
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
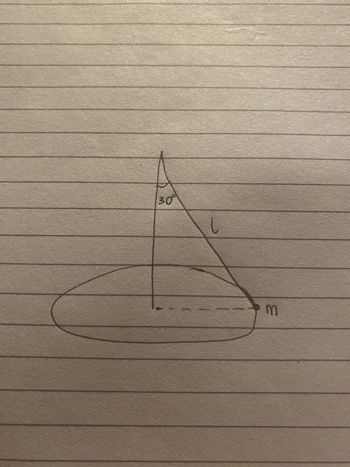
A ball of mass 0.320 kg is attached to one end of a light inextensible string of length 0.600 m, whose other end is attached to a fixed pivot. The ball performs uniform circular motion in a horizontal plane, with the string making an angle of 30.0° with the vertical.
What is the angular speed of this circular motion?
Transcribed Image Text:30°
1
m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A professor sits on a rotating stool that is spinning at 10.0 rpm while she holds a heavy weight in each of her hands. Her outstretched hands are 0.795 m from the axis of rotation, which passes through her head into the center of the stool. When she symmetrically pulls the weights in closer to her body, her angular speed increases to 20.5 rpm. Neglecting the mass of the professor, how far are the weights from the rotational axis after she pulls her arms in?arrow_forwardA horizontal platform in the shape of a circular disk rotates on a frictionless bearing about a vertical axle through the center of the disk. The platform has a radius of 2.36 m and a rotational inertia of 218 kg-m2 about the axis of rotation. A 72.6 kg student walks slowly from the rim of the platform toward the center. If the angular speed of the system is 2.07 rad/s when the student starts at the rim, what is the angular speed when she is 0.433 m from the center? Number i Unitsarrow_forwardJohn wanted to measure the objects angular speed at the bottom of the hill. He built the inclined frictionless ramp of height d, release the object from the top, and measure the angular speed at the Bottom. First, John released a hollow sphere [Ip(2/3) mr^2] from the rest. The diameter and the mass of the sphere were 317 cm and 45.2 kg, respectively. How much was the angular speed John measures at the bottom of the incline he built. Tip: the object rotates down the incline without slipping. Use following values: d=3.57 m and g=9.80 m/s^2arrow_forward
- In testing an automobile tire for proper alignment, a technician marks a spot on the tire 0.230 m from the center. He then mounts the tire in a vertical plane and notes that the radius vector to the spot is at an angle of 33.0° with the horizontal. Starting from rest, the tire is spun rapidly with a constant angular acceleration of 1.60 rad/s2.(Assume the spot's position is initially positive, and assume the angular acceleration is in the positive direction.) (a) What is the angular speed of the wheel after 1.20 s? rad/s (b) What is the tangential speed of the spot after 1.20 s? m/s (c) What is the magnitude of the total acceleration of the spot after 1.20 s? m/s2 (d) What is the angular position of the spot after 1.20 s?arrow_forwardA solid disk of uniform density and mass M = 0.950 kg with radius R = 0.250 m is suspended vertically and is free to rotate about its center without friction. A point object that has the same mass as the disk is placed at an angle 0 = 25.0° clockwise from the top along the rim, causing the disk to rotate. The acceleration due to gravity is g=9.81m/s². What is the angular speed wf of the disk when the point object is directly below the center of the disk? R 0.arrow_forwardA 5 kg ball with a 0.4 meter radius is rolling on a horizontal surface at 3 m/s. The rotational inertia of the ball is 0.4mr2. The ball rolls up a 30-degree inclined plane. What is the maximum height that the ball reaches?arrow_forward
- Two girls (26 kg each) are standing on the edge of a solid, rotating disk of mass 70 kg and radius 1.3m. The initial angular speed of the disk is 0.71 rev/s. If one of the girls moves slowly toward the center while the other stays put at the edge, what is the new angular speed of the disk when she reaches the halfway point?arrow_forwardA small 0.360-kg object moves on a frictionless horizontal table in a circular path of radius 3.00 m. The angular speed is 4.97 rad/s. The object is attached to a string of negligible mass that passes through a small hole in the table at the center of the circle. Someone under the table begins to pull the string downward to make the circle smaller. If the string will tolerate a tension of no more than 160 N, what is the radius of the smallest possible circle on which the object can move?arrow_forwardA Texas cockroach walks from the center of a circular disk (that rotates like a merry-go-round without external torques) out to the edge at radius R. The angular speed of the cockroach–disk system for the walk is (va = 5.0 rad/s and vb = 6.0 rad/s). After reaching R, what fraction of the rotational inertia of the disk does the cockroach have?arrow_forward
- A spinning globe is slowed at a constant acceleration of 0.750 rad/s2 until it stops. One of the points on the equator moves 23.0° in the first 0.700 s of the slowing phase. (a) Find the total angular displacement of the globe during the acceleration phase. (b) Find the initial angular speed of the globe.arrow_forwardPoint A of the circular disk is at the angular position 0 = 0 at time t = 0. The disk has angular velocity wo = 0.29 rad/s at t = 0 and subsequently experiences an angular acceleration a = 1.8t where t is in seconds, and a is in radians per second squared. Determine the velocity and acceleration of point A in terms of fixed i and j unit vectors at time t = 2.7 s. Assumer = 145 mm. α Answers: VA = aд = 90 (i ( i 0 6.806 i + i + i i 1 0.705 j) m/s j) m/s²arrow_forwardA cylinder has a cone removed from it. The cylinder and the conical hole have the same radius (2.06 meters) and height (4.56 meters). The cylinder has a density of 447 kg/m3. What is the rotational inertia of the cylinder with the cone removed in kg m2? You can set your origin at the tip of the cone, which is also the center of the base of the cylinder.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON