
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
![**Part A**
Two negative charges are separated by a distance \(d\), as shown in the figure. Which of the following statements is or are true?
I. The two charges are attracted to one another.
II. The electrostatic potential energy of this system is positive.
III. As \(d\) increases, the electrostatic potential decreases.
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram features two negative charges positioned at a distance \(d\) apart, with arrows pointing away from each other symbolizing repulsion.
**Answer Options:**
- \( \bigcirc \) I and III are true.
- \( \bigcirc \) Only one of the statements is true.
- \( \bigcirc \) II and III are true.
- \( \bigcirc \) I and II are true.
- \( \bigcirc \) All three statements are true.
[Submit] [Request Answer]](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/bb31c72c-4045-4dee-afe2-8fb7977f2141/529fc86c-dd5d-4c9c-986a-77fc3bd5b3ed/ppztxmc_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:**Part A**
Two negative charges are separated by a distance \(d\), as shown in the figure. Which of the following statements is or are true?
I. The two charges are attracted to one another.
II. The electrostatic potential energy of this system is positive.
III. As \(d\) increases, the electrostatic potential decreases.
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram features two negative charges positioned at a distance \(d\) apart, with arrows pointing away from each other symbolizing repulsion.
**Answer Options:**
- \( \bigcirc \) I and III are true.
- \( \bigcirc \) Only one of the statements is true.
- \( \bigcirc \) II and III are true.
- \( \bigcirc \) I and II are true.
- \( \bigcirc \) All three statements are true.
[Submit] [Request Answer]
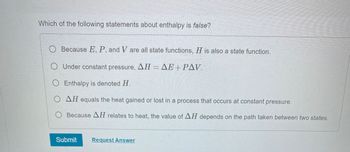
Transcribed Image Text:**Question:**
Which of the following statements about enthalpy is false?
**Options:**
- \( \heartsuit \) Because \( E, P, \) and \( V \) are all state functions, \( H \) is also a state function.
- \( \heartsuit \) Under constant pressure, \( \Delta H = \Delta E + P \Delta V \).
- \( \heartsuit \) Enthalpy is denoted \( H \).
- \( \heartsuit \) \( \Delta H \) equals the heat gained or lost in a process that occurs at constant pressure.
- \( \heartsuit \) Because \( \Delta H \) relates to heat, the value of \( \Delta H \) depends on the path taken between two states.
**Buttons:**
- Submit
- Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a boron-chlorine bond (B-Cl). Which atom would have a partial positive charge and which would have a partial negative charge?arrow_forwardThe charges and sizes of the ions in an ionic compound affect the strength of the electrostatic interaction between the ions and thus the strength of the lattice energy of the ionic compound. Arrange the compounds according to the magnitudes of their lattice energies based on the relative ion charges and sizes. Highest lattice energy Lowest lattice energy Answer Bank KCI MgO NaF MgF₂arrow_forwardWhich one of the following trends appears when considering lattice energies? Anion A) The higher the charge on the ions, the higher the lattice energy. Cation F- CI- Br- |- O2- B) The more ions present in an ionic compound, the smaller the lattice energy. Lit 1036 853 807 757 2925 Na+ 923 787 747 704 2695 C) The larger the distance between ions in the ionic compound, the higher the lattice energy. K+ 821 715 682 649 2360 Mg2+ 2957 2524 2440 2327 3791 D) In general, alkali metals have larger lattice energies than alkaline earth metals with the same anions. Ca2+ 2630 2258 2176 2074 3401 Al3+ 5215 5492 5361 5217 15,916arrow_forward
- Which one of the following ions has the greatest lattice energy? A. KCI = KF = KBr = KI B. KCI C. KI D. KBr E. KFarrow_forward8. Given the following six figures (at room temperature). Match them to the following compounds/molecules: HI, P₂H4, Fe₂O3, Na2S (cation dark sphere, anion open sphere), CaF2(cation dark sphere, anion open sphere), KF.arrow_forwardWhat is an atom?What is atomism?What is alchemy?What is protoscience and pseudoscience?What is atomic theory?On a bond paper, draw the different model of an atom.arrow_forward
- Say which atom is the C and the O is bonded with for reactants and productsarrow_forwardChemistry: Bonding 4a. Draw the Lewis structure for CH4, (methane), NH3, (ammonia), and H20 (water). b. Calculate the bond polarity for the C-H bond, N-H bond, and O-H bond. c. Classify these molecules as either polar or nonpolar. If the molecule is polar, label the partial negative and partial positive sides of the molecules you drew above.arrow_forwardAs seen in the table, compounds containing an integer ratio of elements depend on how many cations combine with how many anions to form a stable compound. For example, in table 1, to form a NaCl compound, first Na ionizes from the Na+ cation which is having +1 positive charge, which will lose 1 electron, it is having +1 charge, this electron then goes to Cl and it will change to Cl- anion by gaining the electron, so here 1:1 ratio charge which means 1 Na+ combines with 1 Cl-1 to form NaCl. So here integer ratio is 1:1 for this sodium chloride compound. As listed in table 2, Mg(OH)2, the integer ratio is 1:2 which means, Mg is a neutral atom that loses 2 electrons and forms an Mg+2 cation, which combines with OH which gains 1 electron to form OH- anion, So here Mg2+ can combine with 2 OH- anion, so they both combine to form Mg(OH)2 which has integer ratio as 1:2 . Thus, atom forms as ions by losing or gaining electrons and combines together in whole number ratio to form stable…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY