
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
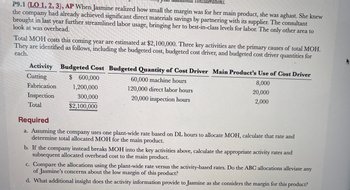
P9.1 (LO 1, 2, 3), AP When Jasmine realized how small the margin was for her main product, she was aghast. She knew the company had already achieved significant direct materials savings by partnering with its supplier. The consultant brought in last year further streamlined labor usage, bringing her to best-in-class levels for labor. The only other area to look at was overhead .
Total MOH costs this coming year are estimated at $2,100,000. Three key activities are the primary causes of total MOH. They are identified as follows, including the budgeted cost, budgeted cost driver, and budgeted cost driver quantities for each.
Activity Budgeted Cost Budgeted Quantity of Cost Driver Main Product’s Use of Cost Driver
Cutting $ 600,000 60,000 machine hours 8,000
Fabrication 1,200,000 120,000 direct labor hours 20,000
Inspection 300,000 20,000 inspection hours 2,000
Total $2,100,000
Required
Assuming the company uses one plant-wide rate based on DL hours to allocate MOH, calculate that rate and determine total allocated MOH for the main product.
If the company instead breaks MOH into the key activities above, calculate the appropriate activity rates and subsequent allocated overhead cost to the main product.
Compare the allocations using the plant-wide rate versus the activity-based rates. Do the ABC allocations alleviate any of Jasmine’s concerns about the low margin of this product?
What additional insight does the activity information provide to Jasmine as she considers the margin for this product?
Transcribed Image Text:### Activity-Based Costing Application and Analysis
**Scenario Overview:**
Jasmine, upon realizing the low margin of her main product, discovered that the company's overhead cost was the last area to be optimized after achieving savings in direct materials and labor. The estimated total Manufacturing Overhead (MOH) costs for the coming year are $2,100,000, linked to three key activity areas.
**Activity Cost Breakdown:**
| **Activity** | **Budgeted Cost** | **Budgeted Quantity of Cost Driver** | **Main Product’s Use of Cost Driver** |
|------------------|-------------------|-------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|
| Cutting | $600,000 | 60,000 machine hours | 8,000 |
| Fabrication | $1,200,000 | 120,000 direct labor hours | 20,000 |
| Inspection | $300,000 | 20,000 inspection hours | 2,000 |
| **Total** | **$2,100,000** | | |
**Required Analysis:**
a. **Plant-Wide Overhead Rate Calculation:**
- Assuming a plant-wide rate based on direct labor hours (DL hours), calculate the rate and determine total allocated MOH for the main product.
b. **Activity-Based Costing (ABC) Rate Calculation:**
- Calculate activity rates if the company utilizes activity-based costing for the activities listed. Subsequently, allocate overhead costs to the main product.
c. **Comparative Analysis:**
- Compare allocations derived from plant-wide rate and activity-based costing. Determine if the ABC method helps mitigate any concerns related to the low product margin.
d. **Additional Insights:**
- Analyze what further insights the activity-based information provides Jasmine as she considers the margin for her product.
This exercise intends to help understand the financial impacts of different overhead allocation methods and their implications for product profitability.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I don't want image in Solutions thanksarrow_forwardMorgan Inc. manufactures ergonomically correct office chairs. They have a contribution margin of $110,000 and fixed expenses of $28,500. They are adding a warehouse space that will add $20,000 to their fixed expenses. What is their DOL after adding this new expense? O 2.50 O 1.35 O 1.79 O 2.27arrow_forwardPlease help and break it down to understand.arrow_forward
- Please helparrow_forwardI could use a hand with thisarrow_forwardE8.8 (LO 3), AN Antonio is evaluating some of last year’s manufacturing costs for his business, Work It Out, which creates custom-fit exercise equipment for high-end clients. He is trying to strengthen his own analytical skills by looking at some of the total cost amounts and working backward to make sure he can find the detailed amounts that comprised these totals. Last year’s manufacturing costs are as follows. Total manufacturing costs $580,000 Total applied MOH (based on an MOH rate of $1.80/DL dollar) 270,000 Total cost of goods completed 630,000 Beginning balance in WIP Inventory 56,000 Required a. How much direct labor cost was incurred last year? b. What was the cost of direct materials used? c. What was the ending balance in WIP Inventory last year? d. If FG Inventory had no ending balance but Cost of Goods Sold was $675,000, what was the beginning balance in FG Inventory last year? e. Given the company’s goal to generate a 65% gross margin on these products, how much revenue…arrow_forward
- Parker Pottery produces a line of vases and a line of ceramic figurines. Each line uses the same equipment and labor; hence, there are no traceable fixed costs. Common fixed cost equals $40,000. Parker's accountant has begun to assess the profitability of the two lines and has gathered the following data for last year: VasesFigurinesPrice$40$70Variable cost3042Contribution margin$10$28Number of units1,000500 Required: If required, round your final answers to nearest whole value. 1. Compute the number of vases and the number of figurines that must be sold for the company to break even. Break-even vasesfill in the blank 1 unitsBreak-even figurinesfill in the blank 2 units 2. Parker Pottery is considering upgrading its factory to improve the quality of its products. The upgrade will add $5,260 per year to total fixed cost. If the upgrade is successful, the projected sales of vases will be 1,500, and figurine sales will increase to 1,000 units. What is the new break-even point in…arrow_forwardPLease ASAP. and show calculations!! Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardParker Pottery produces a line of vases and a line of ceramic figurines. Each line uses the same equipment and labor; hence, there are no traceable fixed costs. Common fixed cost equals $38, 400. Parker's accountant has begun to assess the profitability of the two lines and has gathered the following data for last year: Vases Figurines Price $40 $70 Variable cost 30 42 Contribution margin $10 $28 Number of units 1,000 500 Required: If required, round your final answers to nearest whole value. 1. Compute the number of vases and the number of figurines that must be sold for the company to break even. Break - even vases fill in the blank 1 units Break - even figurines fill in the blank 2 units 2. Parker Pottery is considering upgrading its factory to improve the quality of its products. The upgrade will add $5, 280 per year to total fixed cost. If the upgrade is successful, the projected sales of vases will be 2,000, and figurine sales will increase to 1,000 units. What is the new break -…arrow_forward
- Please answer fast i give you upvote.arrow_forwardPina Colada Racers makes bicycles. It has always purchased its bicycle tires from the Ivanhoe Tires at $25 each but is currently considering making the tires in its own factory. The estimated costs per unit of making the tires are as follows: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Total relevant cost $8 $4 The company's fixed expenses would increase by $63,000 per year if managers decided to make the tire. (a1) Calculate total relevant cost to make or buy if the company needs 10,300 tires a year. Make $7 $ Buyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education