
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
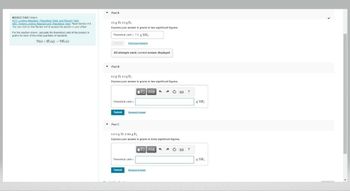
Transcribed Image Text:MISSED THIS? Watch
KCV Limiting Reactant Theoretical Yield and Percent Yield
WE Finding Limiting Reactant and Theoretical Yield Read Section 8.6
You can click on the Review link to access the section in your eText
For the reaction shown, calculate the theoretical yield of the product in
grams for each of the initial quantities of reactants
Ti(s)+2F2(g) → TiF,(s)
Part A
45g Ti 45g F
Express your answer in grams to two significant figures.
Theoretical yield 7.3 g TIF,
Previous Answers
All attempts used; correct answer displayed
Part B
6.0g Ti 40 g F
Express your answer in grams to two significant figures.
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
Theoretical yield=
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
0.412 g Ti 0.362 g F₂
Express your answer in grams to three significant figures.
Theoretical yield=
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
Submit
Request Answer
TIF
g TIF
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider the reaction. 2 Рb's) + O,(g) — 2 PЬО(s) An excess of oxygen reacts with 451.4 g of lead, forming 348.1 g of lead(II) oxide. Calculate the percent yield of the reaction. percent yield: % * TOOLS x10arrow_forwardFor the reaction, compute the theoretical yield of the product in moles for each of the following initial reactants. Ti (s) + 2 Cl2 (g) - TiCl4(s) Express your answers using two significant figures. a) 2 mol Ti; 2 mol Cl2 b) 5 mol Ti; 9 mol Cl2 C) 0.483 mol Ti; 0.911 mol Cl2 d) 12.4 mol Ti; 15.8 mol Cl2arrow_forwardCombining 0.333 mol Fe, O, with excess carbon produced 12.7 g Fe. Fe,0, + 3C → 2 Fe + 3 CO What is the actual yield of iron in moles? actual yield: mol What is the theoretical yield of iron in moles? theoretical yield: mol What is the percent yield? percent yield: %arrow_forward
- Question 25 of 97 Submit DDT was an insecticide used to prevent mosquito borne diseases. Due to the harmful effects on birds and fish, it is now banned in the US. However, other countries still use it to control mosquitos. It can be prepared by the reaction shown below. Determine the amount of DDT that can be produced and the percent yield for this reaction. 2C6H,CI + C2HOCI, – C,4H9CI, + H20 2 3 NEXT If a company in South America started with 1175 g of chlorobenzene (C6H5CI, MW 112.55 g/mol) and 538.5 g of chloral (C2HOCI3, MW 147.39 g/mol), set up the table below that represents 100% yield with the given reaction conditions. 2C6H,CI C2HOCI, C1.H,Cls H2O Before (mol) Change (mol) After (mol) O RESET 3.132 -3.132 3.654 -3.654 7.308 0. + -7.308 10.44 -10.44 MacBook Air F12 II F8 F10 F11 000 F9 20 F3 F7 F4 F5 F6 esc F2 F1 +.arrow_forwardMISSED THIS? Watch KCV: Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield, and Percent Yield, IWE: Limiting Reactant and Theoretical Yield; Read Section 4.4. You can click on the Review link to access the section in your eText. Iron(II) sulfide reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the reaction FeS (s) + 2HCl(aq)→FeCl₂ (aq) + H₂S(s) A reaction mixture initially contains 0.212 mol FeS and 0.636 mol HCl. Part A Once the reaction has reached completion, what amount (in moles) of the excess reactant is left? Express the answer in moles to three significant figures. n = Submit V ΑΣΦ Request Answer ? molarrow_forward8 This is for my reviewer please help me with the step by step solution and answer, thank youarrow_forward
- Iron oxide reacts with carbon to produce elemental iron and carbon monoxide according the the equation shown below. Consider the reaction of 51.4 grams of Fe2O3 with 24.98 grams of C to produce 19.20 grams of Fe. Fe2O3(s)+3c(s)-------2Fe(s)+3CO(g) a. actual yield b. theoretical yield c. percent yieldarrow_forwardFor the reaction shown, find the limiting reactant for each of the following initial amounts of reactants.2Al(s)+3Cl2(g)→2AlCl3(s) Part A: 1.0 g Al; 1.0 g Cl2 Express your answer as a chemical formula. Part B: 2.2 g Al; 1.8 g Cl2 Express your answer as a chemical formula. Part C: 0.353 g Al; 0.482 g Cl2 Express your answer as a chemical formula.arrow_forwardMISSED THIS? Watch KCV: Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield, and Percent Yield IWE: Limiting Reactant and Theoretical Yield; Read Section 4.4. You can click on the Review link to access the section in your e Text. For the reaction Ti(s) + 2 F2 (g) → TiF4(s) compute the theoretical yield of the product (in grams) for each of the following initial amounts of reactants. y Part B Correct The limiting reagent of this reaction is F2 as it only yields 4.89 of TiF4 comp Ti to calculate yield. 2.5 g Ti, 1.7 g F2 Express your answer using two significant figures. m = Submit ΠΫΠΙ ΑΣΦ Request Answer C ? 80arrow_forward
- For the reaction below, find the limiting reactant for each of the initial amounts of reactants. 2 Na(s) + Br2(g) ------> 2 NaBr(s)a. 2 mol Na, 2 mol Br2arrow_forwardSodium and chlorine react to form sodium chloride: What is the theoretical yield of sodium chloride for the reaction of 32.0 g Na with 107.2 g Cl2? A. 1.40 x 104 g NaCl B. 35.4 g NaCl C. 122 g NaCl D. 81.2 g NaClarrow_forwardSTARTING AMOUNT X This question will walk you through the steps of determining which reactant is limiting based on a balanced chemical equation. Step 2a: Use dimensional analysis to determine the theoretical yield of the product. Calculate the theoretical yield in moles CO₂ from the complete combustion of 29.3 grams CH4 according to the following balanced chemical equation: 1 CH4(g) + 2 O₂(g) → 1 CO₂(g) + 2 H₂O(1) 56.2 ADD FACTOR x( ) 1.83 g CO₂ 0.547 44.01 1 29.3 2 ANSWER 16.05 0.915 0.666 g/mol CO₂ mol CO₂ g/mol CH4 mol CH4 RESET 5 18.02 g CH₂ 16.00arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY