
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
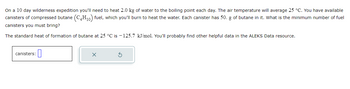
Transcribed Image Text:On a 10 day wilderness expedition you'll need to heat 2.0 kg of water to the boiling point each day. The air temperature will average 25 °C. You have available
canisters of compressed butane (C4H₁0) fuel, which you'll burn to heat the water. Each canister has 50. g of butane in it. What is the minimum number of fuel
canisters you must bring?
The standard heat of formation of butane at 25 °C is -125.7 kJ/mol. You'll probably find other helpful data in the ALEKS Data resource.
canisters:
0
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In this experiment you will place a sample of your salt in water in a constant pressure calorimeter. You will determine the enthalpy change for the dissociation of your salt, Delta Hdiss. A sample of 4.368 grams of the salt SrCl2 was placed in 35.5 g water, the initial temperature was 20.00℃ and the final temperature was 27.086365℃. What is the number of moles of SrCl2? 4.368 g SrCl2 x ( 1 mol SrCl2 / 123.073 g SrCl2 ) = 0.035491131 mol SrCl2 a. 0.035491 mol SrCl2 b. none of these c. 0.035 mol SrCl2 d. 0.03 mol SrCl2 e. 0.0355 mol SrCl2 f. 0.04 mol SrCl2 g. 0.035491131 mol SrCl2 h. 0.03549 mol SrCl2arrow_forwardFructose, C6H12O6(s), is a sugar closely related to glucose. A 0.755 g sample of fructose was combusted with excess oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, containing 500.0 g of water. The heat capacity of the empty calorimeter was 208 J/K. The temperature of the calorimeter and the water rose from 22.00°C to 27.12°C due to the combustion reaction, which formed CO₂(g) and liquid water. What is the energy change, AU (in kJ), for the combustion of one mole of fructose under these conditions? O +254 O-15600 -2810 +520 -804arrow_forwardA quantity of 2.00×102 mL of 0.786 M HCl is mixed with 2.00×102 mL of 0.393 M Ba(OH)2 in a constant-pressure calorimeter of negligible heat capacity. The initial temperature of the HCl and Ba(OH)2 solutions is the same at 20.76°C. For the process below, the heat of neutralization is −56.2 kJ/mol. What is the final temperature of the mixed solutions? H+(aq) + OH−(aq)→H2O(l) _____°Carrow_forward
- When a 4.31 g sample of liquid octane (C8H18) is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter rises by 27.3 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter, measured in a separate experiment, is 6.2 kJ/•C. The calorimeter also contains 3.00 kg of water, specific heat capacity of 4.18 J/g°C. Determine the heat of combustion of octane in units of kJ/mol octane. Enter your answer numerically and in terms of kJ/mol.arrow_forwardAt constant volume, the heat of combustion of a particular compound is -3916.0 kJ/mol. When 1.329 g of this compound (molar mass = 166.62 g/mol) was burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter, including its contents, rose by 7.549 "C. What is the heat capacity (calorimeter constant) of the calorimeter? calorimeter constant: kJ/ "Carrow_forwardFructose, C6H12O6(s), is a sugar closely related to glucose.. A 0.755 g sample of fructose was combusted with excess oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, containing 500.0 g of water. The heat capacity of the empty calorimeter was 208 J/K. The temperature of the calorimeter and the water rose from 22.00°C to 27.12°C due to the combustion reaction, which formed CO2(g) and liquid water. What is the energy change, AU (in kJ), for the combustion of one mole of fructose under these conditions? -15600 -2810 +520 +254 -804arrow_forward
- If we measure the heat change (q) of everything in a system except the calorimeter, we can use the first law of thermodynamics (∆Euniverse = 0) to calculate the heat change of the calorimeter (qcal). In this reaction, we combine 5.85 g of 63.7 ºC water with 6.63 g of 18.9 ºC water in a calorimeter. Since some of the heat is absorbed by the calorimeter, the final temperature of the water is 28.8ºC. Since the hot and cold water are combined, the final temp of the water is the final temp for the hot water and the cold water. Calculate the heat change of the calorimeter in J. Remember that all of the heat changes must add up to zero so you can calculate the heat change of the hot water (qhotwater) and the heat change of the cold water (qcoldwater) using for each where Cs = 4.186 J/gºC. The first law of thermodynamics tells us that all of these changes sum up to zero so Enter your answer to one decimal place (tenths)arrow_forward1.) The molar heat of combustion of octane to form carbon dioxide and water vapour is ─5470.1kJ/mol. Using this value, determine the mass of octane required to increase the temperature of 1.50 L of water from 22.0°C to 85.6°C. 2.) A simple calorimeter is filled with 250g of water initially at 25.0°C. A mass of 0.500g of benzene is completely burned to heat the water in the calorimeter. The highest temperature of the calorimeter water is measured at 44.0°C. What is the experimental value of the molar enthalpy of combustion of benzene?arrow_forwardOn a 14 day wilderness expedition you'll need to heat 3.0 kg of water to the boiling point each day. The air temperature will average 25 °C. You have available canisters of compressed propane (C₂Hg) fuel, which you'll burn to heat the water. Each canister has 50. g of propane in it. What is the minimum number of fuel canisters you must bring? The standard heat of formation of propane at 25 °C is -103.8 kJ/mol. You'll probably find other helpful data in the ALEKS Data resource. canisters: 0 X Śarrow_forward
- Many barbeque grills use propane gas, C3H8(g) as a fuel source. Using standard enthalpies of formation, calculate the quantity of heat produced, in kJ, when 25 liters of liquid propane is completely combusted in air. (The density of liquid propane is 582 kg/m3.) Note: The propane is in the condensed liquid state in the tank but changes to the gas phase as it is released. Calculate the change in enthalpy for the reaction assuming all reactants and products are in the gas phase.arrow_forwardA 25.0 mL portion of dilute HCl (aq) is combined with a 25.0 mL portion of dilute NaOH in a coffee-cup calorimeter. Both solutions are initially at a temperature of 23.3 ºC. The reaction produces enough heat to raise the final temperature of the 50.0 mL of liquid in the calorimeter to 25.3 ºC . What is qrxn in J? Assume the density of the reaction mixture is 1.0 g/mL and the specific heat of the solution is 4.184 J/g· ºCarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY