
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
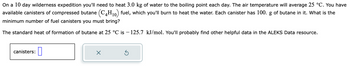
Transcribed Image Text:On a 10 day wilderness expedition you'll need to heat 3.0 kg of water to the boiling point each day. The air temperature will average 25 °C. You have
available canisters of compressed butane (C4H₁0) fuel, which you'll burn to heat the water. Each canister has 100. g of butane in it. What is the
minimum number of fuel canisters you must bring?
The standard heat of formation of butane at 25 °C is −125.7 kJ/mol. You'll probably find other helpful data in the ALEKS Data resource.
canisters:
0
X
Ś
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- On a 7 day wilderness expedition you'll need to heat 2.0 kg of water to the boiling point each day. The air temperature will average 25 °C. You have available canisters of compressed propane (C,H) fuel, which you'll burn to heat the water. Each canister has 25. g of propane in it. What is the minimum number of fuel canisters you must bring? The standard heat of formation of propane at 25 °C is – 103.85 kJ/mol. You'll probably find other helpful data in the ALEKS Data resource. canisters:arrow_forwardTHERMODYNAMICS: A 1.09 g sample of acetic acid (HC2H2O2) was burned in excess oxygen in a bomb calorimeter. The calorimeter, which alone had a heat capacity of 2.67 KJ°C. contained 7g of water. The temperature of the calorimeter and its contents increased from 24.13°C to 27.95°C. What is AH (in kJ) for the combustion per 1.00 mol of acetic acid? MW of acetic acid is 60 gimol. (Round off the final answer to ONE decimal place. Do not include the unit.)arrow_forwardPart B 2.0000 g of the unknown compound is burned in a bomb calorimeter. During the combustion, the temperature of the calorimeter increases from 23.125°C to 28.997 °C. During calibration, the heat capacity of the calorimeter was found to be 9.9897kJ °C-1. In the previous experiment, the molar mass of the substance was found to be 148.16 gmol-1. What is AcombU for the unknown compound? να ΑΣφ ? kJ mol1 Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- Please dont provide hand written solutionarrow_forwardA quantity of 2.00×102 mL of 0.786 M HCl is mixed with 2.00×102 mL of 0.393 M Ba(OH)2 in a constant-pressure calorimeter of negligible heat capacity. The initial temperature of the HCl and Ba(OH)2 solutions is the same at 20.76°C. For the process below, the heat of neutralization is −56.2 kJ/mol. What is the final temperature of the mixed solutions? H+(aq) + OH−(aq)→H2O(l) _____°Carrow_forwardIn Part B of the experiment, a student mixes 30.0 mL of 1.1 M HC1(aq) with 30.0 mL of 1.000 M NaOH(aq) in a well-insultated calorimeter and observes that the temperature of the solution increases by 5.75 °C. These are similar conditions as the previous two problems. How many moles of water are formed? number of moles of water = molarrow_forward
- A 100.0-mL sample of 1.0 M NaOH is mixed with 50.0 mL of 1.0 M H2SO4 in a large Styrofoam coffee cup; the cup is fitted with a lid through which a calibrated thermometer passes. The temperature of both solutions before mixing is 22.3 °C. After the NaOH solution is added to the coffee cup and the mixed solutions are stirred with the thermometer, the maximum temperature measured is 31.4 °C. Assume that the density of the mixed solution is 1.00 g/mL, the specific heat of the mixed solutions is 4.18 J/g•°C, and no heat is lost to the surroundings.(a) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction that takes place.(b) Is there any unreacted NaOH or H2SO4 remaining after the reaction?(c) Calculate the enthalpy change per mole of H2SO4 in the reaction.arrow_forwardAt constant volume, the heat of combustion of a particular compound is -3916.0 kJ/mol. When 1.329 g of this compound (molar mass = 166.62 g/mol) was burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter, including its contents, rose by 7.549 "C. What is the heat capacity (calorimeter constant) of the calorimeter? calorimeter constant: kJ/ "Carrow_forward1. Methanol CH3OH is a potential source of fuel. An experiment was conducted to determine the enthalpy of combustion of methanol. 2.00 g of methanol was used to heat 150 g of water. The temperature of the water increased from 25°C to 87 °C. (Given that the specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J K-1 g-1) Define the term standard enthalpy of combustion with reference to methanol. Use the data above to determine the enthalpy of combustion of methanol (show solutions). 2. Calculate the e.m.f of the following cell in the image (show solutions).arrow_forward
- On a 14 day wilderness expedition you'll need to heat 3.0 kg of water to the boiling point each day. The air temperature will average 25 °C. You have available canisters of compressed propane (C₂Hg) fuel, which you'll burn to heat the water. Each canister has 50. g of propane in it. What is the minimum number of fuel canisters you must bring? The standard heat of formation of propane at 25 °C is -103.8 kJ/mol. You'll probably find other helpful data in the ALEKS Data resource. canisters: 0 X Śarrow_forwardThe heat of combustion of ethanol, C2HOH(1), is-1367 kJ/mol. A batch of sauvignon blanc wine contains 12.1 % ethanol by mass. Part A You may want to reference (Pages 191 - 192) Section 5.8 while completing this problem. Assuming the density of the wine to be 1.0 g/mL, what is the caloric content due to the alcohol (ethanol) in a 6-oz glass of wine (177 mL)? Express your answer using two significant figures. ΑΣΦ Cal Submit Request Answer < Return to Assignment Provide Feedback Esc DII F1 F2 F3 F4 PrtScn Home End F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 IIarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY