
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
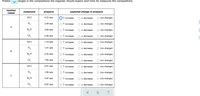
Transcribed Image Text:Predict
hanges in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions.
reaction
compound
pressure
expected change in pressure
vessel
HCl
4.22 atm
f increase
O 1 decrease
(no change)
2.69 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
A
H,0
2.80 atm
f increase
O I decrease
(no change)
Cl,
6.40 atm
f increase
O I decrease
O (no change)
HCl
1.10 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
O2
1.91 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
В
H,0
4.36 atm
f increase
O I decrease
(no change)
Cl,
7.96 atm
f increase
O 1 decrease
O (no change)
HCl
0.91 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
02
1.86 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
C
H,0
4.45 atm
f increase
decrease
(no change)
Cl2
8.05 atm
f increase
(no change)
decrease
?

Transcribed Image Text:A chemical engineer is studying the following reaction:
4 HCl(g)+O,(9) → 2 H,O(g)+2C12(9)
At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction is 5.7.
The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with hydrogen chloride and oxygen, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the
mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below.
Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions.
reaction
compound
pressure
expected change in pressure
vessel
HCl
4.22 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
2.69 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
A
H,0
2.80 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
Cl,
6.40 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
HCl
1.10 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
1.91 atm
f increase
Į decrease
(no change)
В
H,O
4.36 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
Cl,
7.96 atm
O f increase
I decrease
(no change)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (please type answer no write by hend)arrow_forwardplease help I do not understand this questionarrow_forwardⒸMacmillan Learning Write the chemical reaction for chlorous acid in water, whose equilibrium constant is K₂. Include the physical states for each species. K₁ reaction: HCIO, (aq) + H₂O(aq) → H₂O¹(aq) + C1O₂ (aq) = Write the chemical reaction for the chlorite ion in water, whose equilibrium constant is K. Include the physical states for each species. Kreaction: CIO₂ (aq) + H₂O(aq) ⇒ HC10₂(aq) + OH¯(aq)|arrow_forward
- Image uploaded answer is not allowed please dear expert.arrow_forwardMacmillan Learning At a certain temperature, 0.800 mol SO3 is placed in a 2.00 L container. 2 SO3(g) 2 SO₂(g) + O₂(g) At equilibrium, 0.200 mol O₂ is present. Calculate Ke. Kc = 0.040arrow_forwardA researcher put 0.890 mol and 1.07 mol into a 3.00 L vessel at a given temperature to produce phosphorus pentachloride,PCl5 : PCl3(g)+Cl2(g)->PCl5(g) What will be the composition of this gaseous mixture at equilibrium? Kc= 25.6 at the temperature of this experiment. [PCl3]= ________ M [Cl2]=_________ M [PCl5]=_________ Marrow_forward
- How can we solve these problems?arrow_forwardY Background Layout 1|¹234|15 8-8 H₂ Reactants Number of hydrogen atoms Number of oxygen atoms Equation 2 speaker notes Theme Transition 61 111711LTI 8|19 go H₂O Product Number of hydrogen atoms Number of oxygen atoms 1₁ Is equation 2 balanced?arrow_forwardCalculate the percent by mass of Azaline engineer expect to find in the equilibrium and gas mixture round your answer to two significant digits. Please check your works.arrow_forward
- 2. a. Answer: Complete the ICE table for a solution of nitrous acid, HNO₂(aq), one of the acids associated with acid deposition. ( HNO,(aq) H,O'(aq) NO₂ (aq) 0.045 0.0043 Concentratio n Initial (mol/L) Change (mol/L) Equilibrium (mol/L) dinn to markedarrow_forwardI Review I Constants | Periodic Table Leaming Goal: To understand how to calculate the equilibrium constants for chemical equations that can be produced by the addition of other chemical equations with known equilibrium constants. Part A For a chemical reaction equation with the general form aA + BB = cC+ dD Given the two reactions the equilibrium equation is given by 1. H2S(aq) = HS (aq) + H*(aq), K = 9.22x10-8 and 2. HS (aq) S (aq) +H*(aq), K2 = 1.55x1019 what is the equilibrium constant Knnai for the following reaction? K1 [A" B* s- (aq) + 2H*(aq) H,S(aq) Thus, for a chemical reaction equation with the general form cC + dD eE + fF Enter your answer numerically. • View Available Hint(s) the equilibrium equation is given by K2 C"ID Templates Symbols undo regio Tese keyboard shortcuts Help If the first two equations are added together such that Knai = 1.4 • 10-26 aA + bB t eE + fF then the equilibrium equation is given by Submit Prevlous Anawere K3 [A)" (B] [A" B" * CD X Incorrect; Try…arrow_forwardasap in TYPED FORM ONLYarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY