
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:O Attempt 3
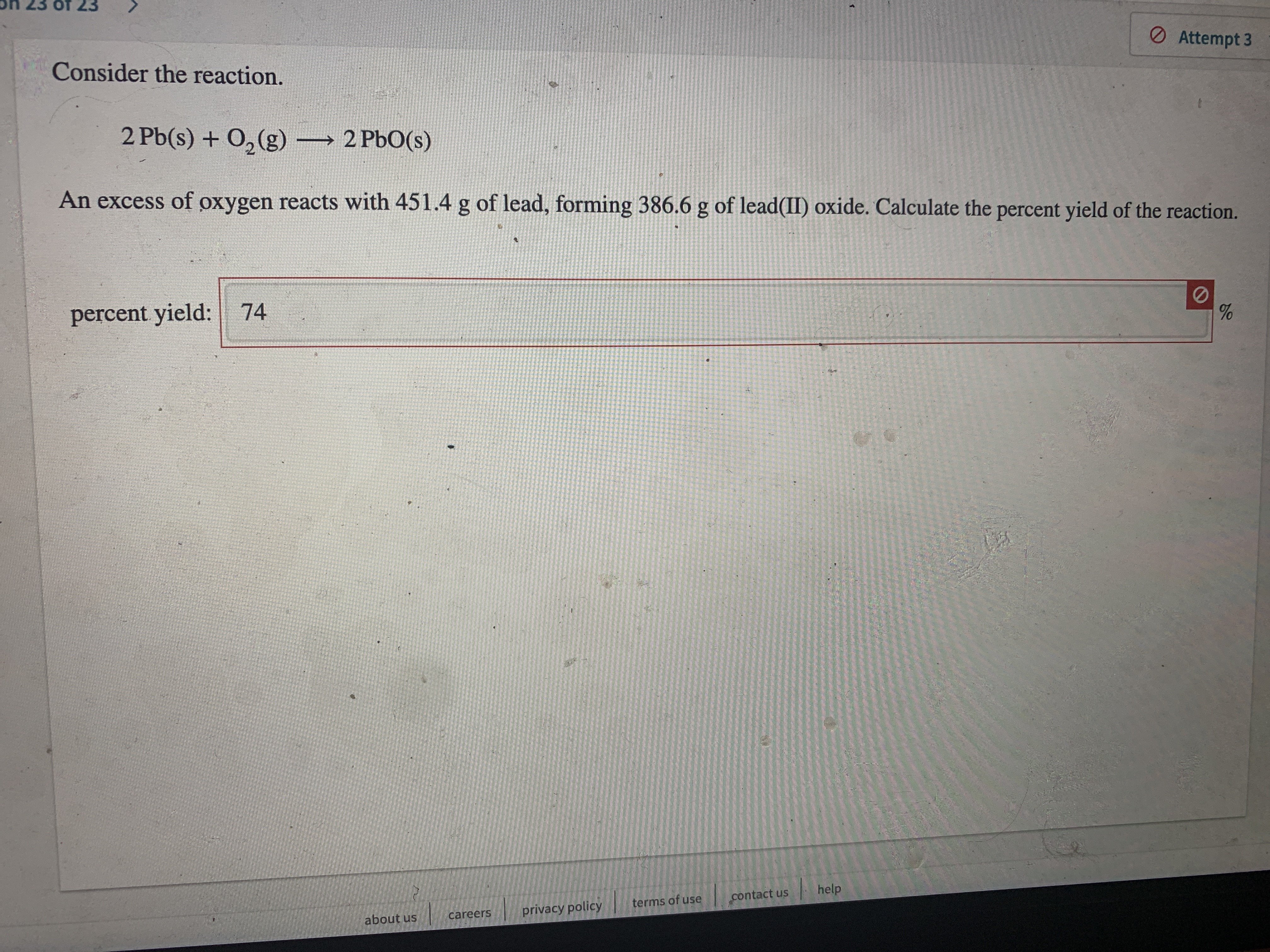
Consider the reaction.
