
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
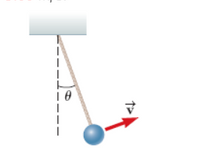
One end of a cord is fixed and a small 0.250-kg object is attached to the other end, where it swings in a section of a vertical circle of radius 3.00 m, as shown in the figure below. When ? = 21.0°,the speed of the object is 5.00 m/s.
(a) At this instant, find the magnitude of the tension in the string.
N
(b) At this instant, find the tangential and radial components of acceleration.
|
at =
|
m/s2 downward tangent to the circle |
|
ac =
|
m/s2 inward |
(c) At this instant, find the total acceleration.
inward =
and
below the cord at = °
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A Ferris wheel has a diameter of 10.0m and makes one revolution in 8.00 seconds. A girl weighing 321 N is sitting on one of the benches attached at the rim of the wheel. What is the force exerted on her by the bench as she passes through the lowest point of her motion?arrow_forwardA car traveling on a flat (unbanked), circular track accelerates uniformly from rest with a tangential acceleration of 1.75 m/s. The car makes it one quarter of the way around the circle before it skids off the track. From these data, determine the coefficient of static friction between the car and track. 0.56 You appear to have forgotten that the static force of friction is also responsible for the tangential acceleration of the car.arrow_forwardOne end of a cord is fixed and a small 0.500-kg object is attached to theother end, where it swings in a section of a vertical circle of radius 2.00 m as shown. When θ = 20.0°, the speed of the object is 8.00 m/s. At this instant, find (a) the tension in the string, (b) the tangential and radial components of acceleration, and (c) the total acceleration. (d) Is your answer changed if the object is swinging down toward its lowest point instead of swinging up? (e) Explain your answer to part (d).arrow_forward
- The figure shows a conical pendulum, in which the bob (the small object at the lower end of the cord) moves in a horizontal circle at constant speed. (The cord sweeps out a cone as the bob rotates.) The bob has a mass of 0.025 kg, the string has length L = 1.2 m and negligible mass, and the bob follows a circular path of circumference 0.69 m. What are (a) the tension in the string and (b) the period of the motion? Сord L. Bob (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA roller coaster loaded with passengers has a mass of 2 x 10³ kg; the radius of curvature of the track at the lowest point of the track is 24 m. If the vehicle has a tangential speed of 18 m/s at this point, what force is exerted on the vehicle by the track? O 9.33 x 10^4 N O 1.91 x 10^4 N O 5.27 x 10^4 N O 4.66 x 10^4 Narrow_forwardA child is holding a string with a ball tied at the end. The child spins around in a circle causing the ball to travel in uniform circular motion. While doing this, the 1.3 m long string makes a 48.8◦ angle below horizontal. What is the tangential speed of the ball?arrow_forward
- A Ferris wheel has radius of 4.8 m and makes one revolution in 7.4 seconds. A person weighing 686 N is sitting on one of the benches attached at the rim of the wheel. What is the apparent weight (that is, the normal force exerted on her by the bench) of the person as she passes through the highest point of her motion?arrow_forwardA 30 kg child slides down a slide with h = 4.0 m and arrives at the ground with a speed of 6.0 m/s. The slide forms the arc of a circle with a radius of 21 m with the ground tangent to the bottom of the slide. Determine the average friction force acting on the child. Hint: Use h = R(1 - cos(θ)) and s = Rθ where θ is in radians and s = arc length.arrow_forwardA planet orbits a star, in a year of length 4.46 x 107 s, in a nearly circular orbit of radius 2.46 x 1011 m. With respect to the star, determine (a) the angular speed of the planet, (b) the tangential speed of the planet, and (c) the magnitude of the planet's centripetal acceleration.arrow_forward
- A 50.0-kg child stands at the rim of a merry-go-round of radius 2.90 m, rotating with an angular speed of 3.65 rad/s. (a) What is the child's centripetal acceleration? m/s2(b) What is the minimum force between her feet and the floor of the carousel that is required to keep her in the circular path? N(c) What minimum coefficient of static friction is required?Is the answer you found reasonable? In other words, is she likely to stay on the merry-go-round?arrow_forwardOne end of a cord is fixed and a small 0.700-kg object is attached to the other end, where it swings in a section of a vertical circle of radius 2.50 m, as shown in the figure below. When 8 = 30.0°, the speed of the object is 8.50 m/s. (a) At this instant, find the magnitude of the tension in the string. N (b) At this instant, find the tangential and radial components of acceleration. at = m/s² downward tangent to the circle m/s² inward a = (c) At this instant, find the total acceleration. inward and below the cord at (d) Is your answer changed if the object is swinging down toward its lowest point instead of swinging up? O Yes O No (e) Explain your answer to part (d).arrow_forwardPls answer all of it and box the answers thank youarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON