
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
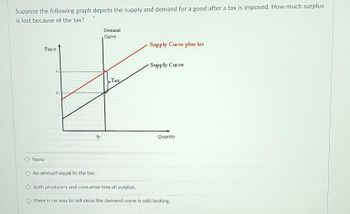
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the following graph depicts the supply and demand for a good after a tax is imposed. How much surplus
is lost because of the tax?
Price
None
Pi
P₁
An amount equal to the tax.
9
Demand
Curve
Tax
Supply Curve plus tax
Supply Curve
Quantity
both producers and consumer lose all surplus.
Othere is no way to tell since the demand curve is odd looking.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Help plz 3 6arrow_forwardIf buyers pay more of a tax than do the sellers اختر أحد الخيارات a. demand is more elastic than supply O .b. supply is more elastic than demand O C. None of the above answers is correct O .d. the equilibrium price paid by buyers rises by less than half the amount of the tax „e. the amount of tax revenue collected by the government is almost zeroarrow_forwardIf a constant $1 per unit tax is imposed on producers, A. producers can always pass the tax burden to consumers by raising the price by a dollar. B. producers will pay more than $0.5 tax for each unit of the good sold if supply is less elastic than demand. C. producers will pay less than $0.5 tax for each unit of the good sold if demand is more elastic than supply. D. producers must absorb the tax themselves and cannot raise the price.arrow_forward
- Figure 8-8 Suppose the government imposes a $10 per unit tax on a good. Price 24 22- 20 18 Supply 16+ 14+ 12 F G 10+ H 6- 4- K M Demand 3 69 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 36 39 Quantity Refer to Figure 8-8. One effect of the tax is to O reduce producer surplus from $96 to $24. O create a deadweight loss of $72. O reduce consumer surplus from $180 to $72. All of the above are correct. 00 2.arrow_forwardQuestion 4 Figure #3: The graph below represents a $10 per unit tax on a good then the amount bought and sold in the market is only 4 units. Note that Q represents quantity and P represents price. P. 24 20 A 16 Supply 12 GIH 8. 4. K M Demand 4 6 10 12 14 16 Refer to Figure #3. The government collects tax revenue that is (or are) the area(s) represented by the area OF-G-L OL OB-D Oc-Farrow_forwardFigure 8-5 Price Pa P₁ P₂ 0 < B D 41 F -Tax- G 9₂ a. A b. C+EX C. B+C Od. D+E C E H Q₁ Quantity Refer to Figure 8-5. Assume the tax was levied on the producer. Which area represents the reduction in consumer surplus?arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardUsing the supply and demand data for wheat below, what would happen if the government placed a $3 per bushel tax on wheat? Bushels demanded 45 50 56 61 67 Price per bushel $6 $5 $4 LA LA LA $3 $2 Bushels supplied 77 73 68 61 57 O the producer price would fall, the consumer price would rise, and the quantity sold would increase. The producer price would fall, the consumer price would rise, and the equilibrium quantity would fall O Both the consumer price and the producer price would rise the consumer price would rise by less than $3 while the producer price would fall by more than $3 O the equilibrium consumer price would rise by $3arrow_forwardThe graph shows the market for basketballs in which sellers are taxed $6 a ball. Draw a shape that shows the excess burden of the tax on basketballs. The excess burden of the tax on basketballs is $ million. The supply of basketballs is more pays most of the tax. A. elastic; seller OB. elastic; buyer OC. inelastic; buyer O D. elastic; seller than the demand for basketballs, and thearrow_forward
- Use Exhibit to answer question a. A. b. C. c. B. d. B + C + E + F. Price e. C + F. 22 PB Po Ps I FIBI U O Size of tax per unit 'm/ F If a tax is placed on the product in this market, tax revenue paid by the sellers is the area Qo Supply Demand Quantityarrow_forwardQuestion 6arrow_forwardOnly typed answer and please don't use chatgptarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education