2 Pb(s) + O, (g) 2 PbO(s)
→ 2
An excess of oxygen reacts with 451.4 g of lead, forming 386.6 g of lead(II) oxide. Calculate the percent yield of the reaction.
percent yield: 74
contact us
help
terms of use
careers
privacy policy
about us
Transcribed Image Text:Check Answer
estion 21 of 23 >
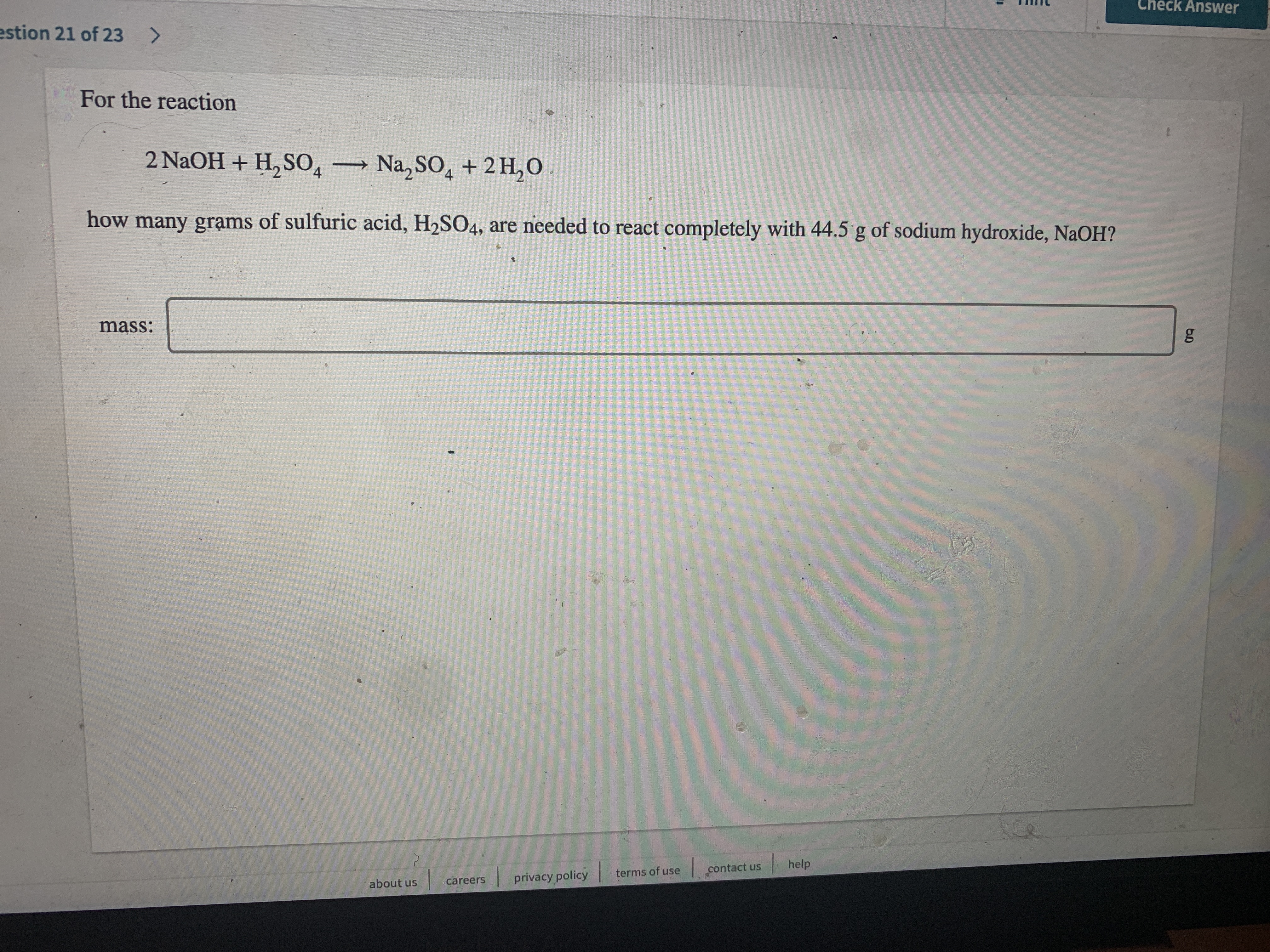
For the reaction
2 NaOH + H, S0, Na, SO, + 2 H,O
how many grạms of sulfuric acid, H2SO4, are needed to react completely with 44.5 g of sodium hydroxide, NaOH?
