
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305632134
Author: J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
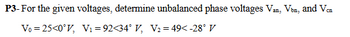
Transcribed Image Text:P3-For the given voltages, determine unbalanced phase voltages Van, Von, and Vcn
V₁ =25<0°V, V₁ =92<34° V, V2=49<-28° V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Impedances Z2 and Z3 in parallel are in series with impedance Z1 across a 100 V, 50 Hz ac supply. Z1 =6.25 + j1.25 ohm; Z2 = 5+ j0 ohm and Z3 = 5-jXc ohm. Determine the value of capacitance of Xc such that the total curent of the circuit will be in phase with the total voltage. When is then the circuit current and power.arrow_forwardcan you doing this with detail explaination..thank you!arrow_forwardTask 3 A three phase, four wire star connected load consisting of: ZR: a resistor of 9500 in series with a 3H inductor ZB: a resistor of 1950 ZY: a resistor of 1950 in series with a 4µF capacitor Using the equipment available in the power lab (Room T017), connect the given load to a three-phase supply available in the lab and: 3.1. Determine the current of each line and the neutral current and measure the total power supplied by the source. 3.2. Analytically, calculate all currents and the total power and compare with those obtained in measurements. 3.3. Device a method and measure the waveform of the neutral current. Discuss the obtained waveform and the reason for any distortion in the waveform 3.4. Validate your calculations using computer simulationarrow_forward
- I need handwritten only otherwise i will dislike for sure and both parts otherwise skip I'll dislikearrow_forwardI dont understand phase shift and lags?arrow_forwardTwo impedances Z₁ and Z2 are connected in series to a voltage source with voltage Vs volts. Let V₁ be the voltage across Z₁ and V₂ be the voltage across Z2. Then, the total voltage Vs is divided between V₁ and V2 in proportion to impedance values Z₁ and Z2. O a. True O b. Falsearrow_forward
- HW3.pptx Problem 9. Consider the circuit shown in the figure below. Find the phasors a) Vs b) I c) V₁ d) VR e) V th%26view_start%... Download A Alternati Page< 9 of 10 f) Compare the peak value of v₁(t) with the peak value of v(t). Do you find the answer surprising? Explain. + UL 0000 50 mH v₁(t) = 10 cos(104) 1 High pollen Tomorrow + VC 0.2 μF 100 Ω UR amazon Q Search W 2000arrow_forward60. An RLC series circuit connected to a 110-volt and 50-cycle AC source, contains the following series resistances and reactances: R1=10 ohm, R2= 15, XL1=20 ohms, XL2=25 ohms, XC= 40 ohms. Find the real power. a. 65.3899 b. 392.4372 c. 397.848 d. 588.6559arrow_forwardNOTE: Polar form for Voltage & Current. Rectangular form for Impedance Find the total impedance of the circuit, total power (apparent) delivered by the current source, Draw the phasor diagram of the voltage and current at the source, the current passing through the R2 and L1 branch, Draw the phasor diagram of the voltage and current at the R2 and L1 branch. Also, is the circuit inductive, capacitive, or neither (resistive)?arrow_forward
- The instantaneous power absorbed by the load in a single-phase ac circuit, for a general R LC load under sinusoidal-steady-state excitation. is (a) Nonzero constant (b) Zero (c) Containing double-frequency componentsarrow_forwardLet a 100V sinusoidal source be connected to a series combination of a 3 resistor, an 8 inductor, and a 4 capacitor. (a) Draw the circuit diagram. (b) Compute the series impedance. (C) Determine the current I delivered by the source. Is the current lagging or leading the source voltage? What is the power factor of this circuit?arrow_forwardFor the phasor diagram in figure 6 express the voltages in sinusoids for a period of 5ms. Im Re )e,=45° e,=20 Vz=10 V2=8 Figure 7 a. Va(t)=. b. V2(t)=. c. What is the rms voltage of V1 = d. What is the rms voltage of V2=_ e. What is the frequency in Hz = f. What is the angular frequency =. In terms of lagging and leading what is the exact phase relationship between V, (t) and V2(t) g.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:Cengage Learning