
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Don't use
Answer in step by step with explanation
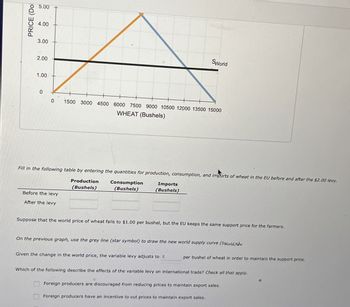
Transcribed Image Text:PRICE (Dol
5.00
4.00
3.00
2.00
1.00
0
0
SWorld
1500 3000 4500 6000 7500 9000 10500 12000 13500 15000
WHEAT (Bushels)
Fill in the following table by entering the quantities for production, consumption, and imports of wheat in the EU before and after the $2.00 levy.
Production
(Bushels)
Consumption
(Bushels)
Imports
(Bushels)
Before the levy
After the levy
Suppose that the world price of wheat falls to $1.00 per bushel, but the EU keeps the same support price for the farmers.
On the previous graph, use the grey line (star symbol) to draw the new world supply curve (SWorld,Now
Given the change in the world price, the variable levy adjusts to $
per bushel of wheat in order to maintain the support price.
Which of the following describe the effects of the variable levy on international trade? Check all that apply.
Foreign producers are discouraged from reducing prices to maintain export sales.
Foreign producers have an incentive to cut prices to maintain export sales.
41
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- PRICE (Dollars per tonne) 1160 Domestic Demand 1110 1060 1010 960 910 860 810 760 710 660 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 QUANTITY (Tonnes of oranges) and is represented by the horizontal black line. satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. price of oranges and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated Domestic Supply A tariff set at this level would raise $ PW 200 If Zambia is open to international trade in oranges without any restrictions, it will import Suppose the Zambian government wants to reduce imports to exactly 40 tonnes of oranges to help domestic producers. A tariff of $ tonnes of oranges. in revenue for the Zambian government. per tonne will achieve this. Q Search this coursearrow_forwardPrice (dollars per ton) 1,000 800 600 400 200 0 1 2 3 4 5 D 6 Steel (millions of tons per year) The figure shows the market for steel in the United States. If the world price for a ton of steel is $200 per ton, how much steel does the United States import? Suppose the United States imposes a tariff of $400 per ton of steel. With this tariff, how much steel does the United States import? If it is possible to calculate the amount of the deadweight loss from the $400 per ton tariff, what is the amount? If it is not possible, explain why it is not possible to calculate it. Next suppose the United States imposes a tariff of only $200 per ton of steel. With this tariff, how much steel does the United States import? How much revenue does the government collect from this tariff? Finally, suppose that instead of a tariff the United States imposes a quota of 2 million tons of steel per year. Illustrate how the market changes with this quota. With the quota, what is the price of steel in the…arrow_forward1._______ The total value of a nation’s exports minus thetotal value of its imports over some period of timearrow_forward
- 4. Effects of a tariff on international trade The following graph shows the domestic demand for and supply of maize in Bolivia. The world price (Pw) of maize is $240 per ton and is displayed as a horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that all countries under consideration are small, that is, the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of maize and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in maize. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. PRICE (Dollars per ton) 440 415 390 365 340 315 290 265 240 215 190 Domestic Demand 0 10 20 Domestic Supply 30 40 50 60 70 QUANTITY (Tons of maize) 80 90 100arrow_forwardQuestions The import duty is a 5% tariff on imported motorcycles. You are given the information shown in the table. Questions Current situation with 5% Estimated situation tariff without tariff World price $2000per cycle $2050per cycle Tariff at 5% $100per cycle 0 Domestic price $2100per cycle $2050per cycle Number of cycles 100,000 105,000 purchased domestically per year Number of cycles 40,000 35,000 produced domestically per year Number of cycles 60,000 70,000 imported per year Questions Calculate the following: • The consumer gain from removing the duty. The producer loss form removing the duty. • The government tariff revenue loss. The net effect on the country's well-being. Why does the net effect on the country as a whole differ from the result in previous questioarrow_forward00 7 F. PRICE (Dollars per ton) 4. Effects of a tariff on international trade The following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for soybeans in Honduras. The world price (Pw) of soybeans is $530 per ton and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of soybeans and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in soybeans. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. 2. Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 770 740 710 680 650 620 06 P, 530 MacBook Pro Search or type URL 4. 51 9.arrow_forward
- PRICE (Dollars perton) 1225 1180 1135 1090 1045 1000 955 910 865 820 775 Domestic Demand + 0 30 Domestic Supply 60 90 120 150 180 210 QUANTITY (Tons of limes) 240 C++ P W 270 300 If Zambia is open to international trade in limes without any restrictions, it will import tons of limes.arrow_forwardof The following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for oranges in Jordan. The world price (Pw) of oranges is $780 per ton and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of oranges and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in oranges. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. PRICE (Dollars perton) 1220 1165 1110 1055 1000 045 + 890 835 780 725 670 Domestic Demand 0 30 60 Domestic Supply 8 00 120 150 180 210 QUANTITY (Tons of nrannee) W 240 270 300arrow_forwardUnder open trade, what will be the international price and quantity traded? (a) $8 and 12 units. (b) $9 and 18 units. (c) $11 and 15 units. (d) $11 and 9 units.arrow_forward
- Price of Rice $/ton €140 €120 €100 с a b rise by 40 units. 80 120 160 200 240 300 Quantity of Rice rise by 40 units. e The graph above reflects the market for rice in Spain. If the world price is 100euros and the government imposes a 20% tax on imports the amount of imports will S drop by 40 units. drop by 80 units.arrow_forward5. Agricultural export subsidies in a small nation The following graph shows the market for wheat in Canada, where De is the demand curve, Sc is the supply curve, and Pw is the free trade price of wheat. Assume that Canada is a relatively small producer of wheat, so changes in its output do not affect the world price of wheat. Also assume that Canada is currently open to free trade, and domestic consumers are able to purchase wheat at the world price with negligible transportation costs. Suppose a subsidy of $80 per ton is granted to exporters in Canada, allowing them to sell their products abroad at prices below their costs. Assume that trade restrictions are also put in place in order to prevent domestic consumers from buying wheat abroad at the world price. Use the grey line (star symbols) to indicate the world price of wheat plus the subsidy on the following graph. Then use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the price of wheat in Canada and the quantity demanded at that…arrow_forward2 Kwame is the purchasing manager for an electronics firm in North Carolina. He purchases a large quantity of diodes from NXP Semiconductors in the Netherlands, a manufacturer of diodes. What kind of export or import transaction does this represent? a indirect export b direct import c indirect import d direct exportarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education