tax burden? Explain your answers without calculation. b. Suppose the government imposes a per-unit tax of $40 on the cigarette sellers. By how much would buyers and sellers of cigarettes share the tax burden respectively? Show your calculation. c. Suppose many small sellers, such as newsstands, complain the heavy tax burden borne by them. Would it be better to these small sellers if the government decides to impose a $20 per-unit tax on both the buyers and the sellers of cigarette? Explain.arrow_forwardHomework: Supply and Demand: An Initial Look 9. Effect of a tax on buyers and sellers The following graph shows the daily market for jeans when the tax on sellers is set at $0 per pair. Suppose the government institutes a tax of $5.80 per pair, to be paid by the seller. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. Hint: To see the impact of the tax, first enter the value of the tax in the Tax on Sellers field. Adjust the value in the price field to move the green line to the after-tax equilibrium so that quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. PRICE (Dollars per pair). 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 no 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 Demand Supply 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 QUANTITY (Pairs of jeans) Graph Input Tool Market for Jeans. Price (Dollars per pair) Quantity Demanded…arrow_forward
- The following graph depicts a market where a tax has been imposed. Pe was the equilibrium price before the tax was imposed, and Qe was the equilibrium quantity. After the tax, PC is the price that consumers pay, and PS is the price that producers receive. QT units are sold after the tax is imposed. NOTE: The areas B and C are rectangles that are divided by the supply curve ST. Include both sections of those rectangles when choosing your answers. Which areas represent the revenue collected from this tax? A + B + F B + C F + G E A + Earrow_forwardQuestion 36 For Questions 36-46, please refer to the following graph. The vertical distance between points A and B represents a per-unit tax in the market. tPrice 12 11 10 t. Supply H. G 4 3- 2- 1- Demand 0s 1 13 2 2s 3 33 4 45 s Deantit Without the tax, the equilibrium price in this market is $ , and the equilibrium quantity is units.arrow_forwardSuppose the Canadian government has decided to place an excise tax of $20 per tire on producers of automobile tires Excise taxes are also called sales or commodity taxes 150 Previously, there was no excise tax on automobile tires. As 140 a result of the excise tax, producers of tires, such as 130 Bridgestone and Michelin, are going to alter their tire prices The graph illustrates the demand and supply curves for 120 Supply Demand 110 100 automobile tires before the excise tax. 90 Please shift the appropriate curve or curves on the graph to demonstrate the new equilibrium 80 70 What is the price consumers pay for a tire post tax? Round 60 to the nearest 10 50 0 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Quantity of tires 100 price paid by consumers: Price per tire coarrow_forward
- The following graph represents the demand and supply for pinckneys (an imaginary product). The black point (plus symbol) indicates the pre-tax equilibrium. Suppose the government has just decided to impose a tax on this market; the grey points (star symbol) indicate the after-tax scenario. Demand Supply A 16, 18 21.00 18.00- D E 15.00 F 12 16 QUANTITY (Pinckneys) PRICE (Dollars per pinckney)arrow_forwardQuestion 5 Suppose that the government imposes a tax on cigarettes. Use the diagram below to answer the questions. D is the demand curve before tax, S is the supply curve before tax and ST is the supply curve after the tax. Price 12 10 - Qua (a) For the market for cioarettes without the tax, Indicate: (0) Price paid by consumers Price paid by producers Quantity of cigarettes sold Buyer's reservation price Sellers reservation pricearrow_forwardThe following graph depicts a market where a tax has been imposed. Pe was the equilibrium price before the tax was imposed, and Qe was the equilibrium quantity. After the tax, PC is the price that consumers pay, and PS is the price that producers receive. QT units are sold after the tax is imposed. NOTE: The areas B and C are rectangles that are divided by the supply curve ST. Include both sections of those rectangles when choosing your answers. What is the amount of the tax, as measured along the y axis? PC + PS Pe – PS PC – PS PC – P* Pe + PSarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education