mass:
help
terms of use
contact us
careers
privacy policy
about us
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- For the following reaction, 6.37 grams of phosphoric acid are mixed with excess potassium hydroxide. The reaction yields 11.3 grams of potassium phosphate. potassium hydroxide (aq) + phosphoric acid (aq) →potassium phosphate (aq) + water (I) What is the theoretical yield of potassium phosphate ? grams What is the percent yield of potassium phosphate ? % Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 4 more group attempts remainingarrow_forwardA kf1.amplifire.c SAM P Pearson Learning: Ch 03R: Chemical Reactions and Chemical Quantities QUESTION Stoichiometry is a term chemists use to describe calculations that determine the relative quantities of reactants or products involved in a chemical reaction. Using stoichiometry, chemists can determine the amount of product that can be formed during a chemical reaction from a given amount of reactant. Chemists can also determine the amount of reactant needed to produce a desired amount of product using the same process. Select the missing conversion factor for the following set of calculations. Assume 171 grams of diborane, B,H¸, reacts with excess oxygen, O̟. The problem requires that you determine the mass of boron oxide, B_O¸, formed from this reaction. B,H (9) * 3 O,(9) → B,0 (s) + 3 H,O(I) 1mol B,03 x 27.68 g B,H, 1mol B,H, 1mol B,H, 171g B,H,x. = 4.30 × 10² g B,0, support © 2021 Knowledge Factor, Inc. All rights reserved. МacBook.arrow_forwardQuestion 86 of 97 According to the balanced reaction below, calculate the moles of NH; gas that form when 4.2 mol of N2H. liquid completely reacts: 3 N2H.(0)→ 4 NH3(g) + N2(g) STARTING AMOUNT ADD FACTOR ANSWER RESET *( ) 4.2 28.02 5.6 17.04 16.8 3.2 32.06 6.022 x 10 mol NH3 mol N2H4 g N2 g NH3 g N2H4 mol N2 MacBook Airarrow_forward
- Magnesium burns in air with a dazzling brilliance to produce magnesium oxide: 2Mg (s) + O2 (g) → 2M9O (s) When 4.00 g of magnesium burms, the theoretical yield of magnesium oxide is g. A) 4.00 B) 6.63 C) 0.165 D) 3.32 E) 13.3 A Darrow_forwardConsider the formation of disodium oxide shown below: 4Na(s) + O₂(g) → 2Na₂O(s) If you want to produce 18.48 moles of Na₂O, how much of each reactant must you start with? Na: Write your response here.. 0 moles Please type your answer to submit O₂ ice your response here... molesarrow_forwardGiven a balance chemical equation , 2 C2H6 (g)+7 O2 (g) —> 4 CO 2 (g)+6 H2O(g) If reaction mixture contains 5 moles of O2 (g) with 6 moles of C2H6 (g) how many moles of CO2 will be produced? Hint: Identify the limiting reactant first Round and report your answer with a number having one decimal point. Enter that number into the answer box Don't include unit.arrow_forward
- gman app.101edu.co Gmail YouTube Type here to search " ? @ 2 Maps In the reaction below, 7.0 mol of NO and 5.0 mol of O₂ are reacted together. The reaction generates 3.1 mol of NO2. What is the percent yield for the reaction? 2 NO (g) + O₂(g) → 2 NO₂ (g) # News 3 $ 10 4 Translate O St % Paraphrasing Tool ... 5 10 Question 16 of 24 6 hp & 7 + * 8 9 foarrow_forwardIn the following reaction, oxygen is the excess reactant.SiCl4 + O2 → SiO2 + Cl2The table shows an experimental record for the above reaction. Experimental Record Trial Starting Amount of SiCl4 Starting Amount of O2 Actual Yield of SiO2 1 150 g 200 g 49.2 g 2 75 g 50 g 25.2 g Calculate the percentage yield for SiO2 for Trial 1. Also, determine the leftover reactant for the trial. Show your work. Based on the percentage yield in Trial 2, explain what ratio of reactants is more efficient for the given reaction. Source StylesNormalarrow_forward5. A student reacts 11.2 g of NİS2 with 5.43 g of O2 according to the following equation: 2 NiS2 (s) + 5 02 (g) → 2 NiO (s) + 4 SO2 (g) a) When the reaction is finished, how many grams of NiO will be produced (theoretically)? b) The student collects 4.86 grams of NiO. What is his percent yield? percent yield = actual х 100 theoreticalarrow_forward
- The theoretical yield of a reaction is the amount of product obtained if the limiting reactant is completely converted to product. Consider the reaction: 2 Fe(s) + O2(g) → 2 FeO(s) If 9.250 g Fe is mixed with 13.39 g O2, calculate the theoretical yield (g) of FeO produced by the reaction. Submit Show Approach Show Tutor Stepsarrow_forward3. When hydrogen sulfide (MW = 34.08 g/mol) gas is bubbled into a solution of sodium hydroxide (40.00 g/mol), their reaction forms sodium sulfide (78.05 g/mol) and water (18.02 g/mol) according to the following reaction. H2S(g) a. Write the properly balanced chemical equation b. What is the theoretical yield of sodium sulfide, if 1.50 g of hydrogen sulfide is reacted with a solution containing 1.65 g of sodium hydroxide, assuming the limiting reagent is completely consumed? c. What is the limiting reactant? d. If the actual yield of sodium sulfide is determined to be 1.00 g. what is the NaOH(aq) Na2słag) H2O(1) percent yield.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY