
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
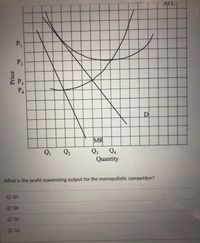
Transcribed Image Text:ATC
P1
P2
P3
P4
MR
Q4
Q3
Quantity
Qi
Q2
What is the profit maximizing output for the monopolistic competitor?
O Q3
O Q4
OQ1
O Q2
Price
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If this is a market for a monopolistically competitive firm selling hair products. Choose all that apply. A It will lose $20 per day if it stays in the market B It will charge a price of $4 C If it stays in the market, there will still be a dead weight loss D Its profit maximizing quantity is 30 unitsarrow_forwardAssuming that the monopolistic competitor faces the demand and costs depicted below and finds the profit maximizing level of output, what will be the firm's revenue? 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 Select one: a. $64 b. $80 c. $120 MC1 d. $0 because the firm will shut down ATC₁ AVC1 MR1 D₁ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 хоarrow_forwardif a monopolistic firm takes over a perfectly competaive market we would expect to see market price of the goof to fall because demand is perfectly eleastic rise and quantity is sold fall as the monopolist tries to increase sales rise and the quantity sold to increasearrow_forward
- A firm in a monopolistically competitive market has a monopoly power because: O There are very few other sellers in the market. There are many firms selling similar products. The firm is not concerned with entry of new firms. The firm's product is differentiated. ◄ Previous MAY 4 Next Not saved Submit tvarrow_forwardPrice and cost per unit MC X P3 P₂ Demand MR 0 Q₁ Q3 Q4 According to the figure above, what is the monopolistic competitor's profit-maximizing output? Q* P₁ Q3 units Q2 units Q4 units Q1 units ATC Quantityarrow_forwardThe diagram below describes a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. On the diagram illustrate. a. The quantity of output, qo , that maximizes profit. b. The quantity of output, qfe , that would represent the firm’s full capacity. c. The quantity of output, qs , that would represent the socially optimal output level.arrow_forward
- A monopolistic competitor has the following information about cost and demand. Price ($) Marginal Revenue ($) Total Cost ($) Marginal Cost ($) Quantity Total Revenue Average Cost($) ($) 15 15 175 14 70 13 180 1 36 10 13 130 11 190 19 15 12 180 207 3.4 13.8 20 11 220 7 225 3.6 11.25 25 10 250 5 250 10 30 270 3 290 8. 9.67 35 8 280 335 9.57 40 7 280 -1 385 10 9.63 45 6. 270 -3 465 16 10.33 50 5 250 565 20 11.3 What will this firm's profits equal in the long run? -$55 $0 $250 $280arrow_forwardWhat is the relationship between product differentiation and monopolistic competition?arrow_forwardIn a market where firms are monopolistically competitive: Group of answer choices There is one firm that produces a standardized product. There are few firms, each producing a very differentiated product. There are market participants who are all price takers. There are many firms producing a differentiated product.arrow_forward
- A monopolistically competitive firm maximizes profits when it اختر احد الخيارات a. produces the quantity at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue and sets the price equal to the marginal cost b. produces the quantity at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue and uses the demand curve to determine the market price o .c. produces the quantity at which marginal cost equals the market price d. produces the quantity at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue and sets the price equal to the marginal revenuearrow_forwardWhat does it mean in a monopolistically competitive market, when the rule for maximizing profit is to set MR = MC? Group of answer choices Price is equal to marginal revenue. Price is equal to marginal cost. Price is lower than marginal revenue. Price is higher than marginal revenue.arrow_forwardIf this monopolistic firm's marginal cost is constant at $30, its profit maximizing output is: (Hint: Demand is linear (P-a-bQ) implying that the MR curve's slope is twice the demand curve slope; find the demand curve and then the MR curve.) Price $70 $50 $30 $10 10 20 30 40 50 units. 40 units. 20 units. 30 units. Demand 50 60 70 Quantityarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education