
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Please make sure to change the angle BCD to 45 degrees before solving! The picture is wrong. Thank you!!
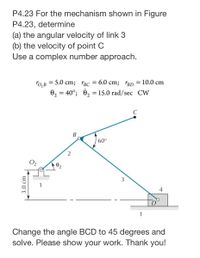
Transcribed Image Text:P4.23 For the mechanism shown in Figure
P4.23, determine
(a) the angular velocity of link 3
(b) the velocity of point C
Use a complex number approach.
Го, в — 5.0 cm; "вс — 6.0 сm; rBD 3D 10.0 cm
02 = 40°; 0, = 15.0 rad/sec CW
%3D
60°
2
3
1
4
1
Change the angle BCD to 45 degrees and
solve. Please show your work. Thank you!
3.0 cm
B.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you explain how this can be solved please. Thanks!arrow_forwardQ3/ For the crank- connecting rod mechanism shown: OA= 10cm , AB= 30 cm, AC= 10 cm, it's single degree of freedom coordinate is e. If angular velocity of OA=30 rad/sec. Find angular velocity AB at e = (30)° crank angle. A C 8.7 rad/sec O23 rad/sec O 16.3 rad/secarrow_forward((I need to solve all parts please)) For the non-offset slider crank shown in the figure below the crank O2A is rotating at constant speed of 10 rad/s CCW O2A = 70 cm, AB = 210 cm, AG3 = 100 cm. When the slider B is at its minimum position, we need to find : W2 G3 3 B 4 2 7777 The angular velocity of AB in rad/s is = Choose... + The velocity of slider B in m/s is = Choose... + The angular acceleration of AB in rad/s2 is = Choose... * The acceleration of slider B in m/s? is = Choose... + The velocity of point A in m/s (in cartesian form) is = Choose... + The acceleration of point A in m/s² (in cartesian form) is = Choose... The velocity of point G3 in m/s (in cartesian form) is = Choose... + The acceleration of point G3 in m/s² (in cartesian form) is = Choose... +arrow_forward
- 1. Suppose a link that is held in a ball joint (spherical pair) at one end rotates with an instantaneous angular velocity. w = - i+j5 - k3 (rad/s) Find the instantaneous velocity of P, a point on the link defined by the radius vector r= 14 - j - k7 (mm).arrow_forwardFind out the velocity of slider D and angular velocity of CD in the mechanism shown below. Take Q1A= Q2B = 2cm; Q1Q2 = 4 cm; CD = 6 cm and wQ,A rad = 1 sec Solve using instantaneous center method. Use CCW direction. 20 QI 1 A Q2 20arrow_forwardPls i need her solve with explanationarrow_forward
- topic:kinematics of rigid bodiesarrow_forwardSolve it using complex algebra; otherwise, do not solve it. Calculate the rotational speed. theta 3' prime, and acceleration, theta 3" double prime for the mechanism in Fie 3 if theta3-50. roa=5cm and Rab= 15cm. using complex algebra method Subject: Theory of machine and mechanismarrow_forward1 of 1 3. A four-bar linkage is shown below. (A) the directions of each. (B) E on link 3. Use the method of velocity vector polygons to calculate w, and wq. Report Find and report the magnitude and direction of the absolute velocity of point RAD = 10 cm, Rap = 15 cm, Ra = 60 cm; R = 65 cm; Rp = 15 cm W2 = 2 rad/s cw (Note: ADB and FEC are right triangles.) link 3 A. link 2arrow_forward
- A four-bar mechanism is used to transmit power to slider E. Link AC rotates counterclockwise at 100 rpm. A and B are fixed points. The following linkages are measured in cm: AC=35, AB=70, CD=45, BD=45, DE=40. Find the instantaneous velocity of slider E in cm/s 1.Draw the mechanism in appropriate scale on your paper2. Find the instantaneous linear velocity of C3. Find a point on your paper to draw the velocity polygon and scale the magnitude of the computed linearvelocity4. Use the relative velocity equation for finding the linearvelocity of D; ? = ? + ?? ? ?/?5. Remember that although the magnitudes are unknown, their directions can be identified6. Obtain the magnitudes of the unknown velocities from the velocity polygon7. For Link DE, repeat the process by using ? = ? + ??the line as much as needed8. Remember that E is a SLIDER therefore it can only goin the direction where its movement is not constrained? . Add the vector ? to the head of ? and extend?/? ?/??arrow_forwardGiven: A shaft rotates about a fixed vertical axis at a constant rate of f, as shown below. A straight bar OA, having a length of L, is pinned to point O on the shaft, with O being on the rotation axis of the shaft. At the instant when 80, bar OA is being raised at a rate of 6 from the horizontal plane, with this rate changing at a rate of . A set of ryz coordinate axes is attached to bar OA with its origin at O. A second set of coordinate axes, XYZ, are fixed to ground. At the instant when = 0, the zyz and XYZ axes are aligned with each other. Find: For the instant when -0°, determine the angular velocity and angular acceleration of har OA. vertical shaft bearing O 8 X bar Use the following parameters in your analysis: f2=5 rad/s, é = 4 rad/s, 6-3 rad/s² and L=2 m.arrow_forwardrad The rod OA rotates clockwise at a constant angular velocity of 0 = (3) Two pin-connected slider block, located at B, move freely on OA. The curved rod is described by the equation r (300 (3-cos)) m. Hint: 1. Remember clockwise rotation is negative velocity. OA Variable 0₁ d₁ d₂ d3 0₁ d2 d3 Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Value 110 degrees 0.45 m 0.1 m 0.275 m Using cylindrical components, a. Determine the cylinders's radial and transverse components of velocity at the instant shown, u, and vg. b. Determine the cylinders's radial and transverse components of acceleration at the instant shown, ar and ag. c. Determine the cylinder's magnitude of the velocity at the instant shown, ·M. d. Determine the cylinder's magnitude of the acceleration at the instant shown, |a1. Round your final answers to 3 significant digits/figures. 7= fr + a= M-C Hr+ m S M 82 He) Fe) m S marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY